Postponing Day Zero in Cape Town for 2018 comes as no surprise. There was no sense to it once the day had been pushed into the winter rainfall period. It also didn’t make sense for the Western Cape and Cape Town governments to continue drafting detailed logistical plans for points of water distribution in the event that taps were turned off across the city.
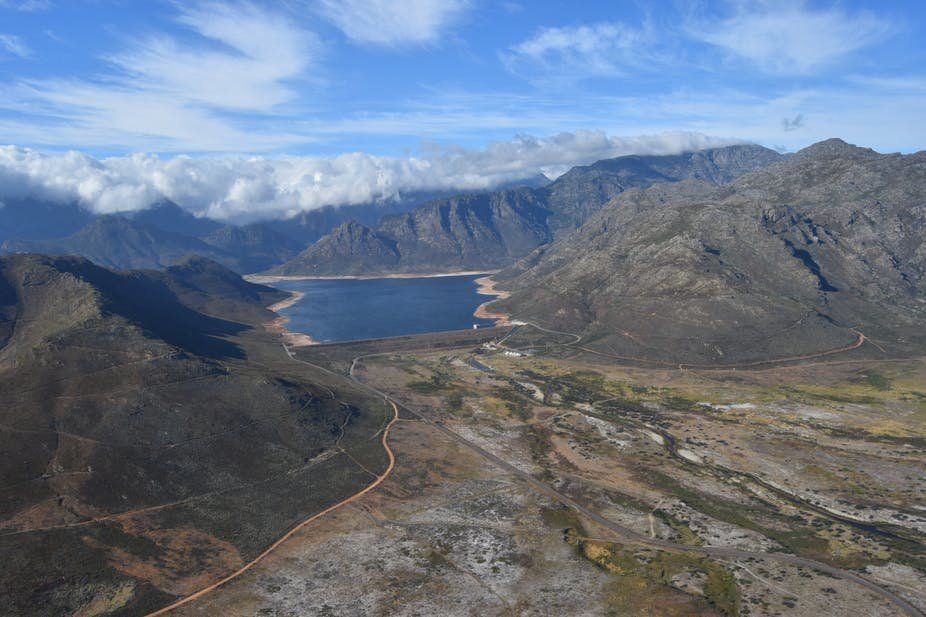
But Cape Town’s water supplies remain at high risk because the long-term predictions for rainfall in the south-western Cape remain uncertain. Dam levels continue to fall while people are struggling to achieve the city’s target of 450 million litres per day. And yields from new water schemes will only be known in the coming months and next year.
The general perception is that the onset of climate change would be slow and measured. This would afford authorities the time to intervene with considered plans. But climate change is a disrupter and takes no prisoners. Over the past three years, Cape Town and the surrounding regions has experienced successive years of well below average rainfall. The experience is changing the way people think about water and how it is managed.