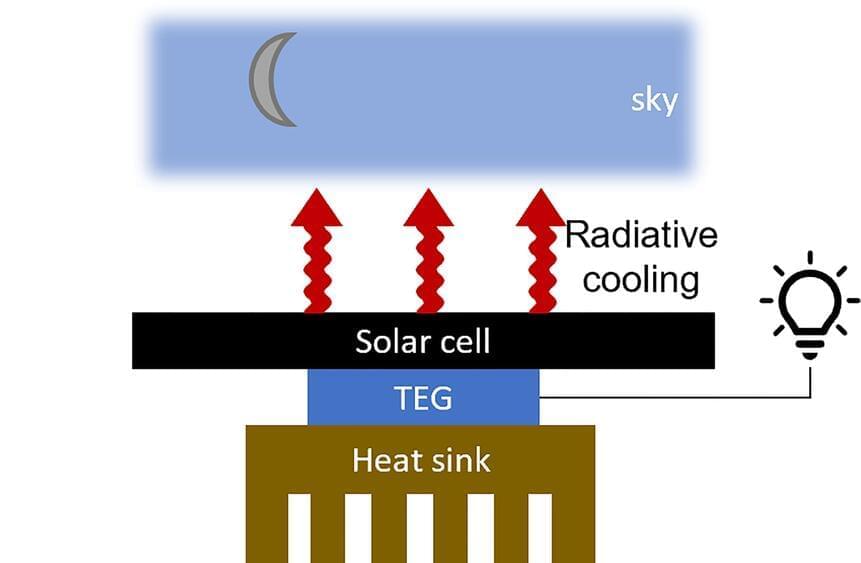
A new PV module makes electricity from thermal radiation. Imagine that.
The electromagnetic spectrum is comprised of thousands upon thousands of frequencies. Sound and light are all part of the spectrum, as are the frequencies that make radio and television broadcasts possible. Today’s solar panels harvest light waves from a small part of the EM spectrum and turn them into electricity, but there are many other frequencies like thermal radiation that could someday stimulate new kinds of photovoltaic cells to generate electricity as well.
Researchers at Stanford have recently published a study in the journal Applied Physics Letters that describes a new type of cell that converts thermal radiation into electricity. When the sun goes down, living organisms and physical structures like buildings, road, and sidewalks radiate heat back into the atmosphere. We call this radiational cooling and it is those electromagnetic waves the Stanford researchers say can be put to work making electricity.