The truth about Cobalt. The demand for colbalt is on the rise as we transition to electric vehicles is at an all time high.
Taken from JRE #1914 w/Siddharth Kara:
The truth about Cobalt. The demand for colbalt is on the rise as we transition to electric vehicles is at an all time high.
Taken from JRE #1914 w/Siddharth Kara:

EPFL
According to a report by Euronews, researchers at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) have discovered a way to create transparent photosensitizers, molecules that can be activated by light and adsorb light across the entire visible light spectrum. Previous versions of DSCs were largely dependent on direct sunlight.

As our Energy Central Community thrives and grows with each passing year, it’s clear to us that we have something special here. This community of power industry professionals who so eagerly and openly share their insights, their lessons learned, and their questions to allow for constant collaboration is unparalleled anywhere else in our sector.
The most critical part of this successful undertaking, though, is of course the people behind it all. The voices in our Community who are driving those conversations and keeping readers and peers coming back again and again. To once again celebrate the importance of our community members in making Energy Central the powerhouse that it is, we’re ending the year by honoring the members on Energy Central who went above and beyond—frequently sharing news and content, reliably starting conversations across the site, and providing some of the most genuinely high-value contributions throughout 2022.
All week, we’ll be publishing articles highlighting the Top Voice of 2022 for each of our 6 Networks. As part of this tradition, some of those community members recognized were kind enough to answer a few questions to highlight what they found valuable in the sector in 2022, their predictions for 2023, and some personal insights to get to know the men and women behind it all.
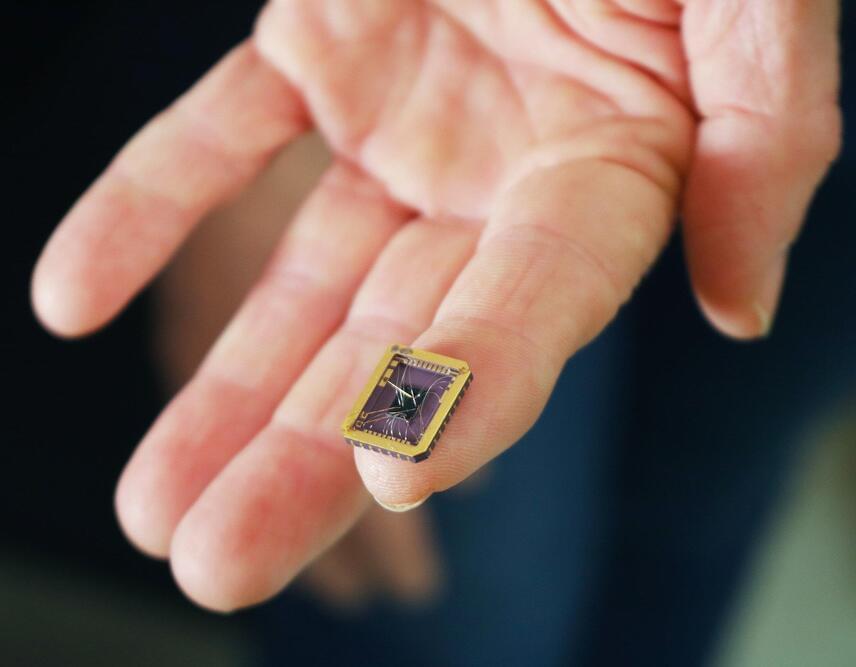
A pressing quest in the field of nanoelectronics is the search for a material that could replace silicon. Graphene has seemed promising for decades. But its potential has faltered along the way, due to damaging processing methods and the lack of a new electronics paradigm to embrace it. With silicon nearly maxed out in its ability to accommodate faster computing, the next big nanoelectronics platform is needed now more than ever.
Walter de Heer, Regents’ Professor in the School of Physics at the Georgia Institute of Technology, has taken a critical step forward in making the case for a successor to silicon. De Heer and his collaborators have developed a new nanoelectronics platform based on graphene —a single sheet of carbon atoms. The technology is compatible with conventional microelectronics manufacturing, a necessity for any viable alternative to silicon.
In the course of their research, published in Nature Communications, the team may have also discovered a new quasiparticle. Their discovery could lead to manufacturing smaller, faster, more efficient and more sustainable computer chips, and has potential implications for quantum and high-performance computing.
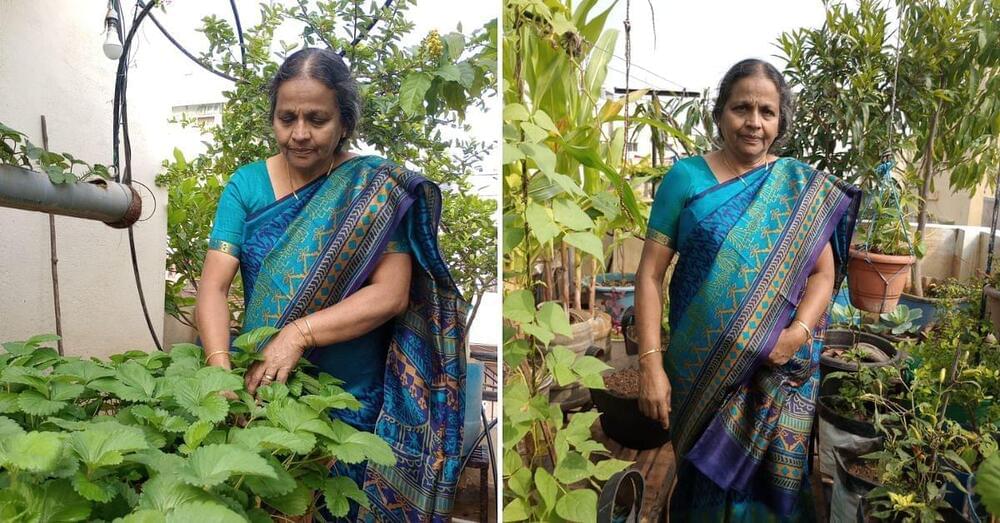

For 70-year-old Lizy John from Bengaluru, Karnataka, nurturing a lush vegetable and fruit garden on her terrace has been highly rewarding and satisfying. Without a second thought, she credits her passion for farming to be the sole reason for staying healthy and energetic even at this age.
After running a snacks business for over 25 years, she decided to retire and focus on expanding her farming venture. Though there wasn’t enough space, she says that it wasn’t a challenge at all.
“Though we have a 1,200 sqft terrace, I grow my veggies in less than 1,000 sqft, as the solar panels and water tanks consume the rest of the space. But it was more than enough for me. I admit that I am happier and at peace ever since I started growing my own food at home,” Lizy tells The Better India.
Their first EV could possibly roll out with an integrated PlayStation 5.
Japanese industrial giants Sony and Honda formally joined forces earlier this year to take on the might of Tesla in the electric vehicle (EV) space. The collaborative effort will first be unveiled at the CES 2023, scheduled to be held in Las Vegas in a fortnight from now, The Verge.
Sony.
The switch of automobiles from internal combustion engines to electric ones has brought forward another revolution, one where the car is not just a means of mobility but also of entertainment. Look at any EV to be launched in the market, and you will find a giant display at the center that can help with navigation and deliver content.
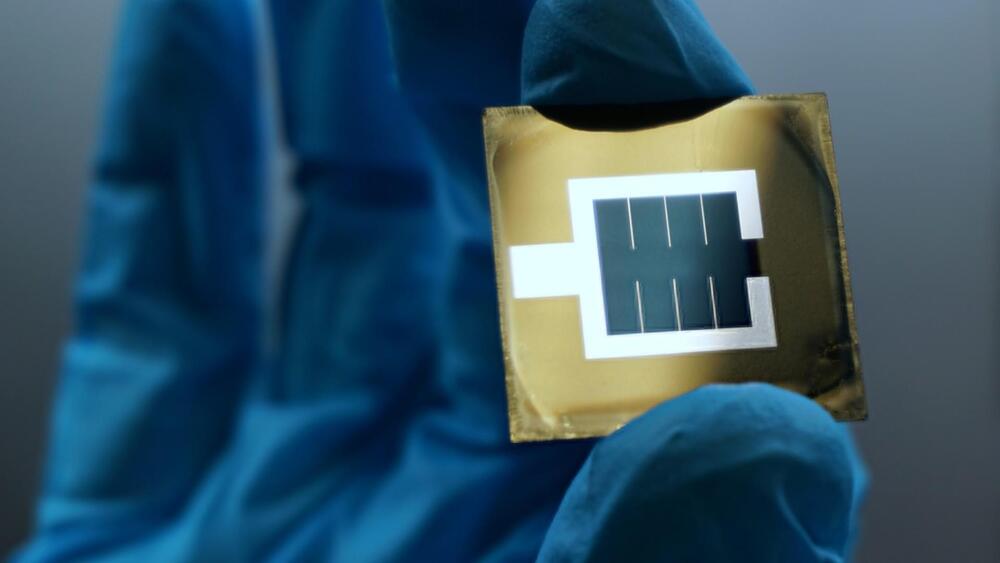
Solar energy is reaching new heights faster than ever.
A tandem solar cell developed by researchers at the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) has converted 32.5 percent of incident solar radiation into electrical energy, a world record. The achievement was certified by the European Solar Test Installation (ESTI) in Italy, a university press release said.
As the demand for renewable energy grows, researchers are looking at ways of increasing the efficiency of solar cells. This enables more energy to be harvested from the same area of land deployed to generate power. There has been significant success when halide perovskites have been used to make solar cells.

Year 2019 face_with_colon_three
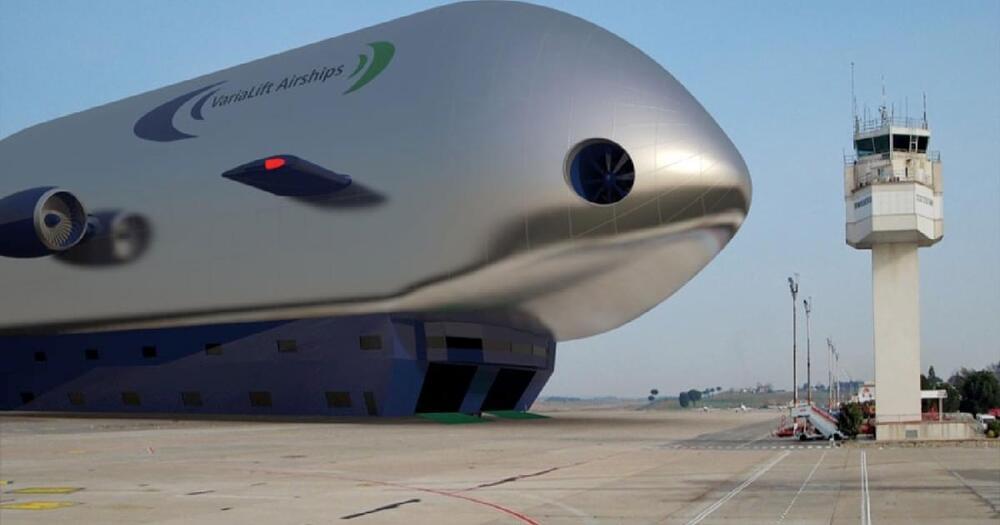
Zeppelins, the rigid airships most famously epitomized by the Hindenburg, now seem kind of retro, rather than the image of futurity they represented in the 1930s. But they could be about to make a comeback in a big way — courtesy of a new aluminum-shelled, solar-powered airship that’s being built by the U.K.-based company Varialift Airships.
According to the company’s CEO Alan Handley, the airship will be capable of making a transatlantic flight from the United Kingdom to the United States, consuming just 8% of the fuel of a regular airplane. It will be powered by a pair of solar-powered engines and two conventional jet engines.
While its lack of onboard battery would limit travel to daylight hours, and its speed will only be approximately half that of a Boeing 747, the Varialift airship does promise to be a useful cargo carrier. Its creators claim that it will be able to carry loads ranging from 50 to 250 tons. Larger models with payloads up to 3,000 tons aren’t out of the question either. Bulky cargo such as electricity pylons, wind turbine blades, and towers, or even prefabricated structures such as oil rigs could be carried underneath using cables. That means that cargo will have a weight limit, but no practical size limit.
The last event of 2022 will take place December 19th: Christmas Special meeting. with our president Prof. Bernard Foing!
We’ll have a look at what we have done in 2022, and we’ll announce the program of 2023.
The Zoom meeting will be open to all of the SRI Members and invited friends – just registered or going to register during the meeting.
All the participants will have the possibility to make questions to the SRI President, the Founder and the Board of Directors, about the 2023 program. Criticisms and proposals will be welcome too.
We have a huge programme for 2023, and we are going through some key steps, to achieve an higher legal status for our association: to be registered as a not for profit entity on the Unic National Register of the Third Sector Entities (RUNTS). Such an achievement will allow SRI to call Italian taxpayers to target the 5×1000 of their yearly tax to SRI, and the donations to be deducted from the tax declaration. These conditions, when achieved, will greatly contribute to the sustainability of our initiatives.
We are asking each of the SRI members and supporters to assume this priority for December 2022: to bring onboard many new members and to seek for donors and sponsors!
We will celebrate together during the Xmas Special event and exchange season greetings and wishes for a vibrant year 2023 for Space Renaissance International!