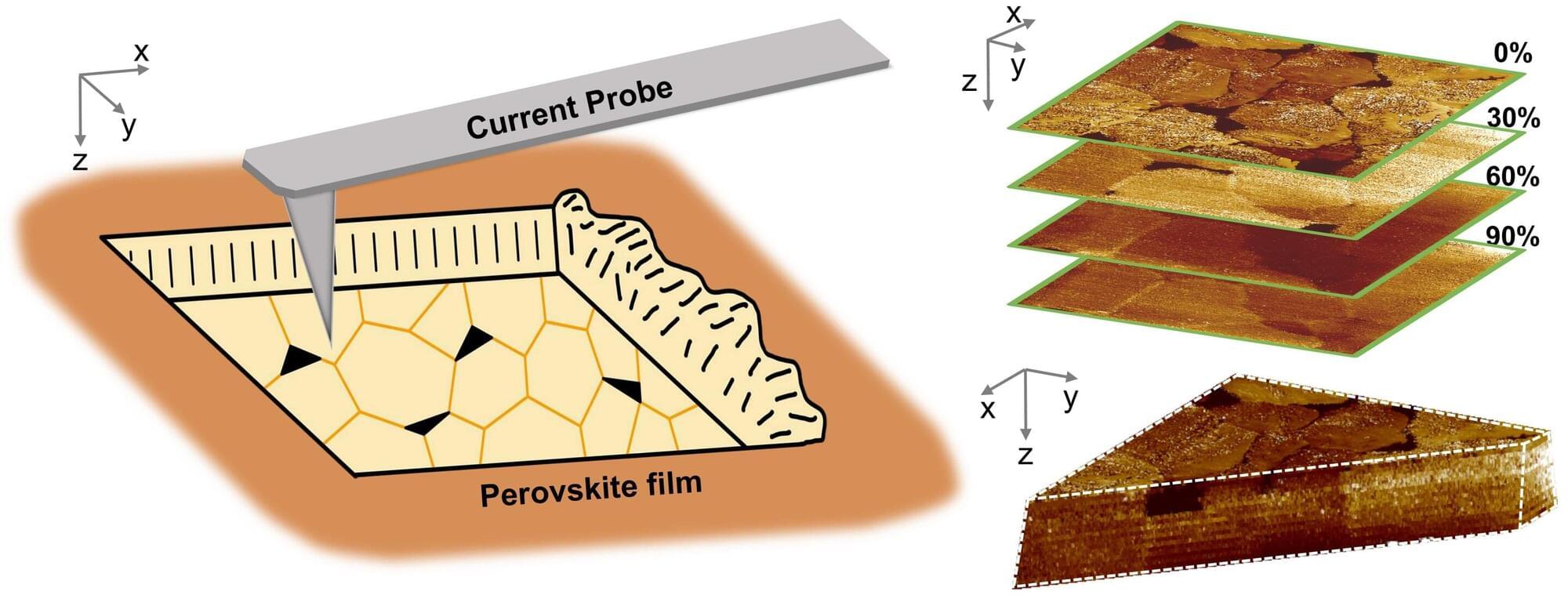
Perovskite solar cells have garnered widespread attention as a low-cost, high-efficiency alternative to conventional silicon photovoltaics. However, defects in perovskite films impede charge transport, resulting in energy loss and compromised operational stability.
One solution to this problem is “passivation treatment”—a process that adds chemicals such as simple salts or organic molecules to the film. These small molecules or ions latch onto defects in the perovskite material, preventing the defects from interfering with electrical flow. Unfortunately, verifying the internal efficacy of various passivation treatments remains challenging since most characterization techniques only probe the surface or provide averaged macroscopic information.
Now, however, researchers at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have made an important breakthrough by developing a three-dimensional (3D) electrical imaging technique that directly reveals how defect passivation treatments work in perovskite films. The study was published in Newton on December 31.