Category: supercomputing – Page 67
New World’s Fastest Supercomputer Explained
The king is dead, long live the king… of supercomputers!
In this video I discuss New Fastest Supercomputer in the World and the first official Exascale supercomputer — Frontier Supercomputer located at Oak Ridge Lab.
***
WATCH NEXT:
➞ This is Killing every CPU: https://youtu.be/Bw4kgXYScXM
➞ Tesla’s DOJO explained: https://youtu.be/QurtwJdb5Ew.
➞ Silicon Quantum Computer from Intel: [https://youtu.be/j9eYQ_ggqJk](https://youtu.be/j9eYQ_ggqJk)
***
➞ Support me on Patreon: [https://www.patreon.com/AnastasiInTech](https://www.patreon.com/AnastasiInTech)
➞ Subscribe for new videos every week! ❤ And tell me what you think in the comments below!

World’s first exascale supercomputer Frontier smashes speed records
The world’s first exascale computer, capable of performing a billion billion operations per second, has been built by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) in the US.
A typical laptop is only capable of a few teraflops, or a trillion operations per second, which is a million times less. The exaflop machine, called Frontier, could help solve a range of complex scientific problems, such as accurate climate modelling, nuclear fusion simulation and drug discovery.
“Frontier will offer modelling and simulation capabilities at the highest level of computing performance,” says Thomas Zacharia at ORNL.

Frontier supercomputer powered by AMD is the fastest in the world
The AMD-powered Frontier supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory has bagged the top spot on the Top500 list of the world’s fastest supercomputers. The Top500 list also said that the Frontier system is the first true exascale machine with an HPL score of 1.102 Exaflop/s. For two years, the top spot was occupied by the Fugaku system at the RIKEN Center for Computational Science (R-CCS) in Kobe, Japan.
Based on the latest HPE Cray EX235a architecture and equipped with AMD EPYC 64C 2GHz processors, the system has 8,730,112 total cores and a power efficiency rating of 52.23 gigaflops/watt. It relies on gigabit ethernet for data transfer.
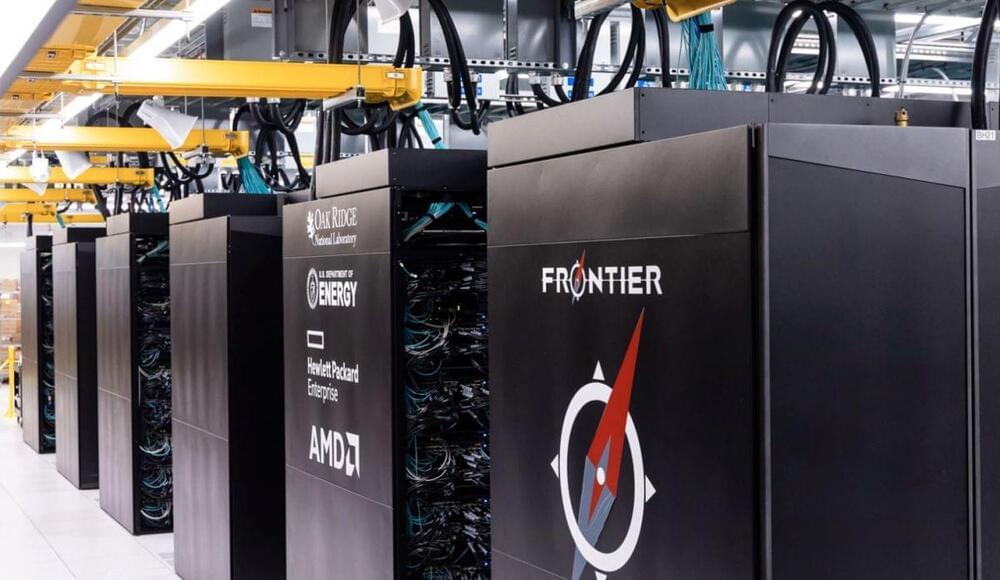


World’s first exascale supercomputer is officially confirmed
In a major milestone for computing, Oak Ridge National Laboratory today announced that Frontier has achieved 1.1 exaFLOPS. https://www.futuretimeline.net/blog/2022/05/30-bird-extincti…e-2027.htm
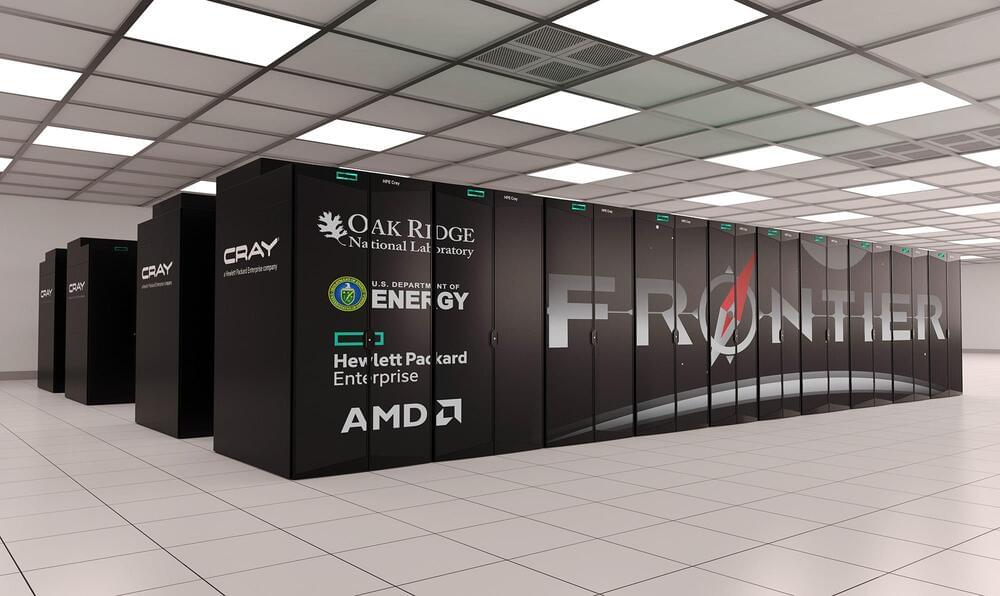

US retakes first place from Japan on Top500 supercomputer ranking
ORNL’s Frontier HPE Cray EX with AMD CPUs is the ‘first true exascale machine.’
The United States is on top of the supercomputing world in the Top500 ranking of the most powerful systems. The Frontier system from Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) running on AMD EPYC CPUs took first place from last year’s champ, Japan’s ARM A64X Fugaku system. It’s still in the integration and testing process at the ORNL in Tennessee, but will eventually be operated by the US Air Force and US Department of Energy.
Frontier, powered by Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s (HPE) Cray EX platform, was the top machine by a wide margin, too. It’s the first (known) true exascale system, hitting a peak 1.1 exaflops on the Linmark benchmark. Fugaku, meanwhile, managed less than half that at 442 petaflops, which was still enough to keep it in first place for the previous two years.
Frontier was also the most efficient supercomputer, too. Running at just 52.23 gigaflops per watt, it beat out Japan’s MN-3 system to grab first place on the Green500 list. “The fact that the world’s fastest machine is also the most energy efficient is just simply amazing,” ORNL lab director Thomas Zacharia said at a press conference.
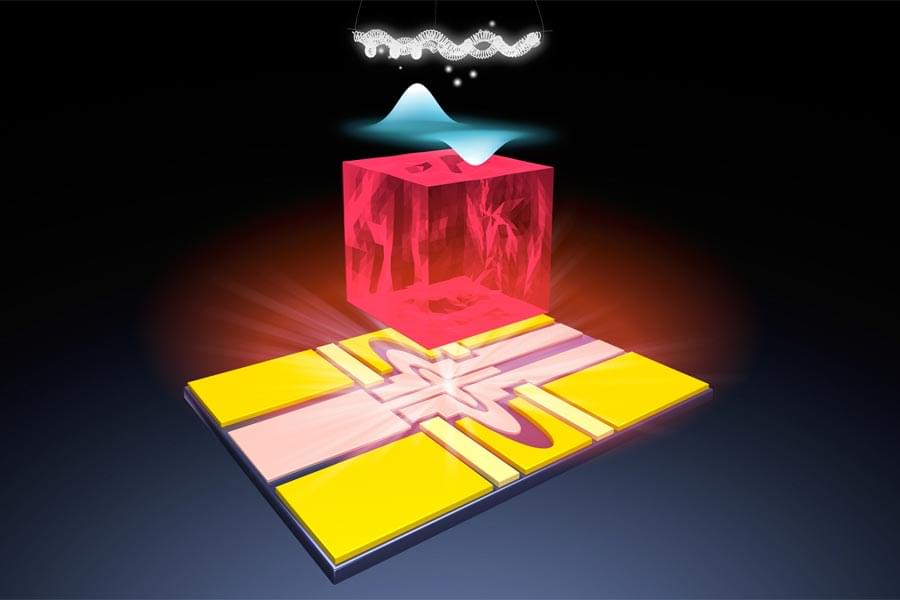
Revolutionary New Qubit Platform Could Transform Quantum Computing
The digital device you are using to view this article is no doubt using the bit, which can either be 0 or 1, as its basic unit of information. However, scientists around the world are racing to develop a new kind of computer based on the use of quantum bits, or qubits, which can simultaneously be 0 and 1 and could one day solve complex problems beyond any classical supercomputers.
A research team led by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, in close collaboration with FAMU-FSU College of Engineering Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Wei Guo, has announced the creation of a new qubit platform that shows great promise to be developed into future quantum computers. Their work is published in the journal Nature.
“Quantum computers could be a revolutionary tool for performing calculations that are practically impossible for classical computers, but there is still work to do to make them reality,” said Guo, a paper co-author. “With this research, we think we have a breakthrough that goes a long way toward making qubits that help realize this technology’s potential.”

Quantum computers vs supercomputers: How do they differ?
Over the years, supercomputers have played a pivotal role in pushing the frontiers of science. Earlier this year, Meta launched one of the fastest AI supercomputers, the AI Research SuperCluster (RSC), to build sophisticated AI models that can learn from trillions of examples; navigate hundreds of different languages; seamlessly analyse text, images, and video together; build AR tools etc.
However, the quest for something even faster than supercomputers led to the development of quantum computers. Last year, the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) introduced the world’s fastest programmable superconducting quantum computer; Zuchongzhi 2.1 is a million times faster than a conventional computer.
At last year’s I/O conference, Google unveiled a Quantum AI campus in Santa Barbara, California, complete with a quantum data centre, quantum hardware research labs, and quantum processor chip fab facilities. The tech giant plans to build a useful, error-corrected quantum computer within a decade.
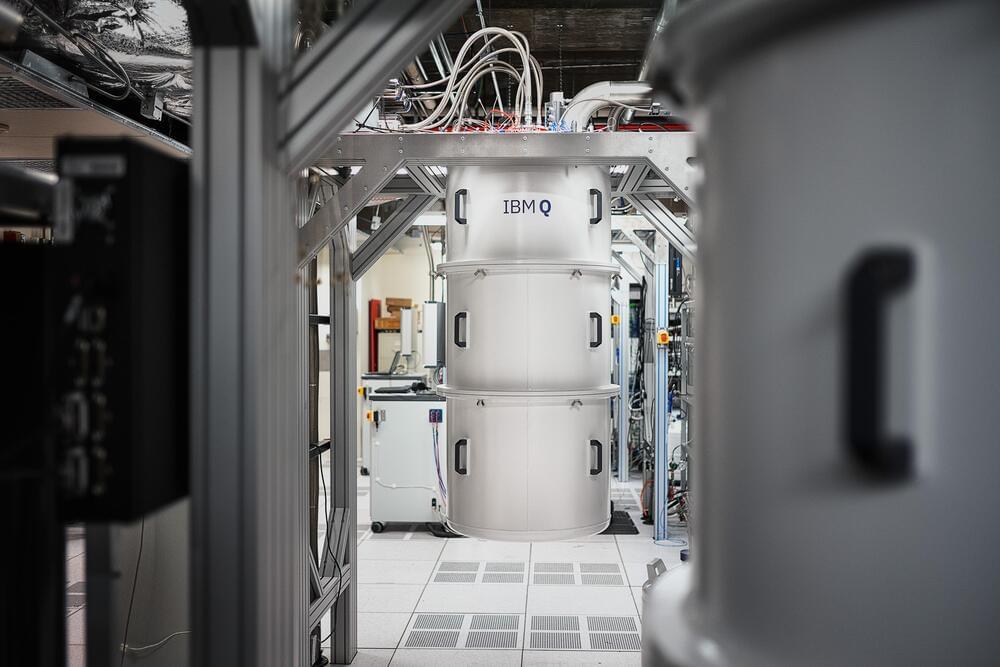

IBM wants its quantum supercomputers running at 4,000-plus qubits by 2025
Forty years after it first began to dabble in quantum computing, IBM is ready to expand the technology out of the lab and into more practical applications — like supercomputing! The company has already hit a number of development milestones since it released its previous quantum roadmap in 2020, including the 127-qubit Eagle processor that uses quantum circuits and the Qiskit Runtime API. IBM announced on Wednesday that it plans to further scale its quantum ambitions and has revised the 2020 roadmap with an even loftier goal of operating a 4,000-qubit system by 2025.
Before it sets about building the biggest quantum computer to date, IBM plans release its 433-qubit Osprey chip later this year and migrate the Qiskit Runtime to the cloud in 2023, “bringing a serverless approach into the core quantum software stack,” per Wednesday’s release. Those products will be followed later that year by Condor, a quantum chip IBM is billing as “the world’s first universal quantum processor with over 1,000 qubits.”
This rapid four-fold jump in quantum volume (the number of qubits packed into a processor) will enable users to run increasingly longer quantum circuits, while increasing the processing speed — measured in CLOPS (circuit layer operations per second) — from a maximum of 2,900 OPS to over 10,000. Then it’s just a simple matter of quadrupaling that capacity in the span of less than 24 months.