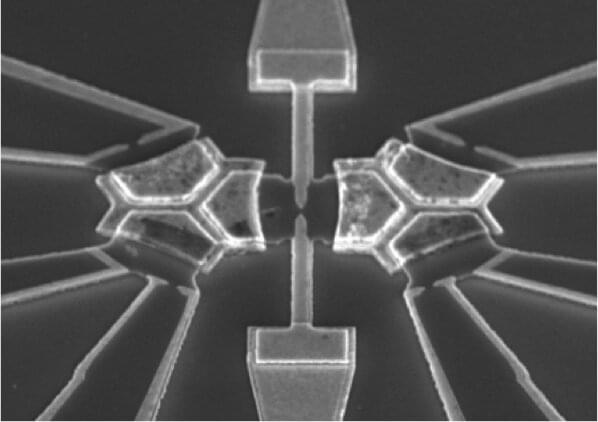
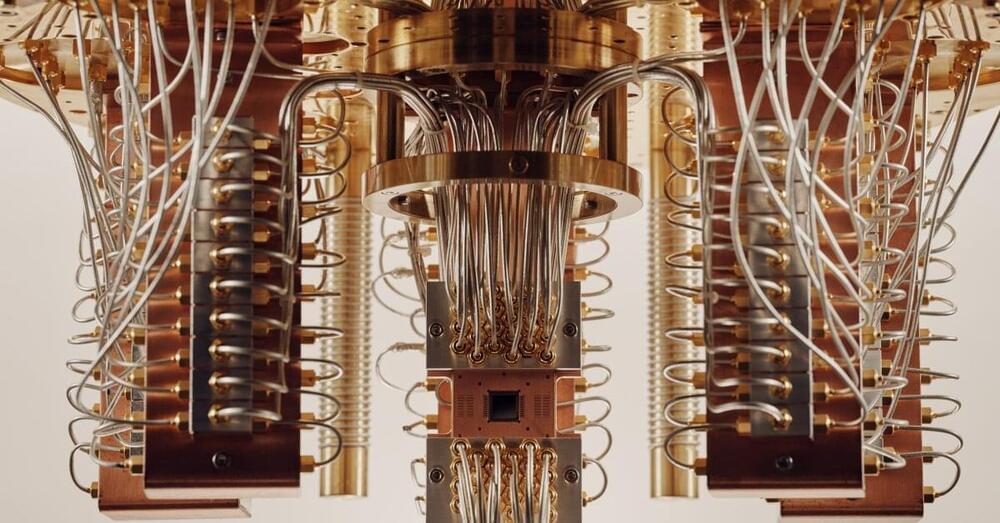
Physicists have invented a new type of analog quantum computer that can tackle hard physics problems that the most powerful digital supercomputers cannot solve.
New research published in Nature Physics by collaborating scientists from Stanford University in the U.S. and University College Dublin (UCD) in Ireland has shown that a novel type of highly-specialized analog computer, whose circuits feature quantum components, can solve problems from the cutting edge of quantum physics that were previously beyond reach. When scaled up, such devices may be able to shed light on some of the most important unsolved problems in physics.
For example, scientists and engineers have long wanted to gain a better understanding of superconductivity, because existing superconducting materials —such as those used in MRI machines, high speed train and long-distance energy-efficient power networks—currently operate only at extremely low temperatures, limiting their wider use. The holy grail of materials science is to find materials that are superconducting at room temperature, which would revolutionize their use in a host of technologies.