Researchers used the Fugaku supercomputer created a realistic digital model that advances brain research, disease studies, and AI-driven neuroscience.

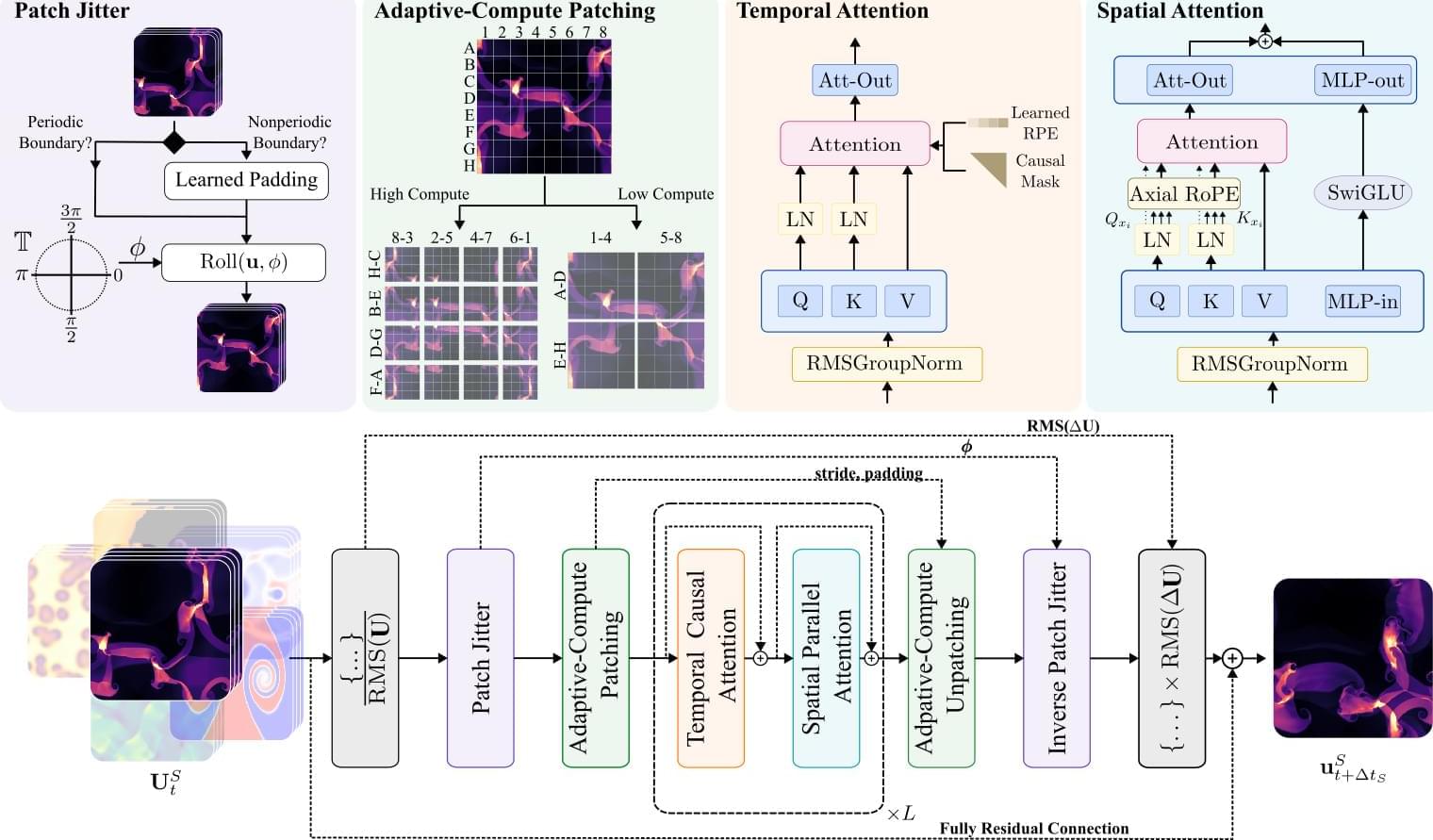
Using simulation-based techniques, scientists can ask how their ideas, actions, and designs will interact with the physical world. Yet this power is not without costs. Cutting edge simulations can often take months of supercomputer time. Surrogate models and machine learning are promising alternatives for accelerating these workflows, but the data hunger of machine learning has limited their impact to data-rich domains. Over the last few years, researchers have sought to side-step this data dependence through the use of foundation models— large models pretrained on large amounts of data which can accelerate the learning process by transferring knowledge from similar inputs, but this is not without its own challenges.


For years, Rick Stevens, a computer scientist at Argonne National Laboratory, pushed the notion of transforming scientific computing with artificial intelligence.
But even as Mr. Stevens worked toward that goal, government labs like Argonne — created in 1946 and sponsored by the Department of Energy — often took five years or more to develop powerful supercomputers that can be used for A.I. research. Mr. Stevens watched as companies like Amazon, Microsoft and Elon Musk’s xAI made faster gains by installing large A.I. systems in a matter of months.
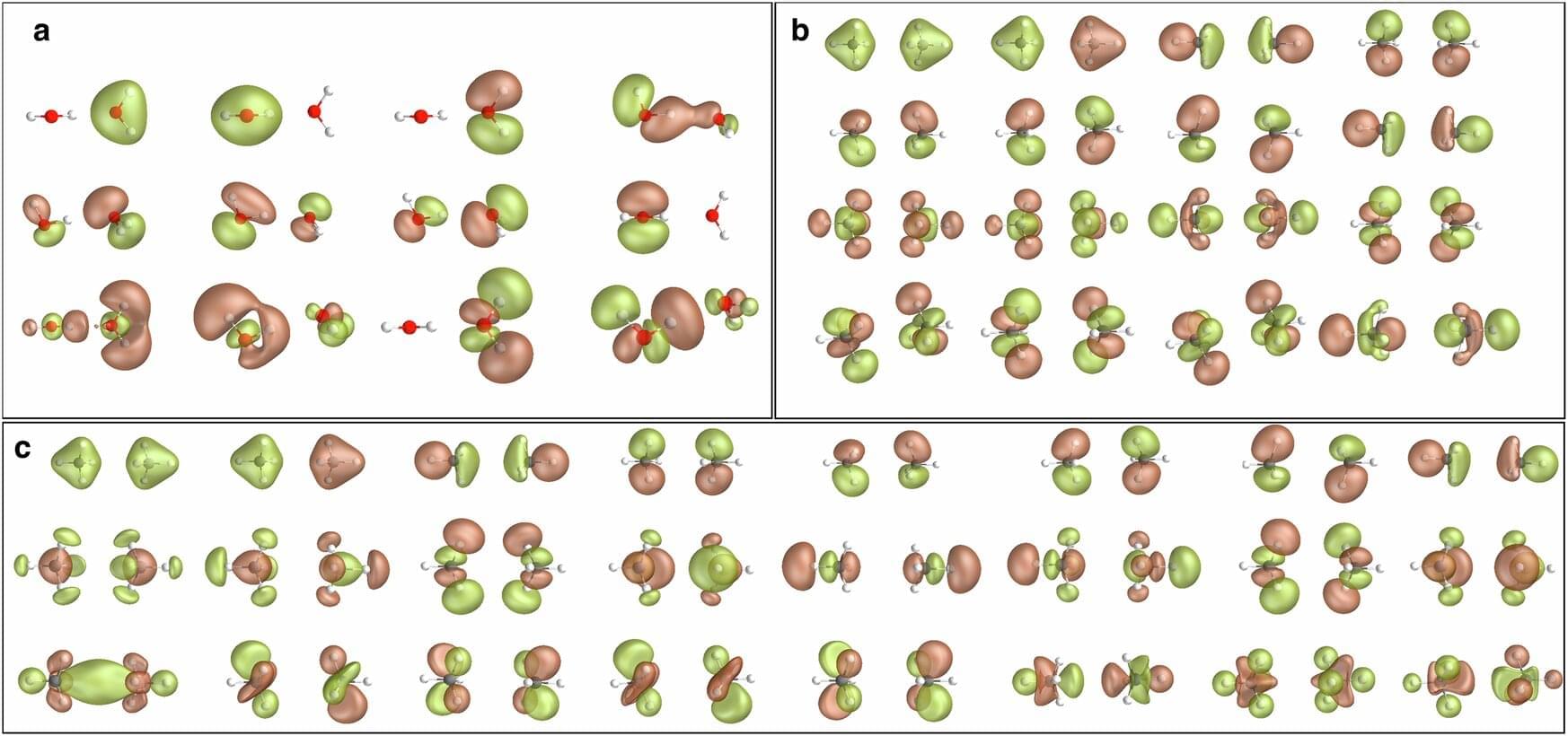
A team led by Cleveland Clinic’s Kenneth Merz, Ph.D., and IBM’s Antonio Mezzacapo, Ph.D., is developing quantum computing methods to simulate and study supramolecular processes that guide how entire molecules interact with each other.
In their study, published in Communications Physics, researchers focused on molecules’ noncovalent interactions, especially hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic species. These interactions, which involve attraction and repulsive forces between molecules or parts of the same molecule, play an important role in protein folding, membrane assembly and cell signaling.
Noncovalent molecular interactions involve an unknowable number of possible outcomes. Quantum computers with their immense computational power can easily complete these calculations, but conventional quantum computing methods can lack the accuracy of classical computers.
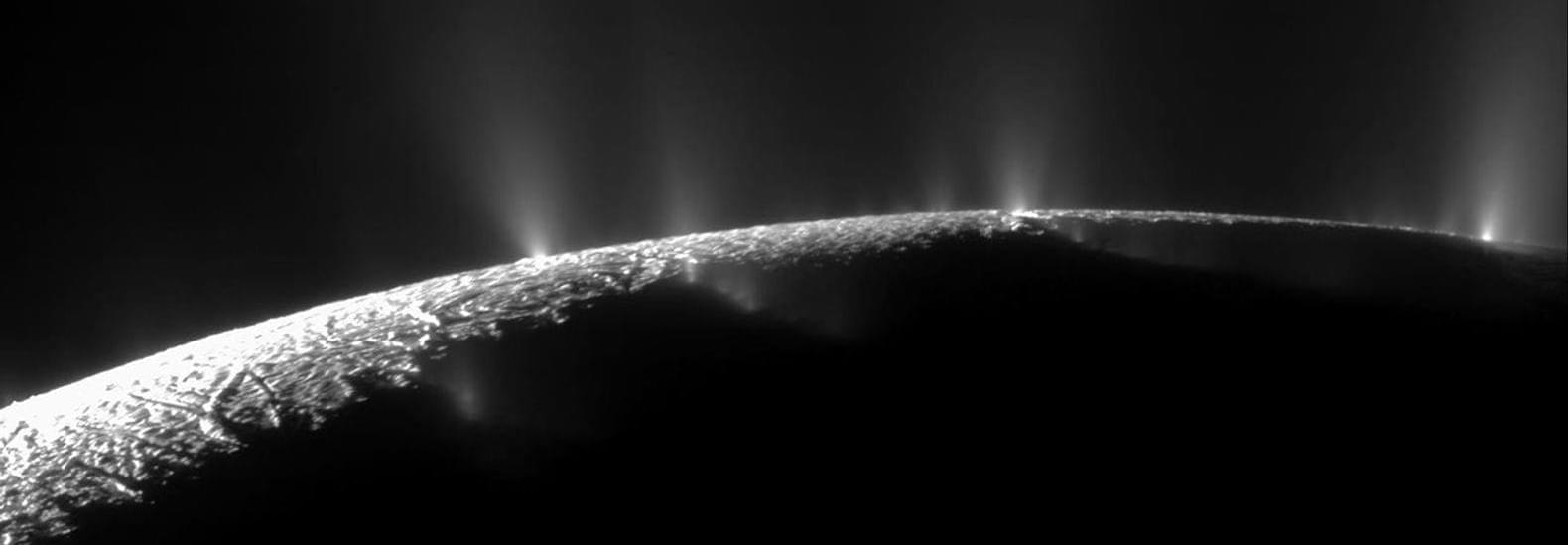
“The mass flow rates from Enceladus are between 20 to 40 percent lower than what you find in the scientific literature,” said Dr. Arnaud Mahieux.
How much ice is Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, losing to space when it discharges its interior ocean? This is what a recent study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated whether Enceladus’ plume environments, including discharge rates, temperatures, and ice particle sizes could be determined strictly from observational data. This study has the potential to help scientists develop new methods for exploring icy bodies, especially those like Enceladus that could harbor life within its liquid water ocean.
For the study, the researchers used a series of computer models to analyze data obtained from NASA’s now-retired Cassini spacecraft, which intentionally burned up in Saturn’s atmosphere in 2017 after running low on fuel. This was done to avoid potentially contaminating moons like Enceladus with microbes from Earth and interfere with potential life there. During its journey at Saturn and its many moons, Cassino both discovered and flew through the plumes of Enceladus, which are at the moon’s south pole and emit large quantities of water ice and other substances into space from its subsurface liquid water ocean. It’s the amount of water and ice these plumes discharge that have intrigued scientists, and the results were surprising.

A research team at the Jülich Supercomputing Center, together with experts from NVIDIA, has set a new record in quantum simulation: for the first time, a universal quantum computer with 50 qubits has been fully simulated—a feat achieved on Europe’s first exascale supercomputer, JUPITER, inaugurated at Forschungszentrum Jülich in September.
The result surpasses the previous world record of 48 qubits, established by Jülich researchers in 2022 on Japan’s K computer. It showcases the immense computational power of JUPITER and opens new horizons for developing and testing quantum algorithms. The research is published on the arXiv preprint server.
Quantum computer simulations are vital for developing future quantum systems. They allow researchers to verify experimental results and test new algorithms long before powerful quantum machines become reality. Among these are the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE), which can model molecules and materials, and the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), used for optimization problems in logistics, finance, and artificial intelligence.
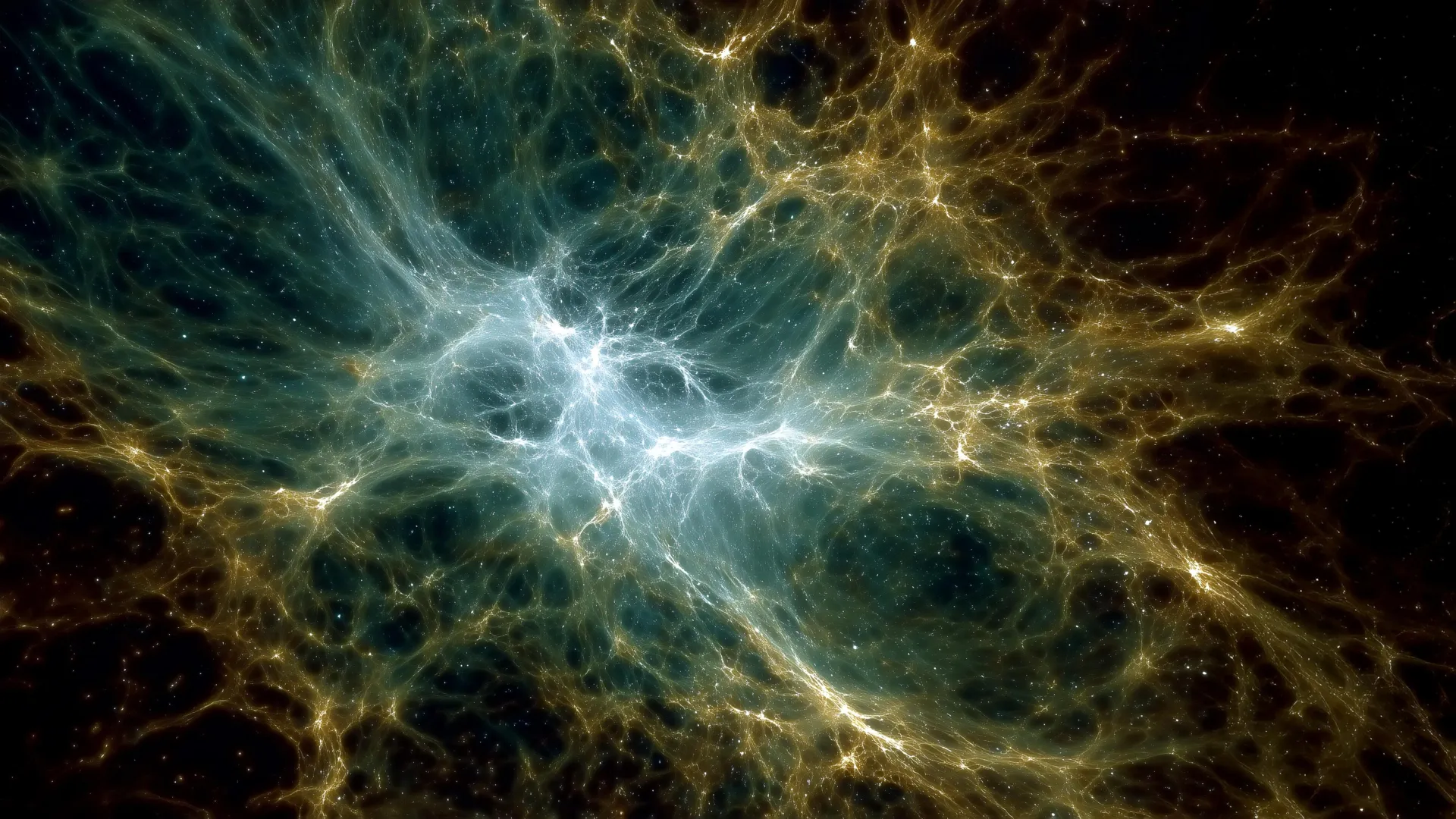

Dark energy may be alive and changing, reshaping the cosmos in ways we’re only beginning to uncover. New supercomputer simulations hint that dark energy might be dynamic, not constant, subtly reshaping the Universe’s structure. The findings align with recent DESI observations, offering the strongest evidence yet for an evolving cosmic force.
Since the early 20th century, scientists have gathered convincing evidence that the Universe is expanding — and that this expansion is accelerating. The force responsible for this acceleration is called dark energy, a mysterious property of spacetime thought to push galaxies apart. For decades, the prevailing cosmological model, known as Lambda Cold Dark Matter (ΛCDM), has assumed that dark energy remains constant throughout cosmic history. This simple but powerful assumption has been the foundation of modern cosmology. Yet, it leaves one key question unresolved: what if dark energy changes over time instead of remaining fixed?
Recent observations have started to challenge this long-held view. Data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) — an advanced project that maps the distribution of galaxies across the Universe — suggests the possibility of a dynamic dark energy (DDE) component. Such a finding would mark a significant shift from the standard ΛCDM model. While this points to a more intricate and evolving cosmic story, it also exposes a major gap in understanding: how a time-dependent dark energy might shape the formation and growth of cosmic structures remains unclear.


Amid the private sector’s race to lead artificial intelligence innovation, The University of Texas at Austin has strengthened its lead in academic computing power and dominance in computing power for public, open-source AI. UT has acquired high-performance Dell PowerEdge servers and NVIDIA AI infrastructure powered by more than 4,000 NVIDIA Blackwell architecture graphic processing units (GPUs), the most powerful GPUs in production to date.
The new infrastructure is a game-changer for the University, expanding its research and development capabilities in agentic and generative AI while opening the door to more society-changing discoveries that support America’s technological dominance. The NVIDIA GB200 systems and NVIDIA Vera CPU servers will be installed as part of Horizon, the largest academic supercomputer in the nation, which goes online next year at UT’s Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC). The National Science Foundation (NSF) is funding Horizon through its Leadership Class Computing Facility program to revolutionize U.S. computational research.
UT has the most AI computing power in academia. In total, the University has amassed more than 5,000 advanced NVIDIA GPUs across its academic and research facilities. The University has the computing power to produce open-source large language models — which power most modern AI applications — that rival any other public institution. Open-source computing is nonproprietary and serves as the backbone for publicly driven research. Unlike private sector models, it can be fine-tuned to support research in the public interest, producing discoveries that offer profound benefits to society in such areas as health care, drug development, materials and national security.