That’s one big space storm.
It’s “vast” and “bright,” says NASA.


The loss of the courageous men and women from Apollo 1, Challenger, and Columbia was not in vain. America will lead the world into a new era of discovery.
President Trump’s full statement: http://45.wh.gov/o81S3D

Go into your backyard about 20:30 p.m. EST or thereabouts this weekend and you can see the most incredible thing – the Andromeda Galaxy – one of the farthest objects visible to the naked eye. If you know where to look. Locating the ‘other ’ major galaxy in our Local Group is an exercise in stargazing on a grand scale, and the beginning of fall is absolutely the best time to take a look at it.

In the early 1990s, I was lucky enough to get some time on a 60 MeV linear accelerator as part of an undergraduate lab course. Having had this experience, I can feel for the scientists at CERN who have had to make do with their current 13 TeV accelerator, which only manages energies some 200,000 times larger. So, I read with great interest when they announced the publication of the initial design concept for the Future Circular Collider (FCC), which promises collisions nearly an order of magnitude more energetic. The plan, which has been in the works since 2014, includes three proposals for accelerators which would succeed CERN’s current big iron, the LHC.
Want to know what’s on the horizon in high-energy physics?

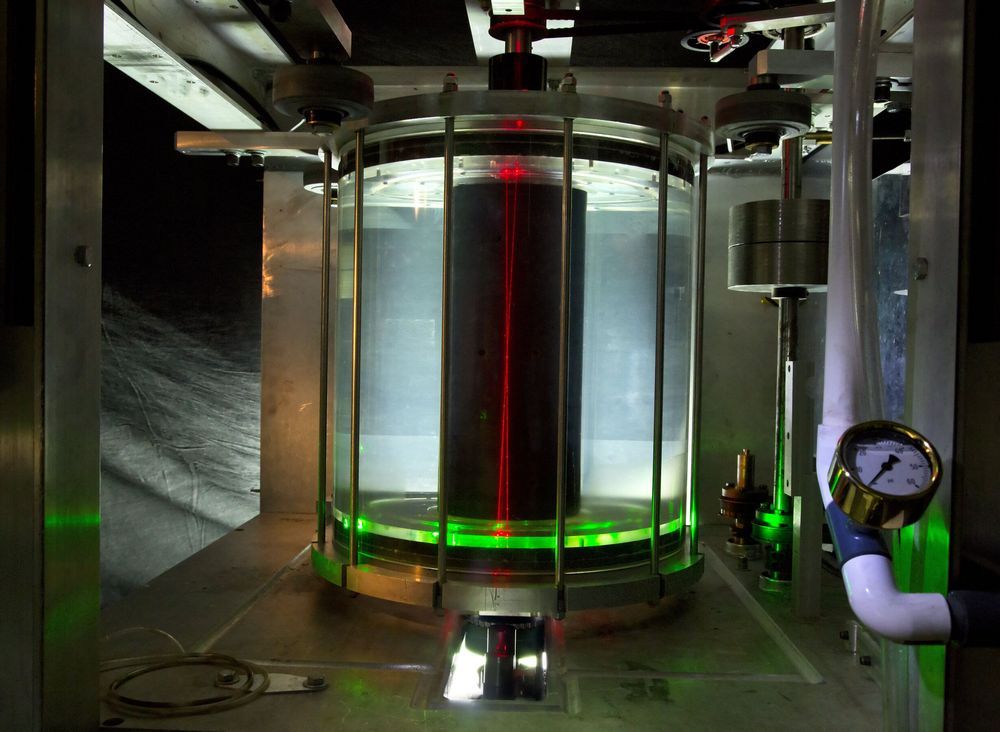
How have stars and planets developed from the clouds of dust and gas that once filled the cosmos? A novel experiment at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has demonstrated the validity of a widespread theory known as “magnetorotational instability,” or MRI, that seeks to explain the formation of heavenly bodies.
The theory holds that MRI allows accretion disks, clouds of dust, gas, and plasma that swirl around growing stars and planets as well as black holes, to collapse into them. According to the theory, this collapse happens because turbulent swirling plasma, technically known as “Keplerian flows,” gradually grows unstable within a disk. The instability causes angular momentum—the process that keeps orbiting planets from being drawn into the sun—to decrease in inner sections of the disk, which then fall into celestial bodies.
Unlike orbiting planets, the matter in dense and crowded accretion disks may experience forces such as friction that cause the disks to lose angular momentum and be drawn into the objects they swirl around. However, such forces cannot fully explain how quickly matter must fall into larger objects for planets and stars to form on a reasonable timescale.


Michael Griffin, the undersecretary for research and engineering, expects future budgets to provide funds for lasers that the missile defense agency can more rapidly develop and field. Space-control needs to have megawatt-class lasers.
Hypersonic weapons’ low signature in flight and high degree of maneuverability upon final approach to targets make the weapons difficult to defend against.
The last time the US really invested in transformative capabilities that overwhelmed adversaries [in Desert Storm] was the Reagan era.
Space rocks come crashing down to Earth with somewhat startling regularity, and when they do they often create a big boom. When a meteorite detonates in Earth’s atmosphere it produces an explosion which researchers call bolides, or simply “fireballs.”
Most of the time, a fireball appears and disappears before anyone is quick enough to grab their smartphone and record it, so we’re left with dash cam videos and still images from stationary cameras to give us a glimpse of the event. Last week, a fireball came crashing down in Cuba and, in a rare treat, we actually get to hear it.
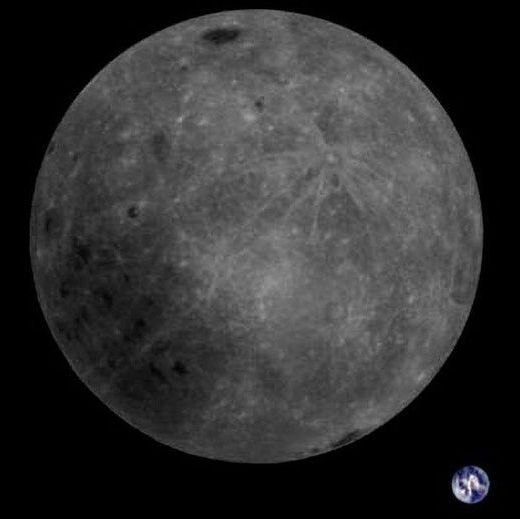

A Chinese satellite currently orbiting the moon has captured a beautiful photo showing both the far side (AKA dark side) of the Moon as well as planet Earth in the background.
The Dwingeloo Radio Observatory in the Netherlands reports that the photo was captured by China’s Longjiang-2 satellite on February 3rd, 2019.