Learn more about the framework that will establish the United States Space Force.
LEADING IN A NEW WARFIGHTING DOMAIN: President Trump knows warfare is changing – space is now a warfighting domain just like the air, land and sea.


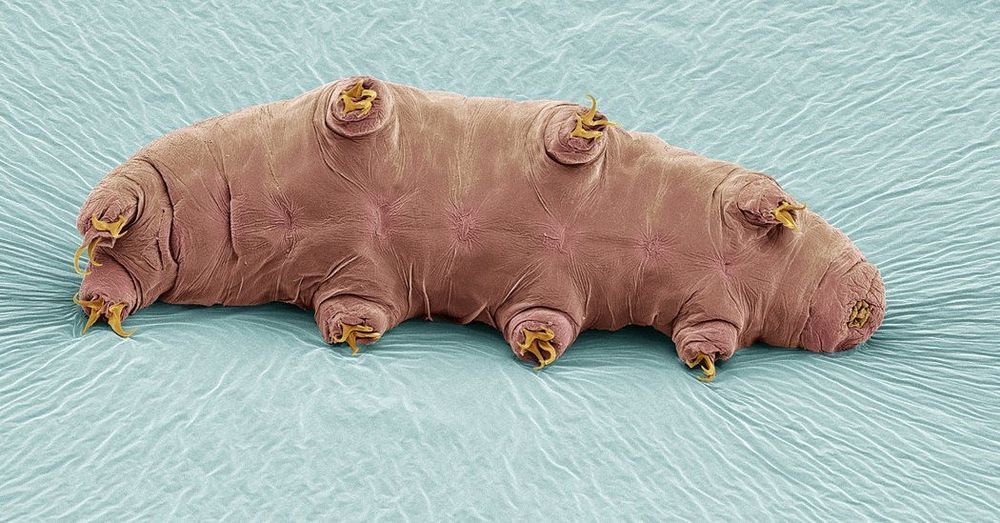
There are many instances in medicine when it would be helpful to stop, or greatly slow down, time. Doing so could spare a limb from amputation, prevent paralysis after a stroke or save your life following a heart attack.
Across the tree of life, there are many organisms that can essentially cheat time by decelerating their biology. Chief among them is the tardigrade, a creature no bigger than a speck of sand that can survive severe temperatures and pressures, outer space and all sorts of apocalyptic scenarios by entering a dormant state called anhydrobiosis.
A team at Harvard Medical School is studying tardigrades in hopes of finding medical treatments that halt tissue damage. In particular, the scientists are drawing inspiration from special proteins suspected to help tardigrades achieve suspended animation. They aim to synthesize a version of these proteins that can enter human cells and pause processes leading to cell death.
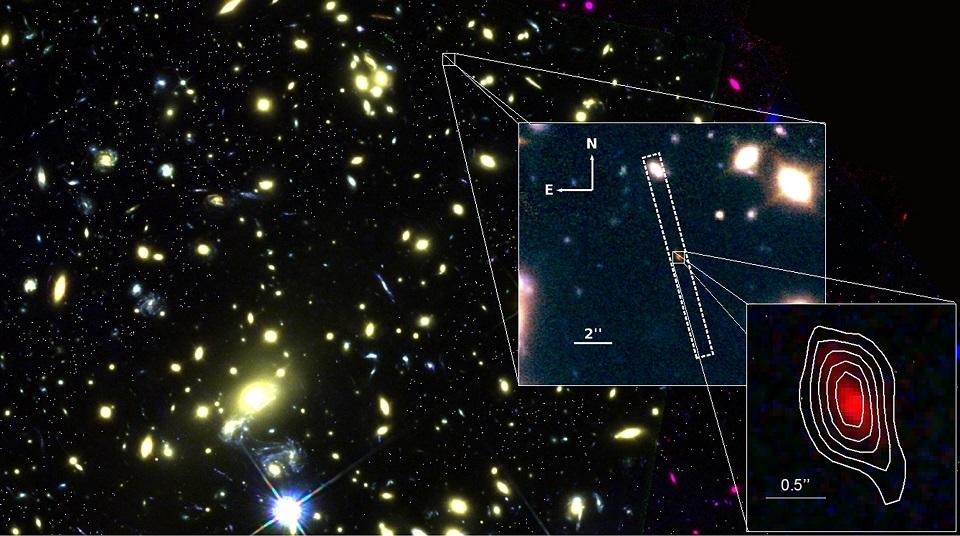

The known Universe just got a lot bigger.
A new map of the night sky published Tuesday charts hundreds of thousands of previously unknown galaxies discovered using a telescope that can detect light sources optical instruments cannot see. Current latest trending Philippine headlines on science, technology breakthroughs, hardware devices, geeks, gaming, web/desktop applications, mobile apps, social media buzz and gadget reviews.
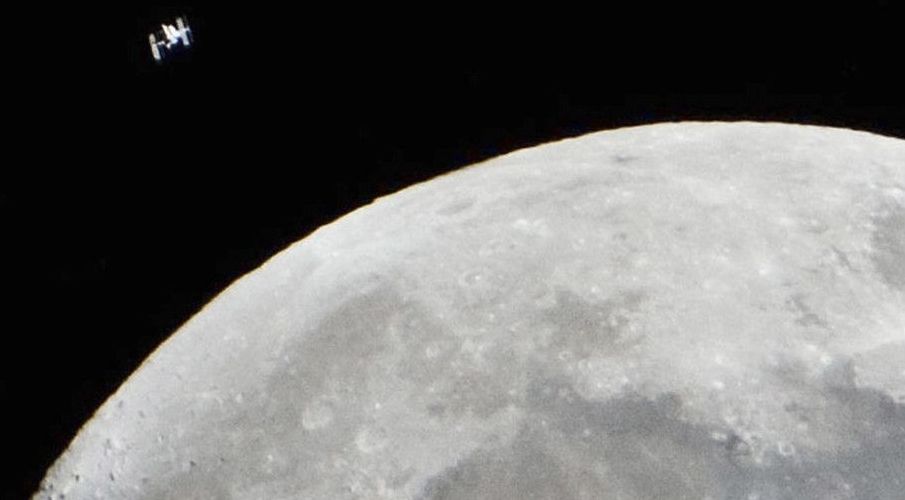

The stars aligned for a London based amateur astronomer, who managed to catch a shot of the International Space Station passing in front of the moon under the perfect conditions, with epic results.
Spotting ISS’s lunar crossings is extremely rare, making the close-up footage of the vessel’s swift passage particularly remarkable. While other amateurs have captured similar crossings, Szabolcs Nagy’s clip is incredibly close and clear, showing the manned satellite streaking through the center of the frame.
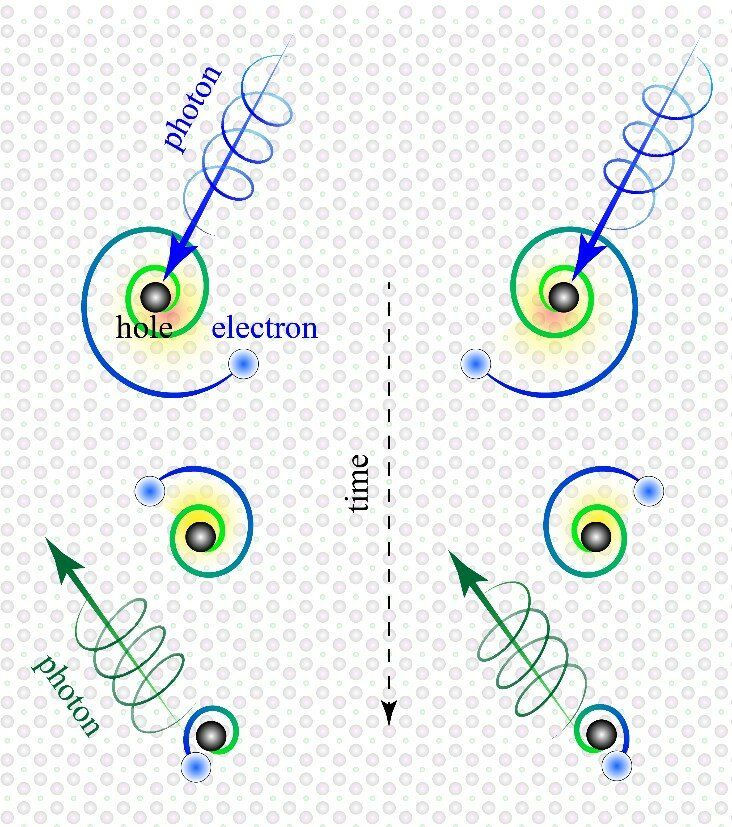
Rutgers and other physicists have discovered an exotic form of electrons that spin like planets and could lead to advances in lighting, solar cells, lasers and electronic displays.
It’s called a “chiral surface exciton,” and it consists of particles and anti-particles bound together and swirling around each other on the surface of solids, according to a study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Chiral refers to entities, like your right and left hands, that match but are asymmetrical and can’t be superimposed on their mirror image.
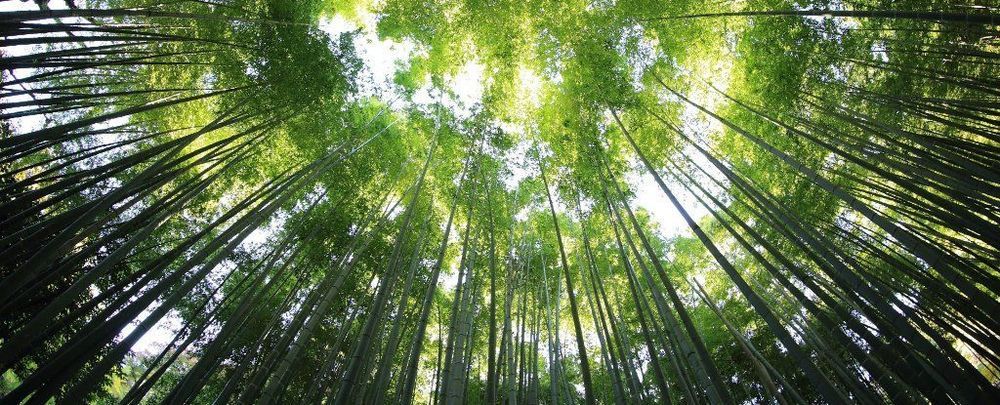


An ambitious new analysis of the world’s forests found that there’s space to plant 1.2 trillion new trees — a number that would absorb more carbon than human emissions.
According to the new data, ETH Zurich researcher Thomas Crowther told The Independent, trees are “our most powerful weapon in the fight against climate change.”
Crowther told The Independent that the new analysis, which he presented at a conference this weekend, suggests that a worldwide tree-planting spree would have a greater impact on the planet’s environment than building wind turbines or vegetarian diets — an effort, he says, that could cancel a decade of greenhouse emissions.
The test is actually the RemoveDEBRIS satellite’s second trick: in September, it successfully deployed a spider-like web that was meant to grab space junk out of the sky.
The team at the University of Surrey is now preparing for its third and final test: RemoveDEBRIS will inflate a sail that will slowly drag it into Earth’s atmosphere where it will burn up and be destroyed.
READ MORE: Space junk harpooned like whale in orbit-cleanup test [Associated Press].

Stargazers will get a close-up look at Earth’s natural satellite this week thanks to the brightest supermoon event of the year.
A supermoon phenomenon occurs when a full moon, on its oval-shaped orbit, is at its closest to us, known as perigee, which is about 356,000 kilometres as measured from the centre of the Earth to the centre of the moon.
It takes place when the moon’s orbit brings it to the closest point to Earth while at the same time bathed in sunlight, giving the moon its bright appearance.