Beth Moses will use her flight to craft future astronaut training.
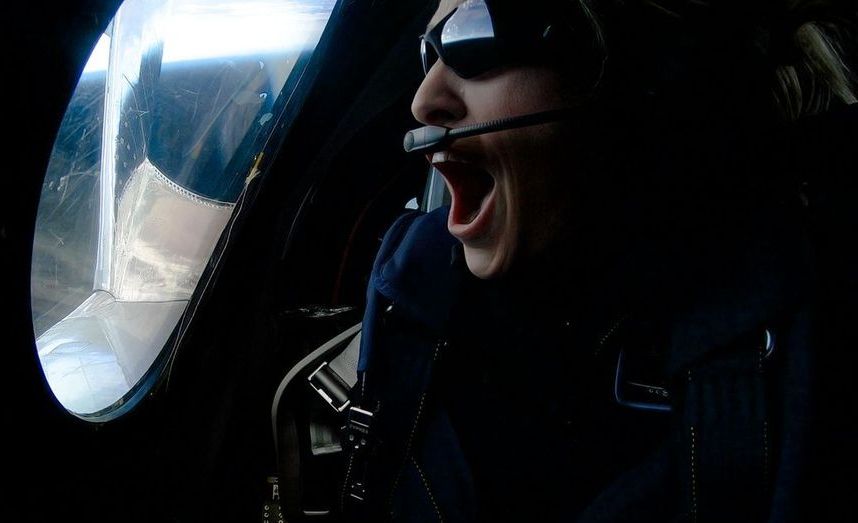



This is something near and dear to me.
The Out Astronaut Project is a collaboration between Stardom Space and Project PoSSUM to address the under-representation of Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer (LGBTQ) people in science and space. We highlight the contributions of LGBTQ members currently working in science and space and provide grants to promising LGBTQ students currently pursuing professions in space-related fields.

Scientists in India observed the highest-voltage thunderstorm ever documented with the help of a subatomic particle you might not hear much about: the muon.
The researchers operate the GRAPES-3 telescope, which measures muons, particles that are similar to electrons but heavier. Specifically, the Gamma Ray Astronomy at PeV EnergieS Phase-3 (GRAPES-3) muon telescope measures high-energy particles from outer space called cosmic rays. It typically picks up 2.5 million muons each minute, mapped on a 13-by-13 grid across the sky. But during thunderstorms, it experiences quick changes to the amount of muons it receives. The GRAPES-3 researchers added electric field monitors to the experiment, and devised a way to turn these muon fluctuations into measurements of the voltage of passing storms.
The Shelton family from Texas sent their first bouquet in 1998 after the Challenger disaster. And they haven’t stopped since.

Today is National Agriculture Day! From enabling higher crop yields to maximizing every drop of water for farmers, NASA is working to help transform the agriculture industry. Check out some of the farming tools that have roots at NASA:
Growing plants can be tough, whether you’re on a spaceship or Earth. A special fertilizer made it easier for astronauts on the International Space Station and farmers down below, resulting in just one of the space program’s many contributions to agriculture.
Numerous farming tools have roots at NASA. Over the years, companies large and small have partnered with the agency, honed technologies and delivered innovations to benefit the industry. These are just a few examples:
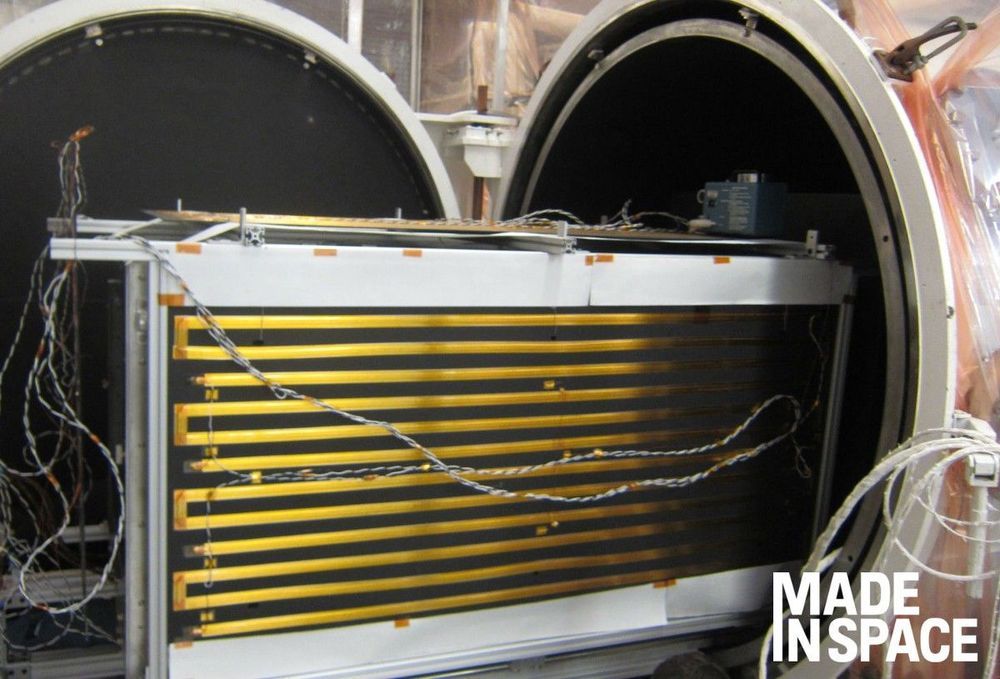

The Made In Space Archinaut program has accomplished another exciting milestone. During recent testing at Northrop Grumman’s Space Park facilities in Redondo Beach, California, we successfully operated Archinaut’s core additive manufacturing and robotic assembly technology suite in a space-like environment. These operations took place in a thermal vacuum (TVAC) chamber, simulating the extreme temperature and vacuum pressure of what a satellite in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) would be exposed to. The completion of this ground-based testing raises the technology readiness level (TRL) of the Archinaut platform and demonstrates that core Archinaut technologies are now prepared to operate in space.
The Archinaut platform looks to provide mission critical, space-optimized structures on orbit that would otherwise be too large to launch, using on-demand, adaptable manufacturing. With the marriage of additive manufacturing and robotic assembly, Archinaut enabled structures can range from:
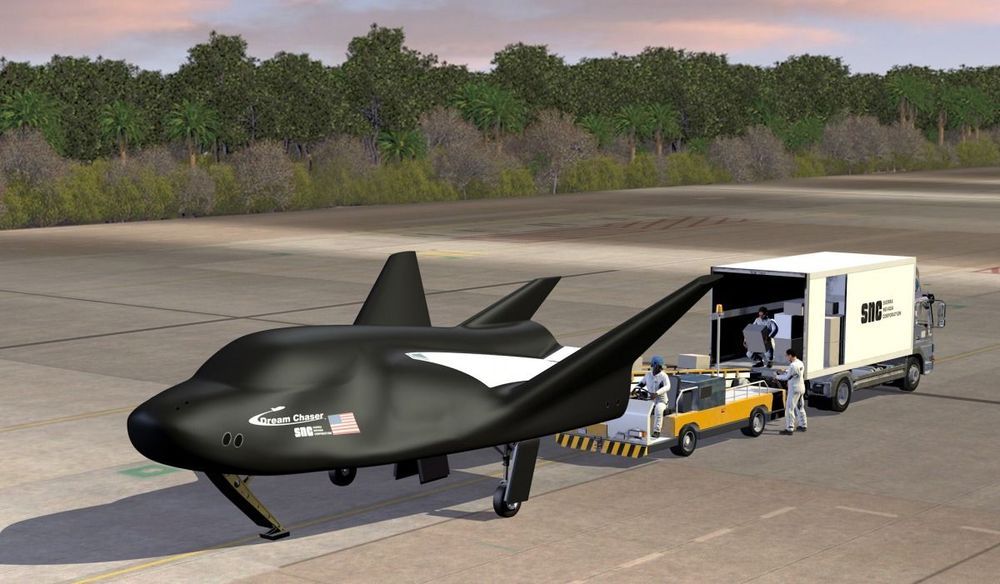

Watch out space, there’s a new commercial cargo carrier entering the race.
Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) has been given the go ahead from NASA to begin full-scale production of it’s “Dream Chaser” commercial space cargo plane. Scheduled to make its first mission in 2020, the company announced on December 18 that it had cleared the last milestone in its Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract. Now the company is able to move ahead with the full-scale production of the carrier which will be used to deliver cargo to the International Space Station (ISS).