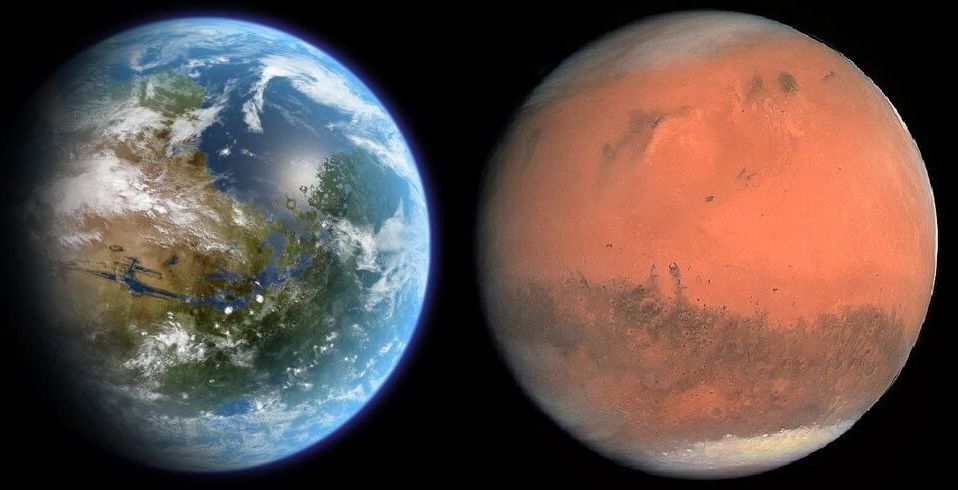
Roughly 4 billion years ago, Mars looked a lot different than it does today. For starters, its atmosphere was thicker and warmer, and liquid water flowed across its surface. This included rivers, standing lakes, and even a deep ocean that covered much of the northern hemisphere. Evidence of this warm, watery past has been preserved all over the planet in the form of lakebeds, river valleys, and river deltas.
For some time, scientists have been trying to answer a simple question: where did all that water go? Did it escape into space after Mars lost its atmosphere, or retreat somewhere? According to new research from Caltech and the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), between 30% and 90% of Mars’ water went underground. These findings contradict the widely-accepted theory that Mars lost its water to space over the course of eons.
The research was led by Eva Scheller, a Ph.D. candidate at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). She was joined by Caltech Prof. Bethany Ehlmann, who is also the associate director for the Keck Institute for Space Studies; Caltech Prof. Yuk Yung, a senior research scientist with NASA JPL; Caltech graduate student Danica Adams; and JPL research scientist Renyu Hu.