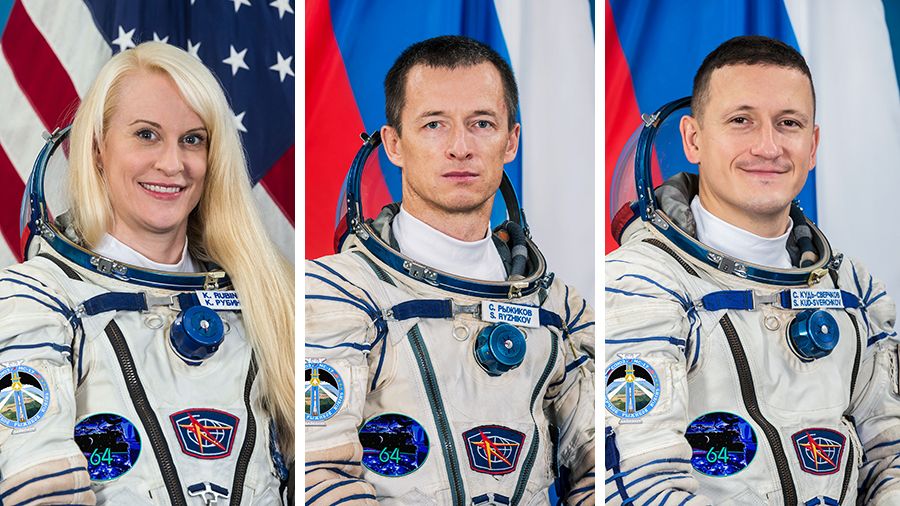
(From left) NASA astronaut Kate Rubins with Roscosmos cosmonauts Sergey Ryzhikov and Sergey Kud-Sverchkov will launch to the space station for a six-month research mission. A trio of space travelers, including NASA astronaut Kate Rubins, is s…
A trio of space travelers, including NASA astronaut Kate Rubins, is scheduled to launch aboard the Soyuz MS-17 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan to the International Space Station at 1:45 a.m. EDT (10:45 a.m. Kazakhstan time) Wednesday, Oct. 14.
Beginning at 12:45 a.m., NASA Television and the agency’s website will provide live coverage of the crew’s launch. Teams at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan are making final preparations for the liftoff of Rubins and Russian cosmonauts Sergey Ryzhikov and Sergey Kud-Sverchkov.
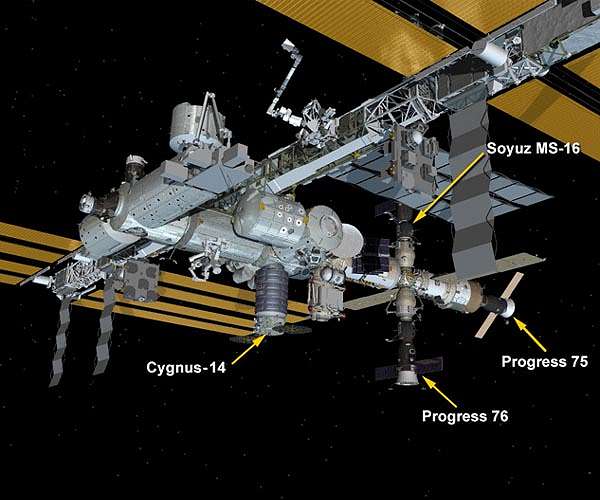
The launch will send the crew members on a two-orbit, three-hour journey to the space station, where they will join Expedition 63 Commander Chris Cassidy of NASA and Roscosmos cosmonauts Anatoly Ivanishin and Ivan Vagner, temporarily increasing the orbiting laboratory’s population to six people.




 As part of the partnership between SpaceWatch. Global and Joint Air Power Competence Centre, we have been granted permission to publish selected articles and texts. We are pleased to present “Space Situational Awareness Together We Stand, Divided We Fall”, originally published in the Joint Air Power Competence Centre Journal 30.
As part of the partnership between SpaceWatch. Global and Joint Air Power Competence Centre, we have been granted permission to publish selected articles and texts. We are pleased to present “Space Situational Awareness Together We Stand, Divided We Fall”, originally published in the Joint Air Power Competence Centre Journal 30.