NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft has detected light with no obvious source coming from beyond our galaxy.
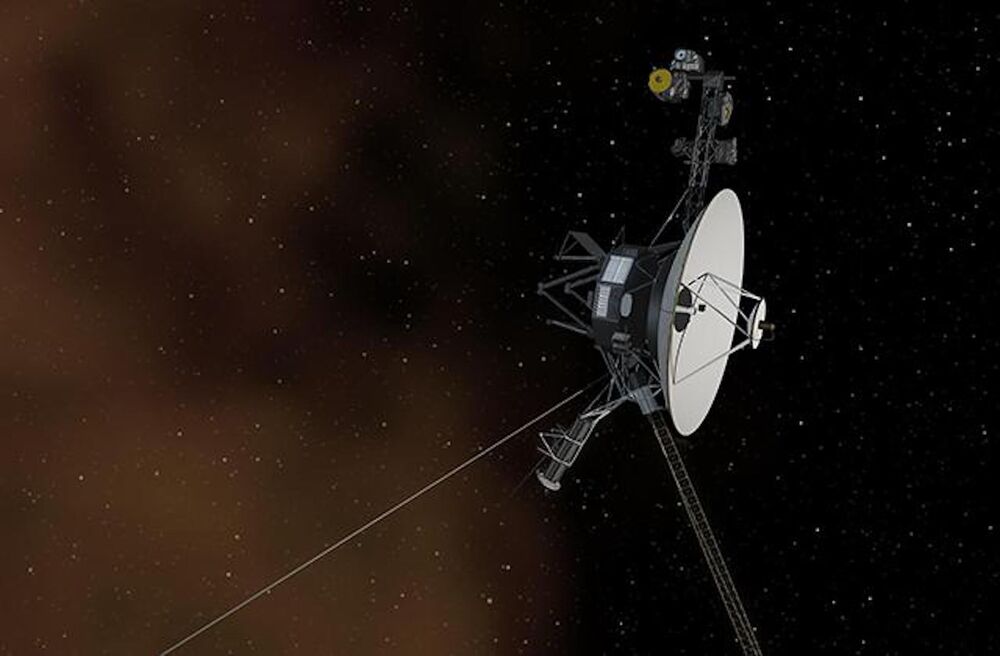



The Voyager probes have detected an entirely new kind of electron burst outside the solar system.
It is the first time this “unique physics” have been detected by a spacecraft, and could allow for new breakthroughs in our understanding of the “interstellar medium”, or the space between the stars.
The two Voyager spacecraft were launched by NASA more than 40 years ago, with the aim of flying to the far reaches of our solar system. They have now gone even further than that, reaching interstellar space, and exploring the gaps between the stars, giving us the first glimpses of what it might be like in that mysterious zone.
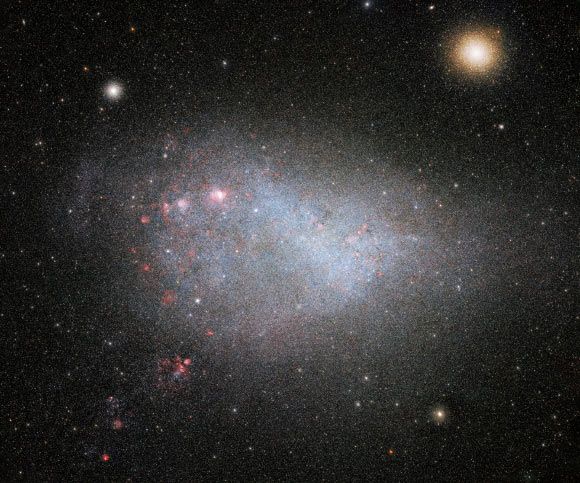

New images, taken with the 520-megapixel Dark Energy Camera (DECam) on the Víctor M. Blanco 4-m Telescope at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, represent a portion of the second data release from the Survey of the MAgellanic Stellar History (SMASH), the deepest, most extensive survey of the Magellanic Clouds (high-resolution images: the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic Cloud).

Astronomers have mapped about a million previously undiscovered galaxies beyond the Milky Way, in the most detailed survey of the southern sky ever carried out using radio waves.
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey (or RACS) has placed the CSIRO’s Australian SKA Pathfinder radio telescope (ASKAP) firmly on the international astronomy map.
While past surveys have taken years to complete, ASKAP’s RACS survey was conducted in less than two weeks — smashing previous records for speed. Data gathered have produced images five times more sensitive and twice as detailed as previous ones.
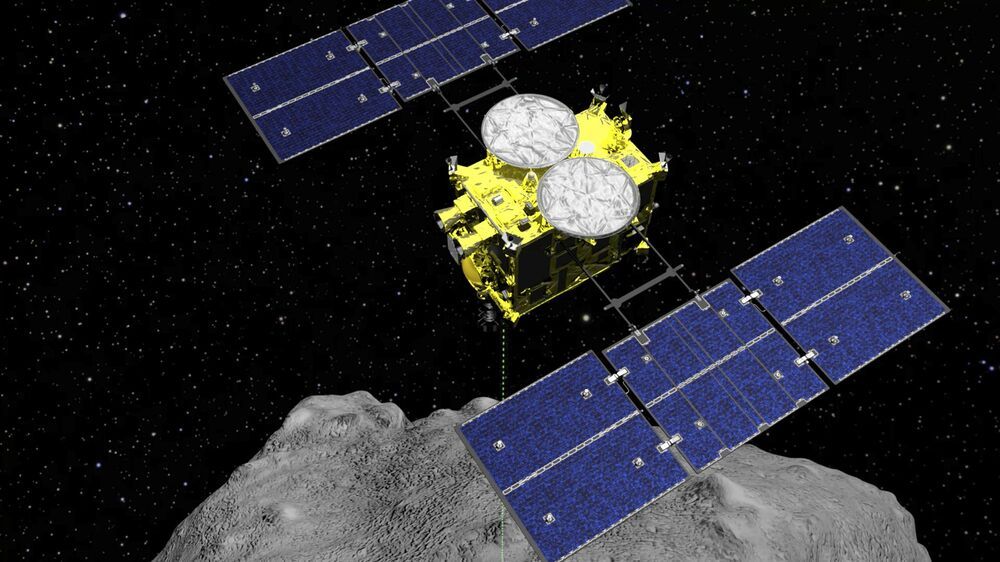
TOKYO (AP) — Japanese space agency officials said Friday the Hayabusa2 spacecraft is on its intended trajectory as it approaches Earth to deliver a capsule containing samples from a distant asteroid that could provide clues to the origin of the solar system and life on Earth.
The spacecraft left the asteroid Ryugu, about 300 million kilometers (180 million miles) away, a year ago. The capsule is to be released 220,000 kilometers (136,700 miles) away in space and land in a remote, sparsely populated area of Woomera, Australia, on Sunday.
Hayabusa2 is flying smoothly according to plan, Yuichi Tsuda, project manager at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, said at a briefing ahead of the critical separation of the capsule from the spacecraft on Saturday.

Europe’s Gaia spacecraft has produced the best-yet map of the Milky Way with measurements of 1.8 billion objects.

