Category: space – Page 127
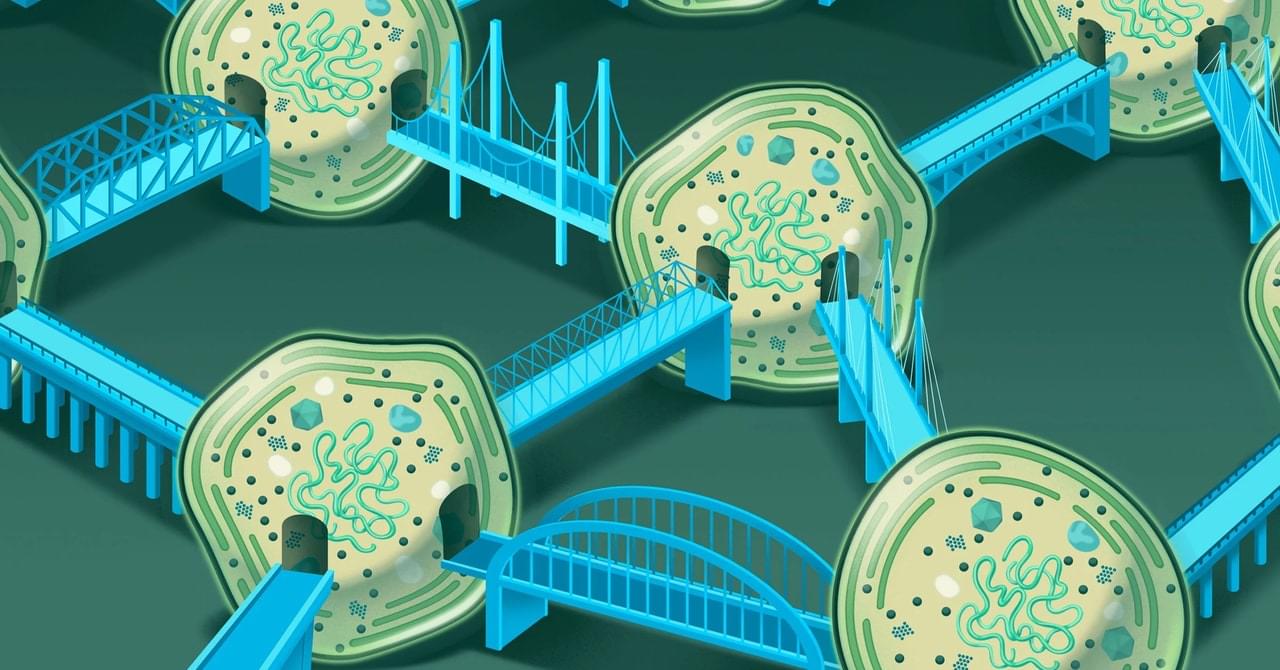
Life on Earth Depends on Networks of Ocean Bacteria
Another question is how bacteria form these tubes, and under what conditions. The tubes are not much longer than an individual cell, and Prochlorococcus, in particular, is thought to spread out in the water column. Muñoz-Marín and her team are curious about the concentrations of bacteria required for a network to form. “How often would it be possible for these independent cells to get close enough to each other in order to develop these nanotubes?” García-Fernandez asked. The current study shows that nanotubes do form among wild-caught cells, but the precise requirements are unclear.
Looking back at what people thought about bacterial communication when he began to study marine cyanobacteria 25 years ago, García-Fernandez is conscious that the field has undergone a sea change. Scientists once thought they saw myriad individuals floating alongside each other in immense space, competing with neighboring species in a race for resources. “The fact that there can be physical communication between different kind of organisms—I think that changes many, many previous ideas on how the cells work in the ocean,” he said. It’s a far more interconnected world than anyone realized.

Scientist publishes fascinating ‘evidence’ that we all live inside a computer simulation
The simulation hypothesis suggests that our entire universe and reality could just be hyper-enhanced reality illusions.
He believes recent developments in the field of information physics ‘appear to support this possibility’ in that the physical world is made up of bits of information.
Vopson goes even further by claiming that information might have physical weight and could be a key part of the universe.
The Last Evolution (SF Audiobook) by John W. Campbell Jr
The Last Evolution, SF Audiobook, Science Fiction by John W. Campbell Jr.
I am the last of my type existing today in all the Solar System. I, too, am the last existing who, in memory, sees the struggle for this System, and in memory I am.
The Last Evolution by John W. Campbell, Jr.
Please subscribe my channel.
Chapter One of the Science Fiction classic that inspired the movie THE THING. Narration by Oscar nominated and Emmy winning Special Makeup Effects Artist.
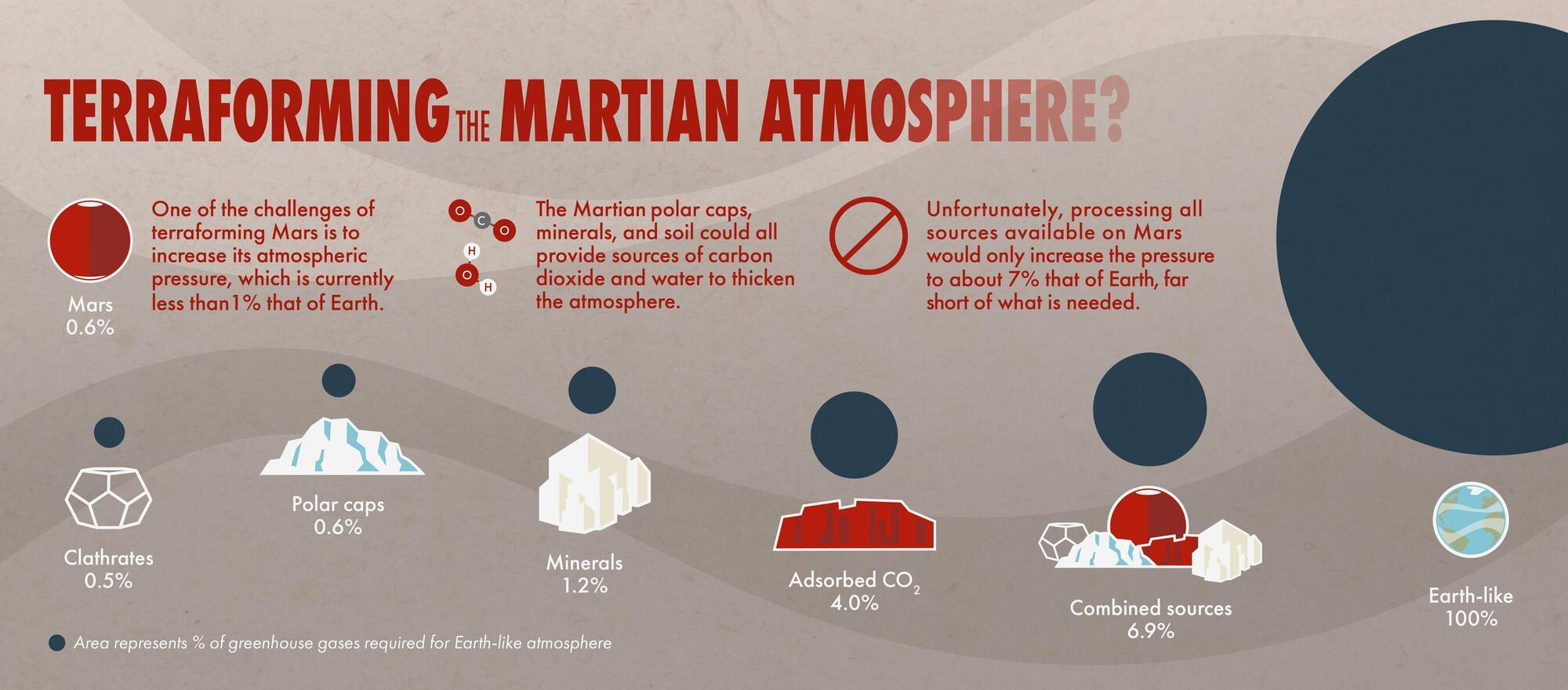
Mars Terraforming Not Possible Using Present-Day Technology
Science fiction writers have long featured terraforming, the process of creating an Earth-like or habitable environment on another planet, in their stories. Scientists themselves have proposed terraforming to enable the long-term colonization of Mars. A solution common to both groups is to release carbon dioxide gas trapped in the Martian surface to thicken the atmosphere and act as a blanket to warm the planet.
However, Mars does not retain enough carbon dioxide that could practically be put back into the atmosphere to warm Mars, according to a new NASA-sponsored study. Transforming the inhospitable Martian environment into a place astronauts could explore without life support is not possible without technology well beyond today’s capabilities.


AI model masters new terrain at NASA facility one scoop at a time
Extraterrestrial landers sent to gather samples from the surface of distant moons and planets have limited time and battery power to complete their mission. Aerospace and computer science engineering researchers at The Grainger College of Engineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign trained a model to autonomously assess and scoop quickly, then watched it demonstrate its skill on a robot at a NASA facility.
Aerospace Ph.D. student Pranay Thangeda said they trained their robotic lander arm to collect scooping data on a variety of materials, from sand to rocks, resulting in a database of 6,700 points of knowledge. The two terrains in NASA’s Ocean World Lander Autonomy Testbed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory were brand new to the model that operated the JPL robotic arm remotely.
The study, “Learning and Autonomy for Extraterrestrial Terrain Sampling: An Experience Report from OWLAT Deployment,” was published in the AIAA Scitech Forum.

Samples from the surface needed to unravel history of Mars
Geologically, Mars is very reminiscent of the moon. But it also looks a lot like the Earth. It all depends on who you ask.
Current understanding of Mars’ evolution is based on spacecraft measurements and meteorite analysis. Those meteorites were ejected from Mars and traversed space before landing on Earth, where they were discovered primarily in African deserts and Antarctica. They come in two categories: shergottites and nakhlites. Each paints a distinctly different picture of Mars’ geologic history.
In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, LLNL researchers argue that samples retrieved from known locations on Mars by sample return missions could solve this conundrum.
All planets to align at the same time in rare planetary parade
Seven planets are set to appear in the night sky this month in a rare full planetary alignment.
Mars, Jupiter, Uranus, Venus, Neptune, Mercury and Saturn will appear in a row on the evening of 28 February, marking the last time for 15 years that all of the planets will be visible at the same time.
Planetary parades of four or five planets happen relatively regularly, though alignments of six or seven are remarkably rare.