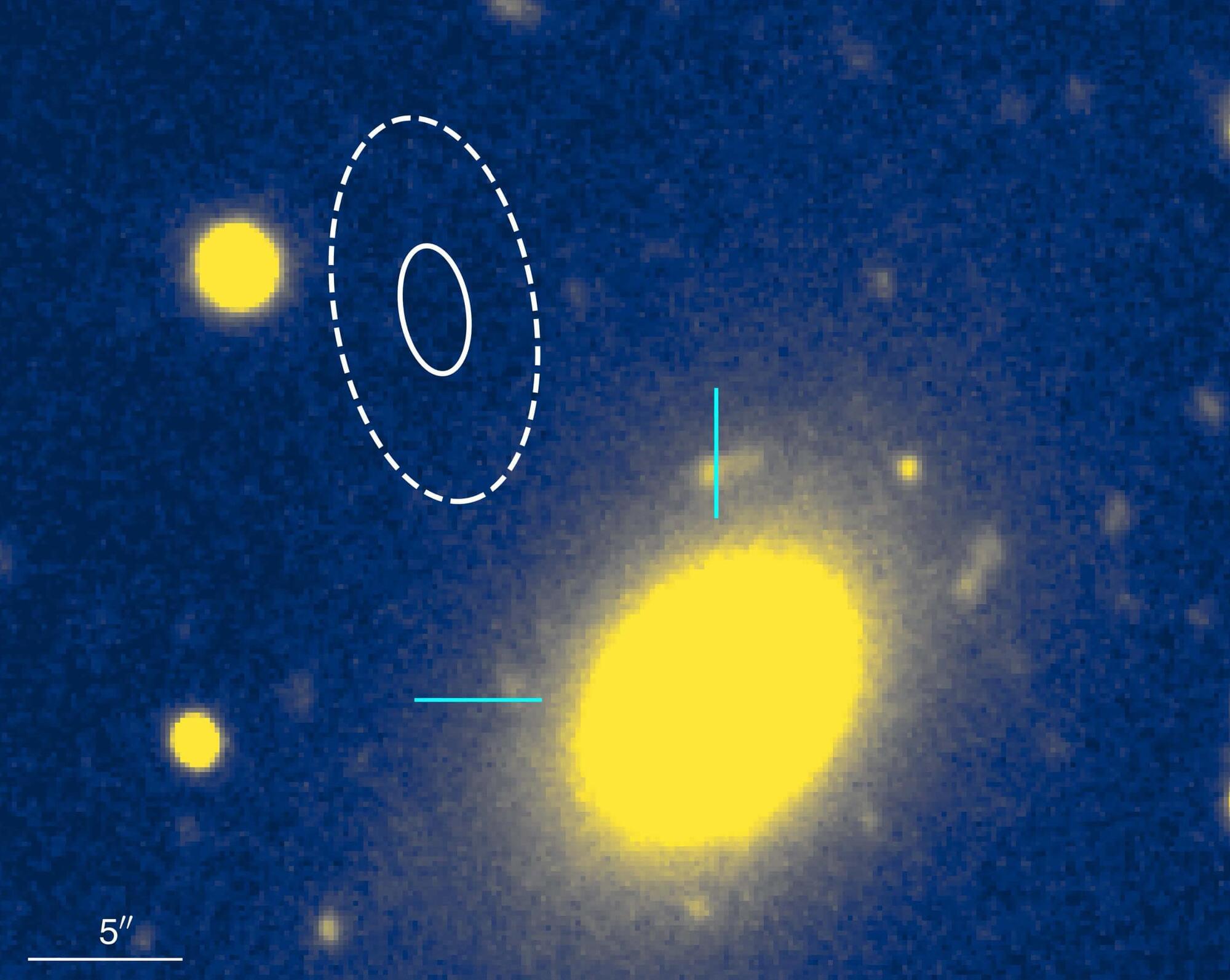
Ugly.
Job losses are always terrible. This will be a dark and painful day at a space agency that brings so much light and joy to the world. Many of the probationary employees are just starting out their careers and were likely thrilled to land a job at NASA to explore the universe. And then all of that youthful energy and hope was extinguished this week.
It’s possible to view these losses through a couple of lenses.
Yes, NASA is clearly losing some capability with these latest cuts. Many of these hires were likely being counted on to bring new energy into the space agency and become its future discoverers and leaders. And their jobs are being sacrificed for no clear purpose. Is it to increase funding for the military? Is it to pay for tax cuts for the rich? There is a lot of anger that the relatively thin budget line of NASA—less than one-half of 1 percent of the federal budget—is being sliced for such purposes.