A major concerned for Lockheed is the long passage of time between the crew’s training and the moment a serious issue does come up during a mission—which could be a few years later. “They may not remember the training. Having the right kind of on-board documentation and flight computer to be able to provide the astronauts the information they need when they need it, is important,” Pratt said. “Not just having the alarm go off but having the alarm go off and the PDF file of the manual come up at the same time. That’s really useful in helping the crew understand how to operate their own vehicle.”
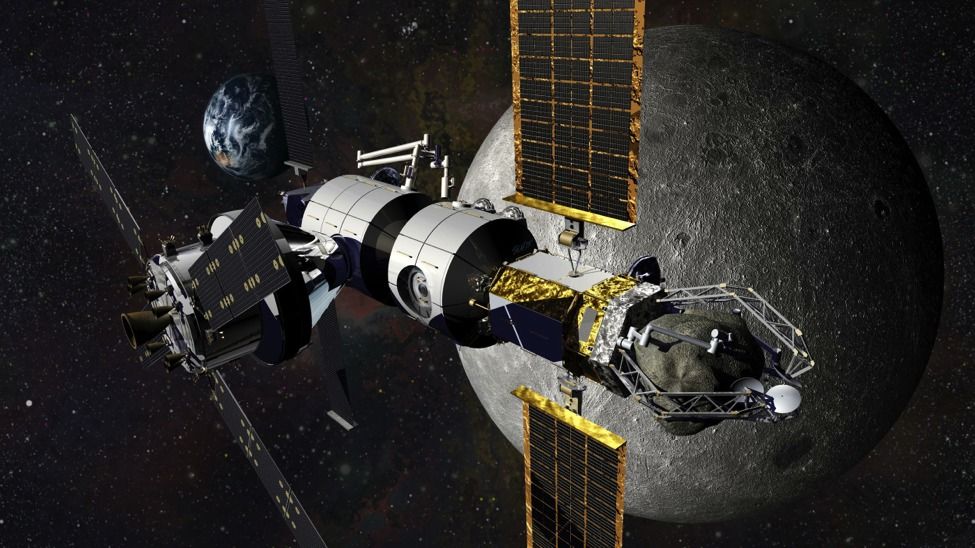
Even though Lockheed Martin’s early habitat concept will service exploration missions near the Moon, the company is always thinking about the manned mission to Mars, which will require a far more advanced successor to their current designs. Engineers will need to go through a few iterations of the concept after the health effects of long-duration human spaceflight are known and as new technology is developed. This is the basis that NASA created NextSTEP on.
The federal space agency is looking for a modular habitat that can grow, evolve and be added to. “New modules are built upon the lessons of the previous modules,” Hopkins said.