Musk said he’s “confident” the plan will be under way within five years.
“I can’t think of anything more exciting than going out there and being among the stars,” Musk said, adding that he thinks SpaceX has figured out a way to make it affordable by using revenues from the company’s satellite launches, service missions to the International Space Station and by making smaller, more efficient rockets that are mostly reusable.
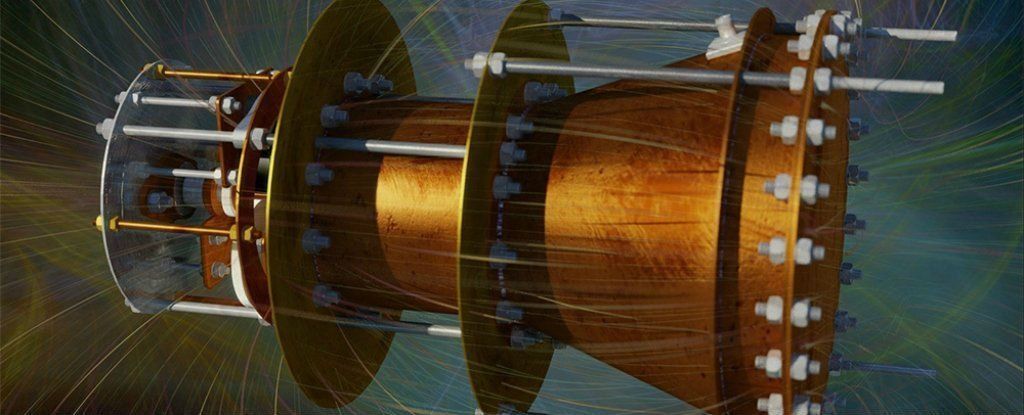
Nine years after SpaceX’s first successful launch — its fourth ever — Musk said his engineers are now perfecting propulsive landing. He believes the BFR rocket can carry out missions to the moon and back without producing propellant, enabling the establishment of a lunar space station.