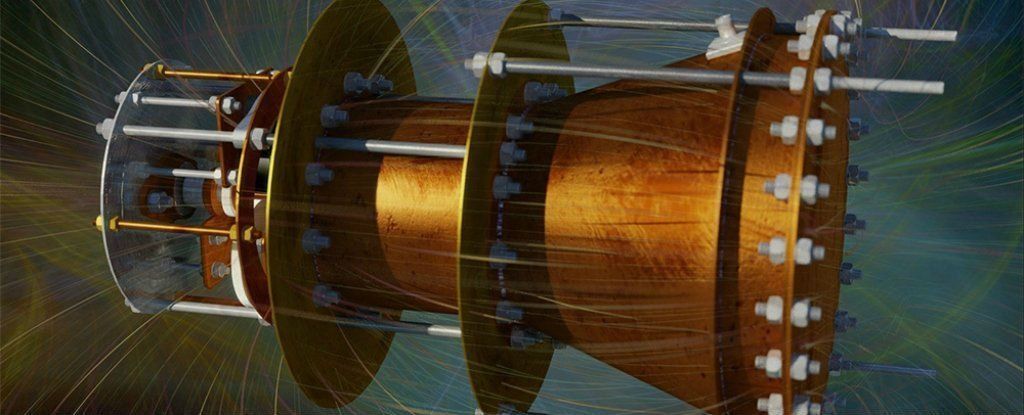
As the U.S. government continues to pursue plans for a crewed mission to Mars, NASA has contracted with BWXT Nuclear Energy Inc. of Lynchburg, Virginia, to advance concepts in Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP), which could drastically reduce travel times to Mars.
This is part of NASA’s Game Changing Development Program, which takes ideas from academia and industry as well as NASA and other government programs, to advance new approaches to space technologies to accommodate the changing needs of U.S. space efforts.
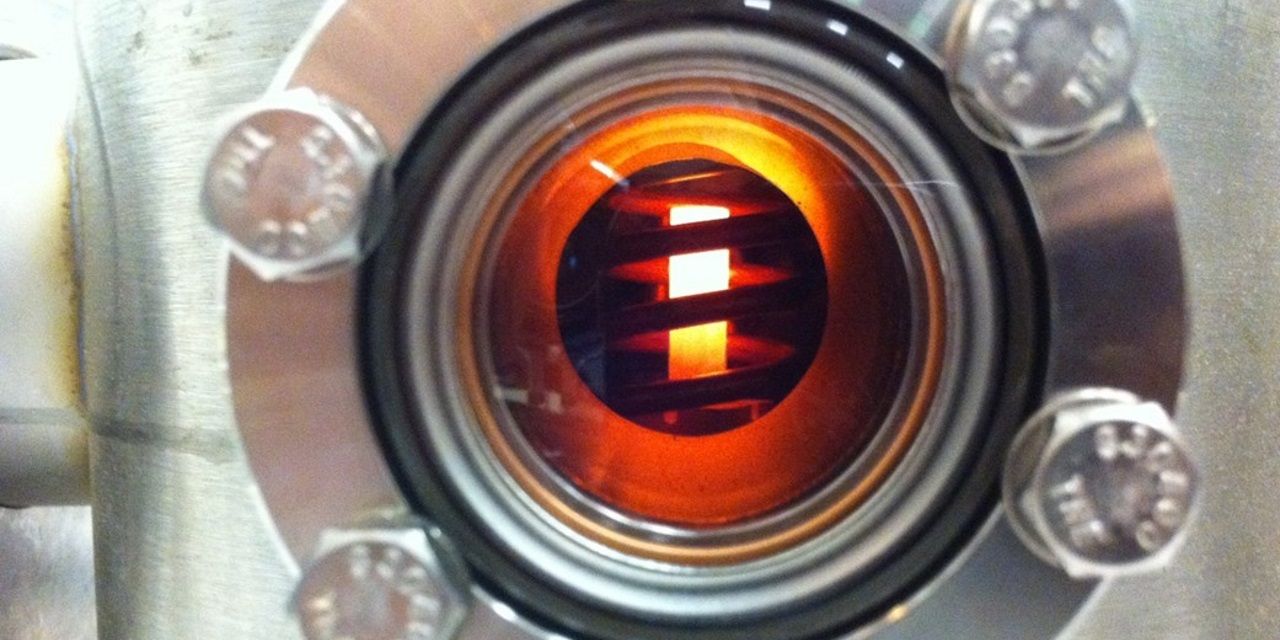
NTP is not a new concept, but it was abandoned in 1972 when plans for a Mars mission were shelved. NASA conducted ground tests since 1955 to determine the viability of NTP and has occasionally been revisited as a conceptual part of Mars mission feasibility studies.