Fan-made video animation — launch & landing of SpaceX Big Falcon Rocket (BFR); created by Reddit user Hazegrayart.
Category: space travel – Page 472

The Origin of Our First Interstellar Visitor
We were recently visited by a traveler from outside our solar system. This is the first time we’ve ever seen an object that came to us from interstellar space. It’s name is ‘Oumuamua. Check out http://curiositystream.com/spacetime
You can further support us on Patreon at https://www.patreon.com/pbsspacetime
Get your own Space Time tshirt at http://bit.ly/1QlzoBi
Tweet at us! @pbsspacetime
Facebook: facebook.com/pbsspacetime
Email us! pbsspacetime [at] gmail [dot] com.
Comment on Reddit: http://www.reddit.com/r/pbsspacetime
Help translate our videos!
Previous Episode:
Understanding the Uncertainty Principle with Quantum Fourier Series.
In this Space Time Journal Club we look into the origins of ‘Oumuamua, an asteroid visiting us from beyond our solar system! We’ll focus on the results of:
“The origin of interstellar asteroidal objects like 1I/2017 U1”

Canadian QEYSSat Quantum Satellite Program Gets Next Round of Funding
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) has awarded $1.85M contract to the University of Waterloo for the Quantum Encryption and Science Satellite (QEYSSat) mission.
The QEYSSat mission was one of two projects cited in the 2017 budget when it was unveiled in March of this year. In April, the government sent Innovation Science and Economic Development (ISED) Minister Navdeep Bains to the CSA’s headquarters to formally announce the funding for the QEYSSat mission along with funding for a radar instrument that will be developed for a future orbiter mission to Mars and to announce the Canadian CubeSat Project. The $80.9M of funding would be over five years.
A short history of the QEYSSat mission.

In-Space Manufacturing Is About to Get a Big Test
A bold plan to rev up off-Earth manufacturing is about to get a big test.
A small, privately built machine designed to make optical fiber is launching toward the International Space Station (ISS) aboard SpaceX’s Dragon cargo capsule tomorrow (Dec. 12).
If all goes according to plan, this little factory — which is owned by California-based startup Made In Space — will churn out stuff that’s good enough to sell here on Earth, opening up space to greater commercial use. [3D Printing: 10 Ways It Could Transform Space Travel].
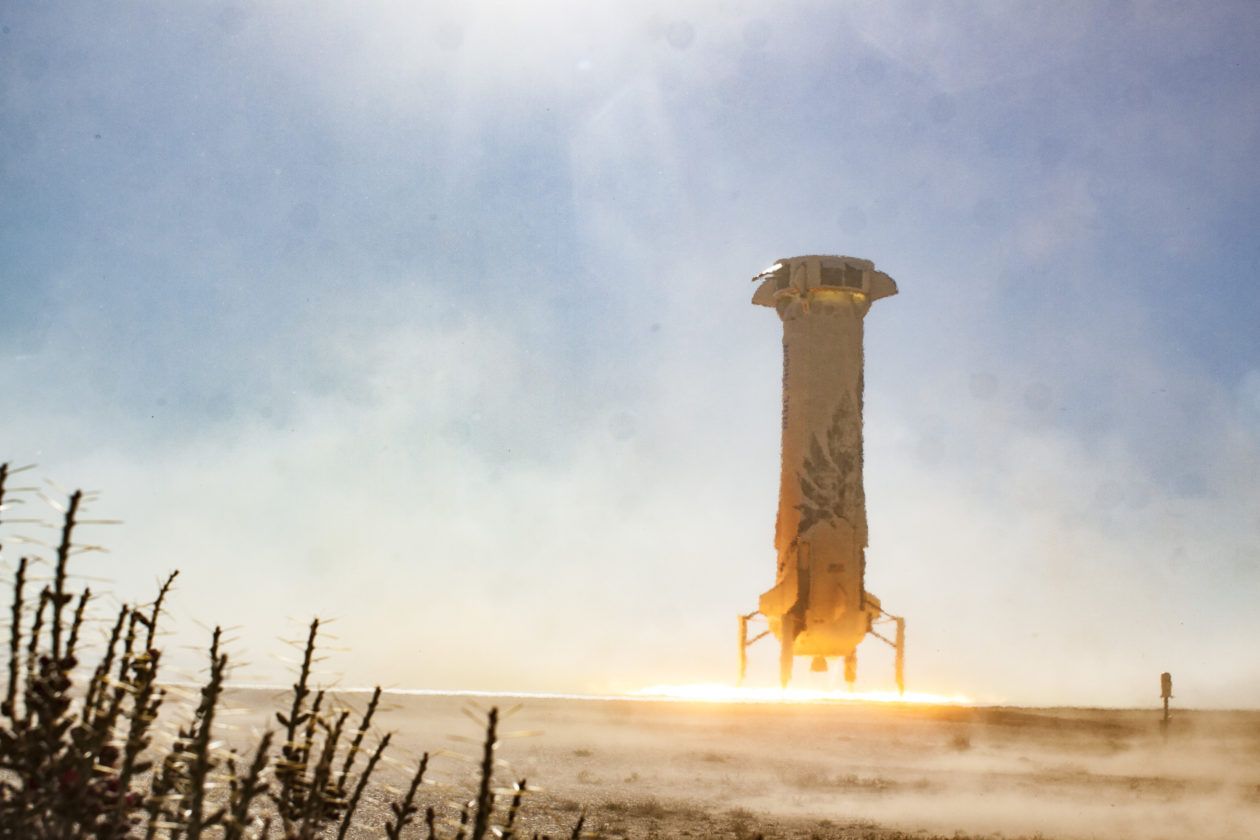

Jeff Bezos says Blue Origin gives test dummy ‘a great ride’ on New Shepard suborbital spaceship
Amazon billionaire Jeff Bezos says his space venture, Blue Origin, launched the latest version of its New Shepard suborbital spaceship today for the company’s first test flight in 14 months, with an instrumented test dummy seated aboard.
“He had a great ride,” Bezos said tonight in a tweet.

AI is now so complex its creators can’t trust why it makes decisions
Artificial intelligence is seeping into every nook and cranny of modern life. AI might tag your friends in photos on Facebook or choose what you see on Instagram, but materials scientists and NASA researchers are also beginning to use the technology for scientific discovery and space exploration.
But there’s a core problem with this technology, whether it’s being used in social media or for the Mars rover: The programmers that built it don’t know why AI makes one decision over another.
Modern artificial intelligence is still new. Big tech companies have only ramped up investment and research in the last five years, after a decades-old theory was shown to finally work in 2012. Inspired by the human brain, an artificial neural network relied on layers of thousands to millions of tiny connections between “neurons” or little clusters of mathematic computation, like the connections of neurons in the brain. But that software architecture came with a trade-off: Since the changes throughout those millions of connections were so complex and minute, researchers aren’t able to exactly determine what is happening. They just get an output that works.


Why human race is 20 years away from guaranteeing its immortality – physicist Brian Cox on space colonies and mining asteroids
“We’re at a stage now where the next 10 or 20 years are the time we become a spacefaring civilisation,” he says. “From then on, our future is guaranteed as a civilisation. The moment we get to the moon and Mars and start to exploit the resources in the solar system is the moment we become essentially immortal as a civilisation. Because we won’t just be confined to one planet that we can damage any more. Now is the time we do that.”
Professor believes we will become a spacefaring civilisation in the next 10 or 20 years, and thereby guarantee our future forever, as long as we don’t do anything stupid like ‘having a war in the Pacific’.