It’s #MarsLanding Day! Today, our NASA InSight spacecraft blazes into the atmosphere of Mars at 12,300 mph and slows to just 5 mph in less than 7 minutes, before gently touching down on the surface. Watch live starting at 2 p.m. EST.
Category: space travel – Page 432
A NASA spacecraft is set to land on Mars today
WATCH: The countdown begins as the Mars Insight Lander is set to touch down today. This will be NASA’s first attempt at landing on Mars since the Curiosity Rover in 2012.
What If Humanity Became an Interstellar Society?
What would it take to become an interstellar civilization?
NASA ScienceCasts: New InSight into the Red Planet
We’ve always referred to Mars as the Red Planet because of its surface color. But what’s below that dusty crust? NASA InSight mission is currently cruising through space, set for our #MarsLanding and determined to find out.
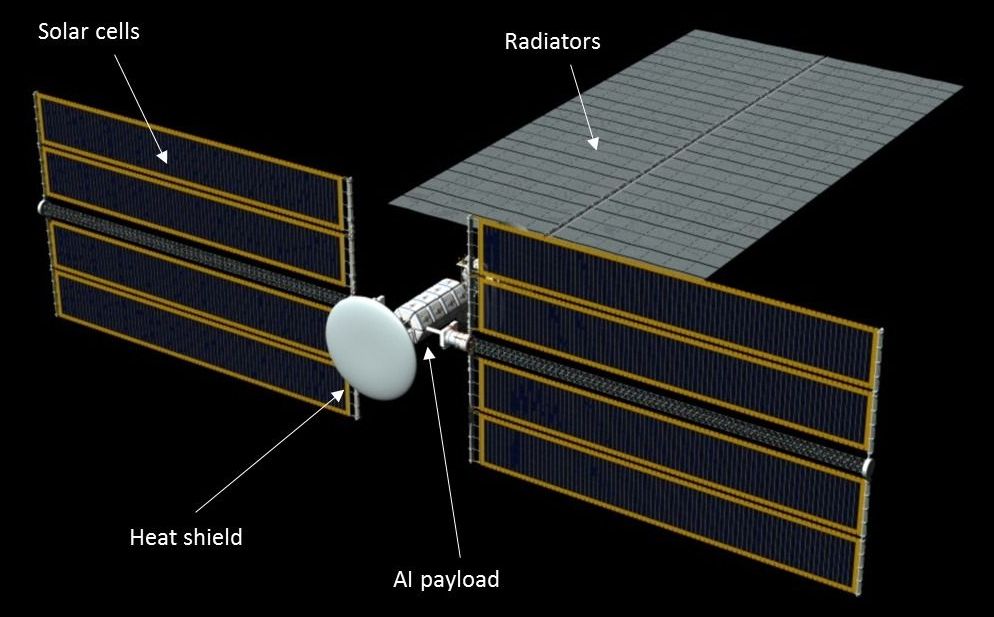
AI for interstellar travel Photo
Stephen Baxter collaborates with i4is on AI for interstellar travel — Andreas Hein and Stephen Baxter explore the potential of artificial intelligence for interstellar exploration and colonization in a brand-new arXiv preprint (Image: Adrian Mann)


Elon Musk Denies That SpaceX’s Mars Colony Will Be a Ticket Out for the Rich
As Mars colonization inches ever closer to becoming a reality, some have argued that the ability to afford a ticket to the Red Planet is a luxury afforded only to the wealthiest members of society. Billionaire Elon Musk has said it’ll run potential Mars inhabitants traveling with his company SpaceX hundreds of thousands of dollars to get there. But in a new interview, he rebuffed the assertion that a one-way ticket to Mars is an easy ticket out for the rich.
The comments were part of an interview with the SpaceX and Tesla CEO that will air Sunday evening in the final episode of Axios’ four-part limited documentary series on HBO. In a clip from the interview, Elon Musk hinted that advancements by his company for Mars colonization have been notable and said there’s a “70 percent” chance that he heads to the Red Planet himself.

Russia’s top space official says their mission to the moon will help verify conspiracy theory
One Russian poll found that 28% of respondents doubted the moon landing.
The head of Russia’s Roscosmos space agency has said that a proposed Russian mission to the moon will be tasked with verifying that the American moon landings were real.
“We have set this objective to fly and verify whether they’ve been there or not,” said Dmitry Rogozin in a video posted Saturday on Twitter.
Rogozin was responding to a question about whether or not NASA actually landed on the moon nearly 50 years ago. He appeared to be joking, as he smirked and shrugged while answering. But conspiracies surrounding NASA’s moon missions are common in Russia.
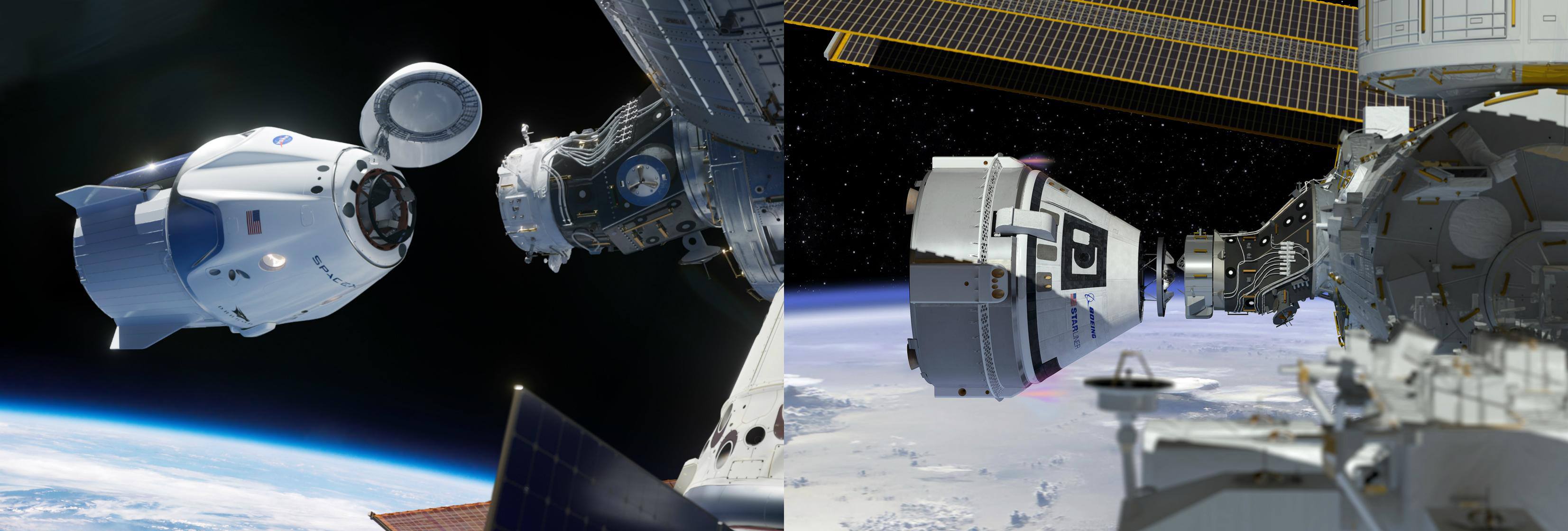

Next year, our NASA Commercial Crew Program returns human spaceflight to American soil
Our partners The Boeing Company and SpaceX are scheduled to launch two uncrewed and two crewed demo flights, beginning with the SpaceX Crew Dragon liftoff on Jan. 7, 2019. The latest: https://go.nasa.gov/2FBi6GI