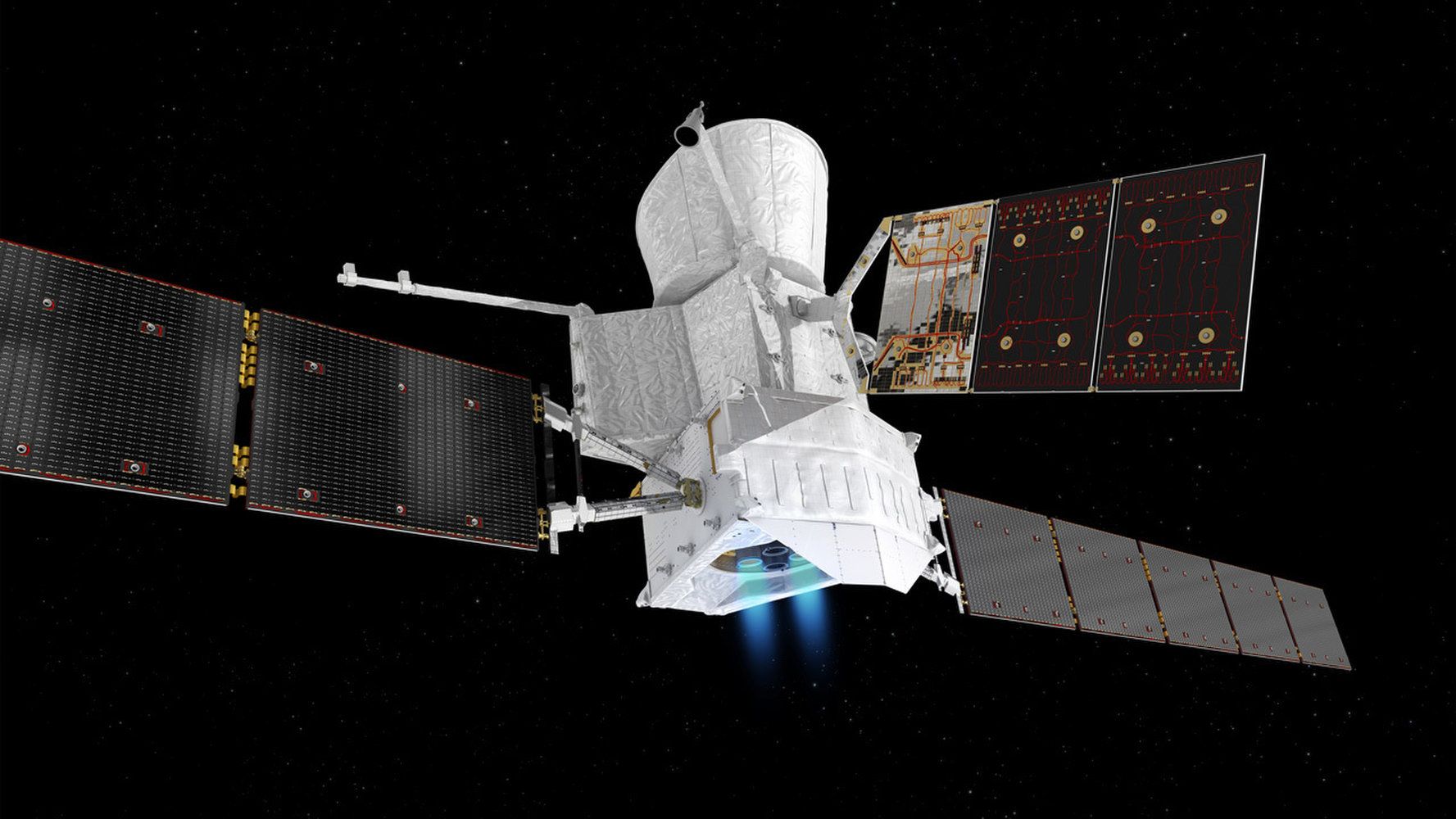
The BepiColombo mission is traveling to Mercury powered by ion thruster engines built into the Mercury Transfer Module component visible at the bottom of this artist’s depiction.
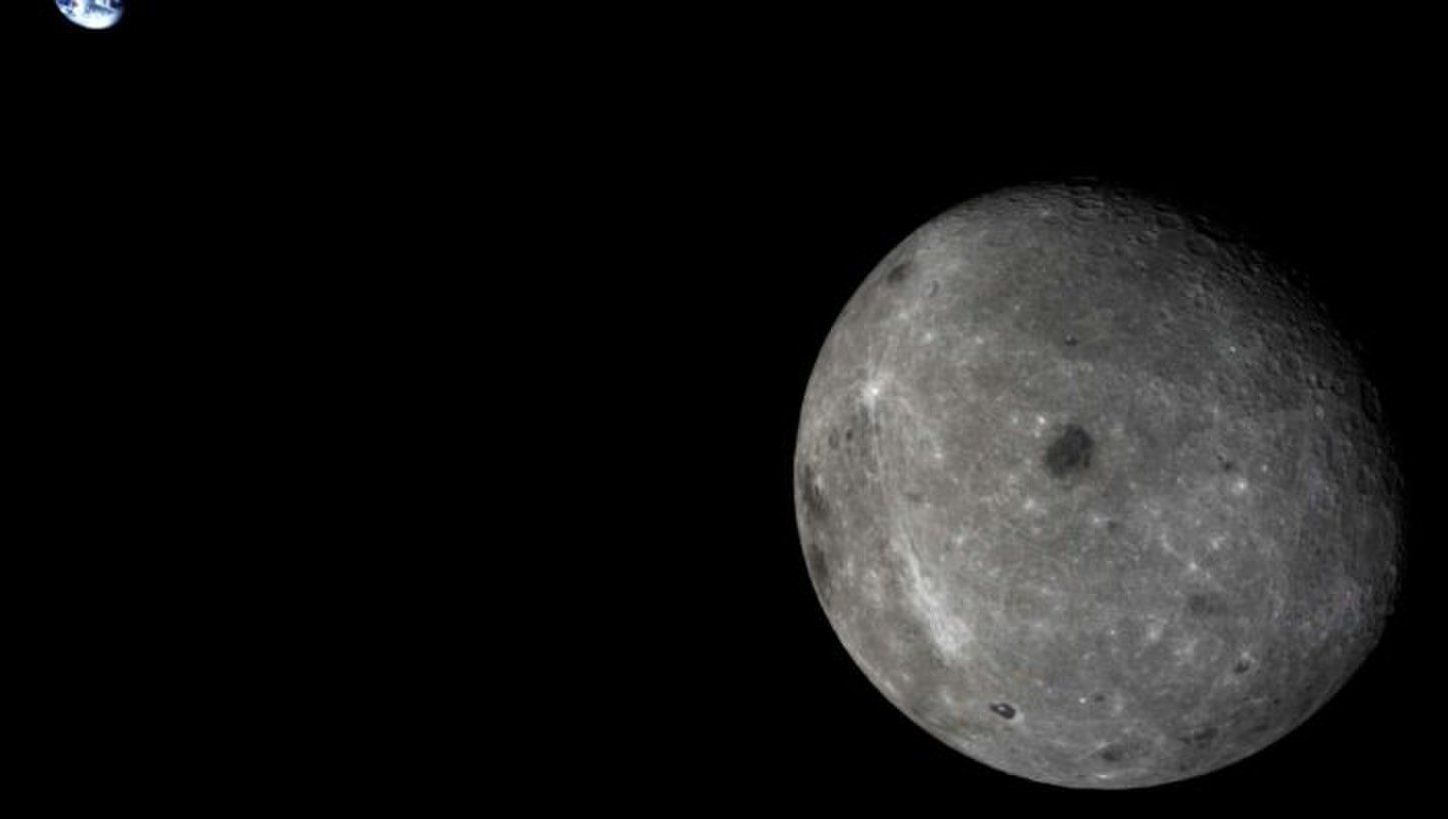



China is getting set to launch the first-ever surface mission to the moon’s far side.
The robotic Chang’e 4 mission is scheduled to launch atop a Long March 3B rocket on Friday (Dec. 7) at around 1:30 p.m. EST (1830 GMT; 2:30 a.m. on Dec. 8 local China time).
If all goes according to plan, Chang’e 4’s lander-rover duo will touch down within the moon’s South Pole‐Aitken (SPA) basin after a 27-day flight, then study both the surface and subsurface of this region. [China’s Moon Missions Explained (Infographic)].

#BepiColombo’s thrusters have fired in space for the FIRST TIME. The electric ion propulsion ‘jetpacks’ are now ready for routine firing from mid-December onwards, steering BepiColombo on its interplanetary trajectory ahead of its swingby of Earth in April 2020. See https://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Operations/BepiColombo_no…LMEBTF7xEw

Click on photo to start video.
LIVE ROCKET LAUNCH! Tune in to see us send approximately 5,600 pounds of research and supplies to the International Space Station aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft. Liftoff of the Falcon 9 rocket is slated for 1:16 p.m. EST from from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Don’t miss the countdown to liftoff!
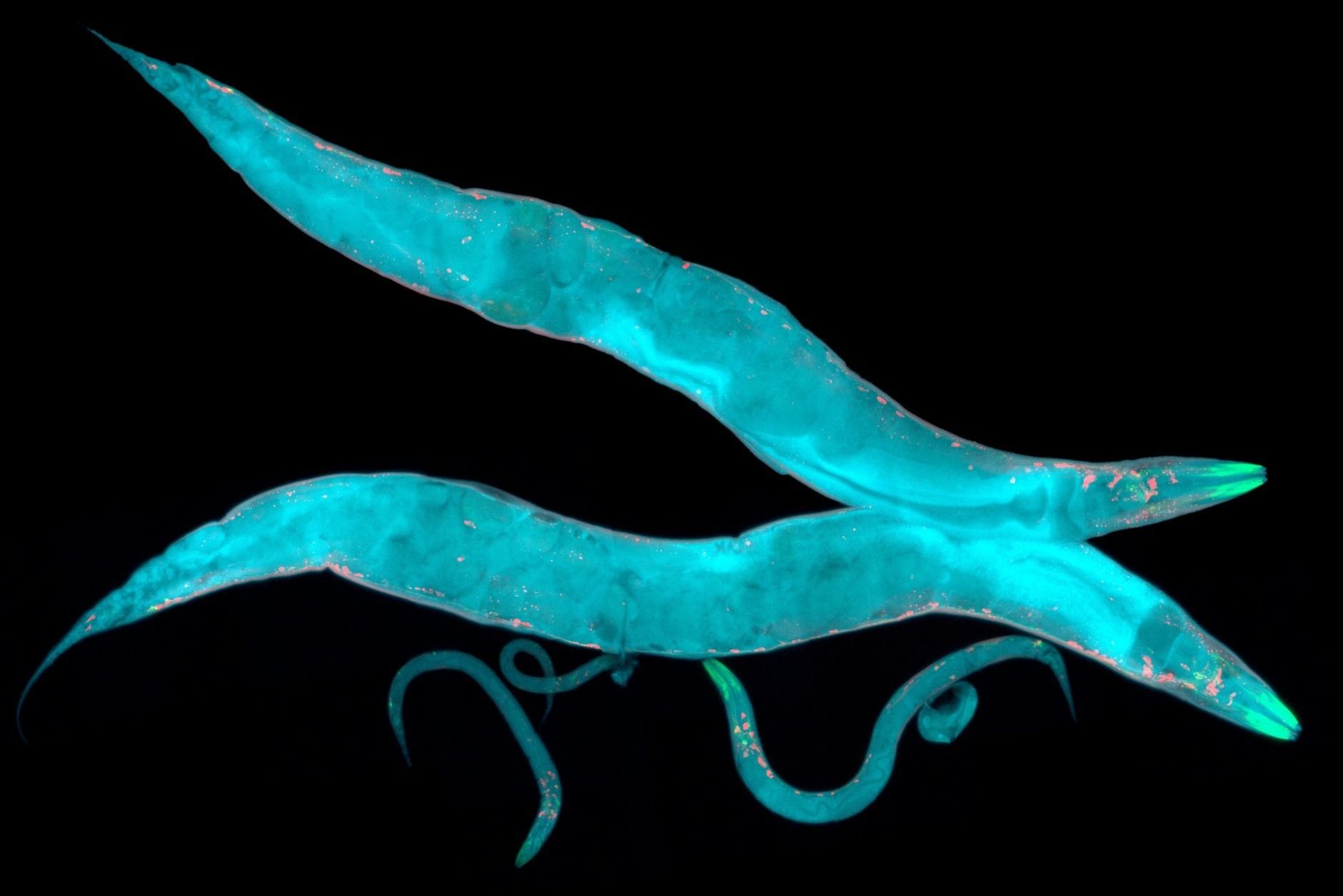
Thousands of microscopic worms will be launched into space — wriggling around in SpaceX’s next cargo shipment to the International Space Station aboard the SpaceX Dragon.
But the launch, which was planned for today (Dec. 4), has been postponed to tomorrow, and scientists are now worried that the worms will be a day “too old” for some of the planned experiments, according to the BBC.
If all goes well in spite of the delay, these tiny but mighty creatures with muscle structures very similar to that of humans, might help us understand why and how astronauts lose muscle mass in space. [Photos: The First Space Tourists].
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx Asteroid Sample Return Mission flew over two billion miles through space to meet you. Here, the spacecraft’s camera captures a full rotation of the asteroid from only about 50 miles away: https://go.nasa.gov/2rhr6a3&h=AT1i_D7IINmmgUy-jZJD7S-NBK6d4F…dBHOk_2iFA OSIRIS-REx will study Bennu for almost a year and eventually select a location to collect a sample to return to Earth. #WelcomeToBennu

Well, there’s some great news for Virgin Galactic as it prepares for an attempt to send SpaceShipTwo to space. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI), which maintains records for aviation and spaceflight, is considering lowering the boundary of space from 100 to 80 km (62.1 to 47.7 miles).
Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo probably can’t reach the 100 km boundary, which is also known as the Karman line.
FAI issued the following statement last week:
As the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft arrives at its target asteroid Bennu, scientists on the ground prepare for a new bounty of planetary samples.
WATCH LIVE: NASA’s Osiris-REx spacecraft is expected to arrive at a 1,640-foot wide, carbon-rich asteroid named Bennu to collect and return samples in hopes of learning more about the origins of life on Earth and perhaps elsewhere in the solar system.
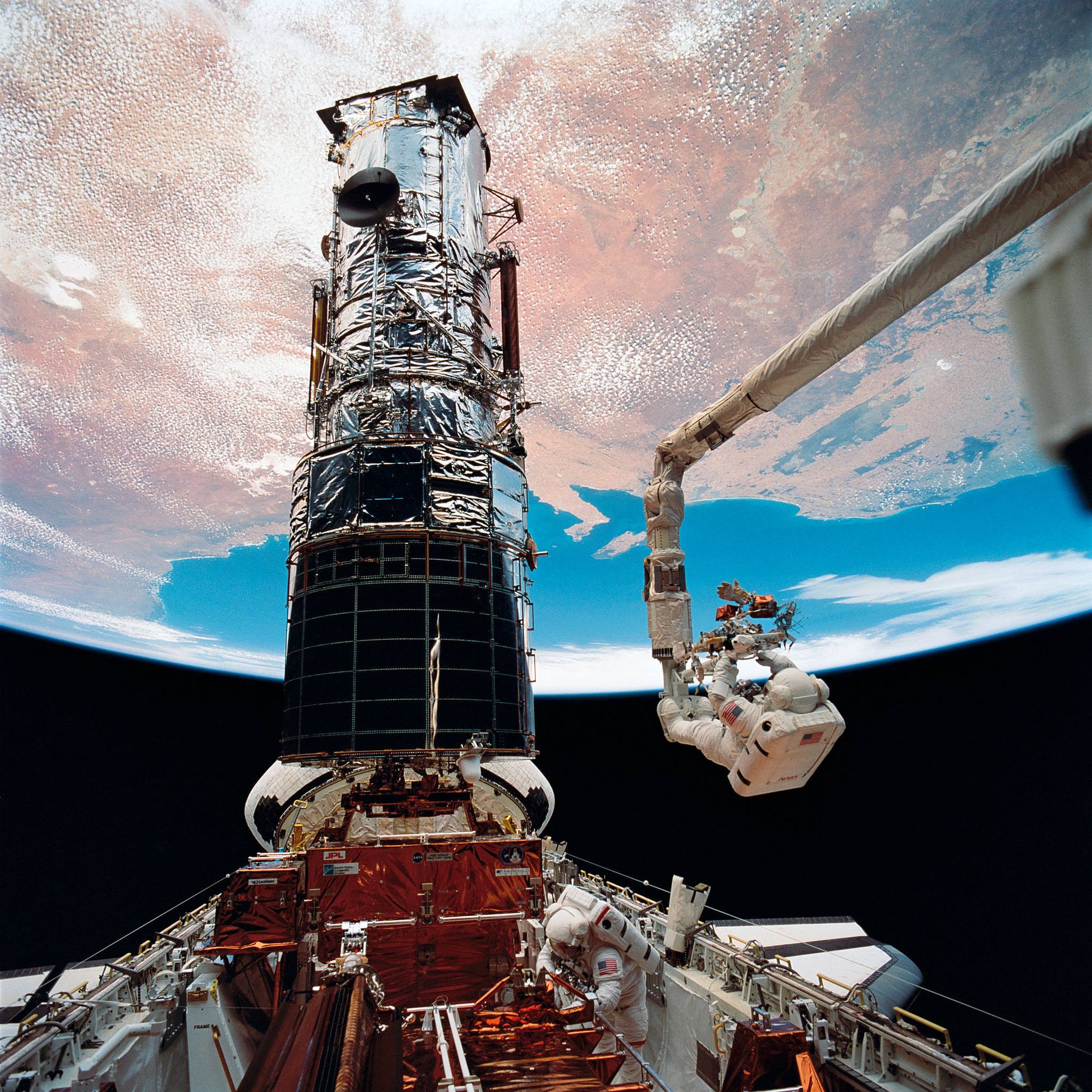

Twenty-five years ago today, a group of astronauts ascended in the space shuttle to accomplish a feat of unprecedented proportions: to fix NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, in space. Learn how the ingenuity of those repairs blazed the way for decades of not only satellite repairs, but also space exploration: https://go.nasa.gov/2FWHuXz&h=AT1qFoI48_v6tgpXkkQf7uBHIj2Xuh…jlZErelV8A