Is US losing plasma engine race to China and Russia ahead of long journey to Mars?
While NASA’s budgetary struggle continues, the red planet may be a step closer for China after it unveiled a powerful new plasma engine.
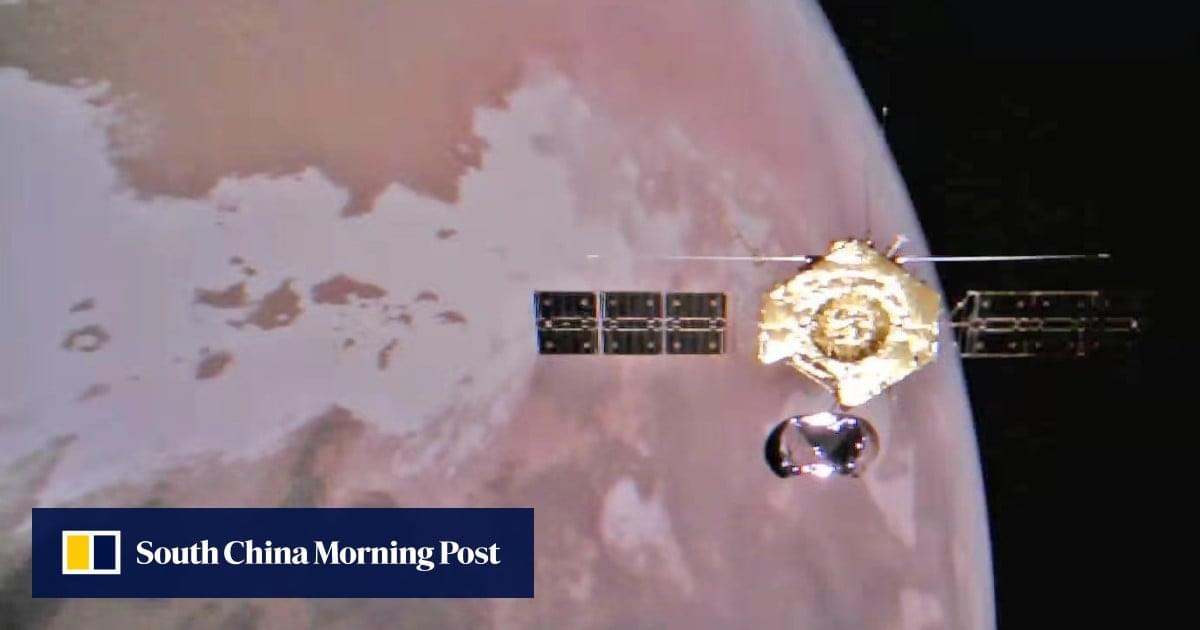


Not long to go now: After more than nine months on the International Space Station, two astronauts are a step closer to returning home following the launch of a crew swap mission on Friday.
A Falcon 9 rocket with a Crew Dragon fixed to its top blasted off from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:03 pm (2303 GMT), carrying a four-member team bound for the orbital outpost.
“We celebrate the countless individuals all over the world that have made this journey possible,” said astronaut Nichole Ayers, the designated pilot of the Crew-10 mission, just before launch.

#eldddir_earth #eldddir_homo #eldddir_animals.
#eldddir_disaster #eldddir_ocean #eldddir_bombs #eldddir_future #eldddir_tech #eldddir_jupiter #eldddir_mars #eldddir_spacex #eldddir_rockets
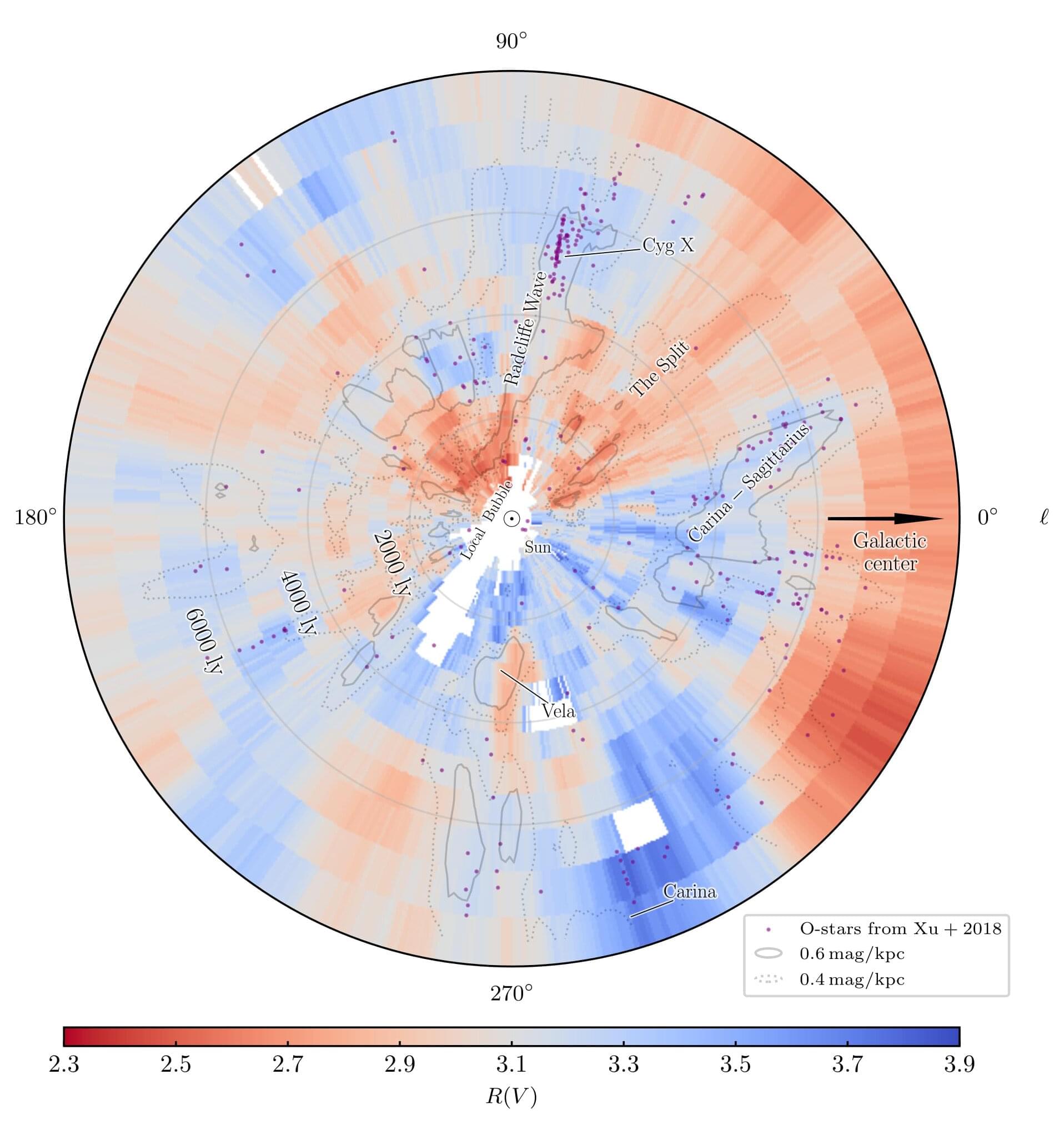
When we observe distant celestial objects, there is a possible catch: Is that star I am observing really as reddish as it appears? Or does the star merely look reddish, since its light has had to travel through a cloud of cosmic dust to reach our telescope?
For accurate observations, astronomers need to know the amount of dust between them and their distant targets. Not only does dust make objects appear reddish (“reddening”), it also makes them appear fainter than they really are (“extinction”). It’s like we are looking out into space through a dirty window. Now, two astronomers have published a 3D map that documents the properties of dust all around us in unprecedented detail, helping us make sense of what we observe.
The research is published in the journal Science.
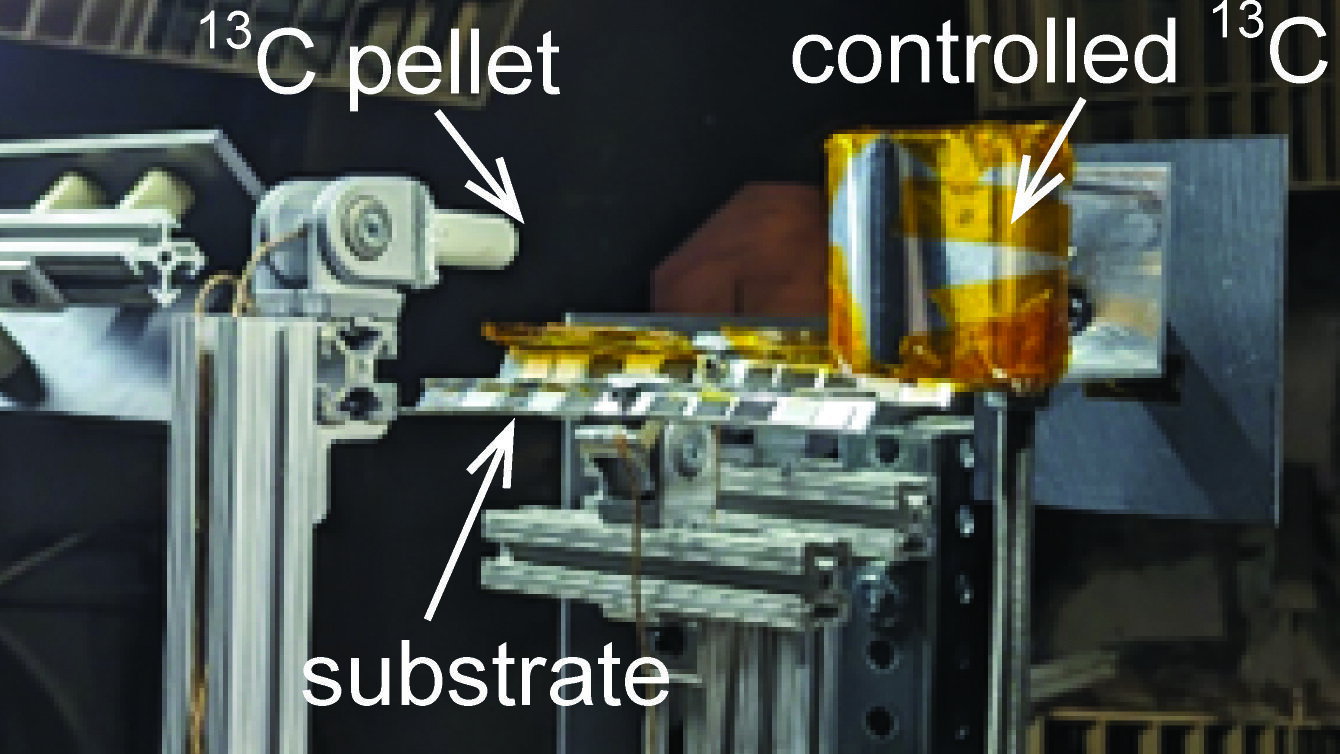
Predicting the lifetime of an electric ion thruster is notoriously difficult. You have to account for the chamber wall effects, which are not present in space environments. Researchers within several different aerospace disciplines in The Grainger College of Engineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign worked together to simulate the ion activity, then validate it in a unique experiment that will help predict the lifespan of electric thrusters.
“We can simulate the damage to the engine caused by sputtering, but until now, we could not validate that our simulations were correct,” said Professor Huck Beng Chew.
“Because both the engine and chamber walls are coated with impact-resistant carbon, we didn’t know whether the coating damage was from accelerated ions directly hitting the engine or whether the coating damage was artificially mitigated by the deposition of carbon from ion bombardment off the chamber walls.”
Yesterday, Pulsar Fusion unveiled a revolutionary new space propulsion design called the Sunbird.
If it lives up to its potential, it will completely revolutionize Interplanetary Spaceflight!
And I got the first EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW!
#space #fusion #nasa.
CHECK OUT MY NEW MERCH (Don’t forget to check out the back of the garments!)
https://sunlineproducts.chipply.com/theangryastronaut/
Please support my channel, and win some EXCLUSIVE MERCH!
DISCORD MEMBERSHIP, EXCLUSIVE CONTENT AND EARLY RELEASES!
https://www.patreon.com/AngryAstronaut.
https://cash.app/$Angry70
https://www.paypal.com/paypalme/AngryAstro.
Follow me on twitter:
Tweets by Astro_Angry

Is NASA still Moonbound, or will the next giant leap mean skipping straight to Mars?
Speculation is mounting that the Trump administration may scale back or cancel NASA’s Artemis missions following the departure of a key official and Boeing’s plans to lay off hundreds of employees working on its lunar rocket.
Late Wednesday, NASA abruptly announced the retirement of longtime associate administrator Jim Free, effective Saturday.

After an initial focus on scientific research, including Sierra’s partnership with Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origins on developing a private space station, the Dream Chaser will be involved in commercial operations by hauling cargo and shuttling scientists and researchers to and from space stations.
Both Sierra Space and Radian also have space-tourism aspirations that go beyond much of what’s currently available, including 11-minute flights by Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin, and longer space-balloon flights by companies like Space Perspective and Zephalto that do not reach Low Earth Orbit. “Passengers will be able to go up and stay in orbit,” says Humphrey, whose company has the most developed passenger plans right now. “We can go around the planet in about 95 minutes, so a typical trip will probably be three laps.”
Visits to one or more of the six space stations currently under development lie ahead as well. “We’re calling it purposeful tourism,” says Angie Wise, Sierra’s chief safety officer and SVP of mission and quality assurance. “You’ll get the experience of going to space, but we’ll also put you to work helping with experiments.”
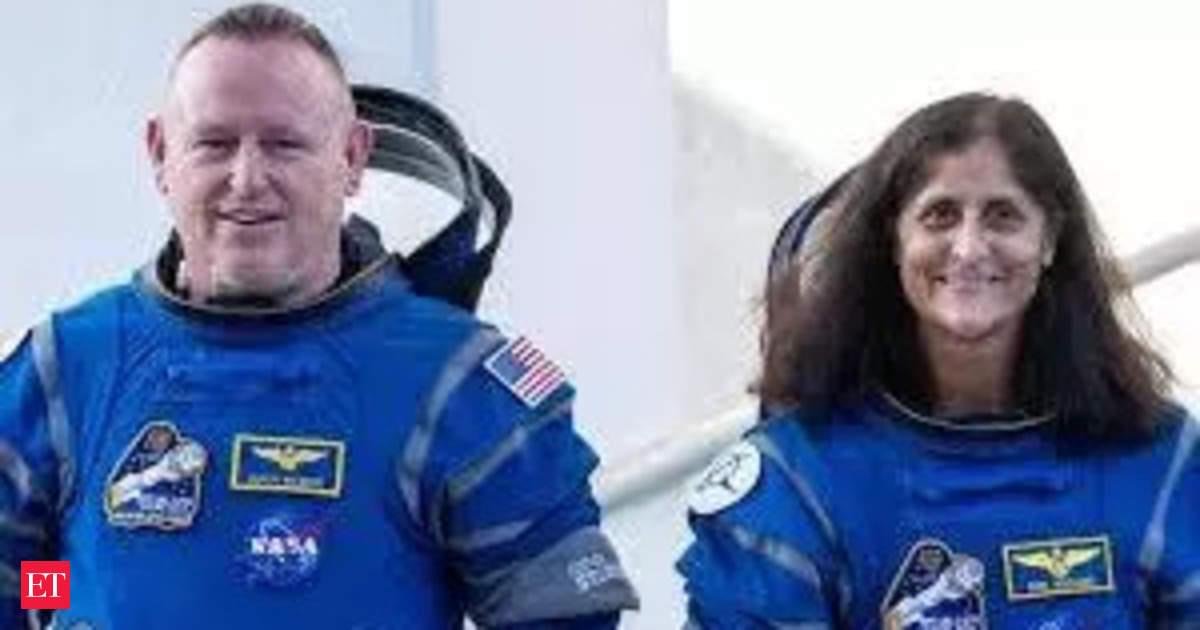

The two astronauts who made Boeing Starliner’s initial crewed flight test in June have now scheduled to return to Earth after their much-awaited return.
NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore will be leaving the International Space Station (ISS) days after the landing of SpaceX’s next Crew-10 mission.
Crew-10, which has four astronauts on board, will launch next week and will take the place of the Crew-9 team that is currently on the ISS.