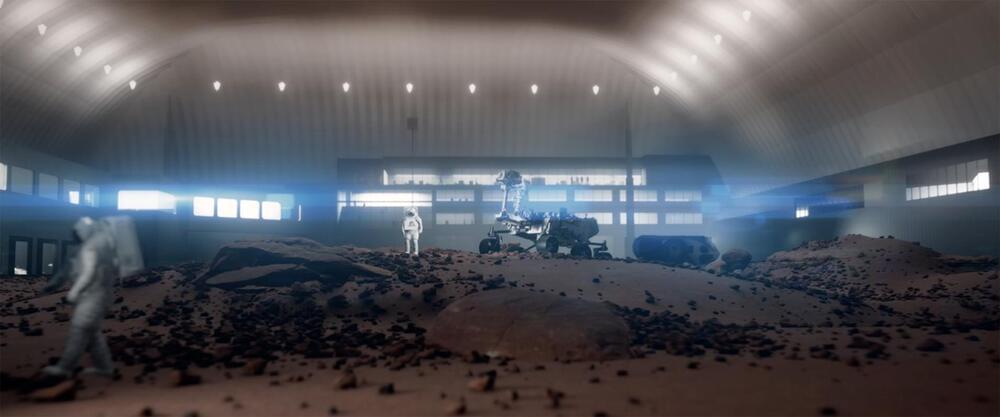
HOUSTON, Oct. 18, 2022 – The nonprofit Space Center Houston is advancing a Facilities Master Plan to support the growing need for space exploration learning and training in two massive structures that will also give the public a front row seat into the development of robotics, rovers, lunar landers and reduced gravity systems. Today, the center offered a glimpse of the facility that will include two enclosed simulated cosmic terrains of the Moon and Mars, as well as modular surface labs and STEM learning centers. An elevated exhibit hall over the two surfaces will offer the public immersive experiences to observe astronaut training first-hand while experiencing the future of space exploration as humans return to the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
Space Center Houston is responding to the opportunities and challenges in a rapidly evolving space sector, including the need for facilities built for current and future missions, while sharing this excitement with the public and addressing critical gaps in the development of the STEM workforce through its education programs. The facility will bring together guests, NASA, commercial space partners, colleges, universities and global space agencies to collaborate on new technologies that are propelling present and future human spaceflight.
For 30 years, Space Center Houston has chronicled the journey of human spaceflight while empowering and inspiring people to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering and mathematics. “Space is expanding once again and a new space age is upon us,” said William T. Harris, President and CEO Space Center Houston. “With new ambitions, new players and new challenges, we will shift our focus from being a curator of past achievements to also facilitating new feats in space.”