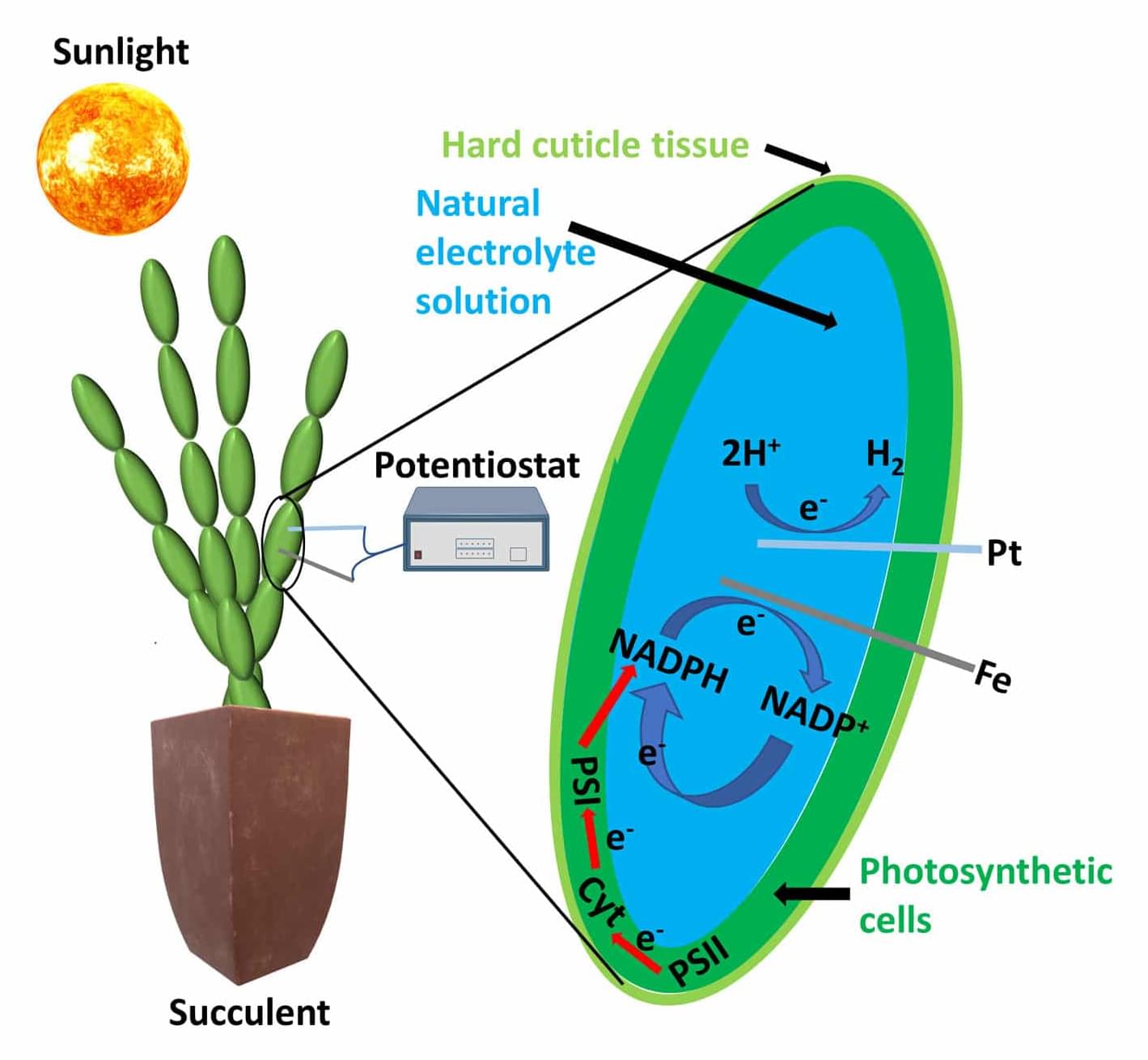
An international team of researchers affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a novel cross-linker additive that significantly addresses the longstanding stability issues associated with organic solar cells, also known as organic photovoltaics (OPVs).
With the incorporation of just 0.05% of this cross-linking agent, the lifespan of OPVs can be improved by over 59%. Industry analysts suggest this breakthrough brings the commercialization of OPVs—regarded as next-generation solar cells—closer to reality.
Led by Professor BongSoo Kim in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST, the research team, in collaboration with researchers from the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB), the University of Lille in France, and the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS), identified the operational principles of this innovative cross-linker using a variety of advanced analytical techniques.