- Researchers figure out a new way to pair perovskites with silicon for a solar boost.
- Hawaiian Electric sets new goals for solar and storage.
- Chicago officially commits to its 100% renewable energy goal for 2035.
- Anaheim builds nine new solar projects at public schools.
- Amazon employees want the company to take action on climate change, stop supporting fossil fuels.
Category: solar power – Page 128

Transparent wood now also stores and releases heat
Three years ago, we heard how scientists from Sweden’s KTH Royal Institute of Technology had created transparent wood – it could serve as a cheaper alternative to the silica-based glass currently used in windows and solar cells. Now, the material is additionally able to store heat and later release it.

Europe Stores Electricity in Gas Pipes
Converting excess wind and solar power into hydrogen can extend renewable energy’s reach.
- By Peter Fairley on April 1, 2019
This Superfluid Is Alive, And It Could Power Machines of the Future
Fluids with zero viscosity seemingly defy the laws of physics and they have endless applications. But they’ve been hard to make, until now. The secret? Bacteria!
Scientists’ Crazy Plan to Power Solar Panels With E. Coli — https://youtu.be/_XZGrZ3DeLg
Get 20% off http://www.domain.com domain names and web hosting when you use coupon code SEEKER at checkout!
Swarming Bacteria Create an ‘Impossible’ Superfluid.
“Researchers explore a loophole that extracts useful energy from a fluid’s seemingly random motion. The secret? Sugar and asymmetry.”
More info about E. Coli
https://www.foodsafety.gov/poisoning/causes/bacteriaviruses/ecoli/index.html
“E. coli is the name of a type of bacteria that lives in your intestines and in the intestines of animals. Although most types of E. coli are harmless, some types can make you sick.”
Swimming bacteria work together to go with the flow
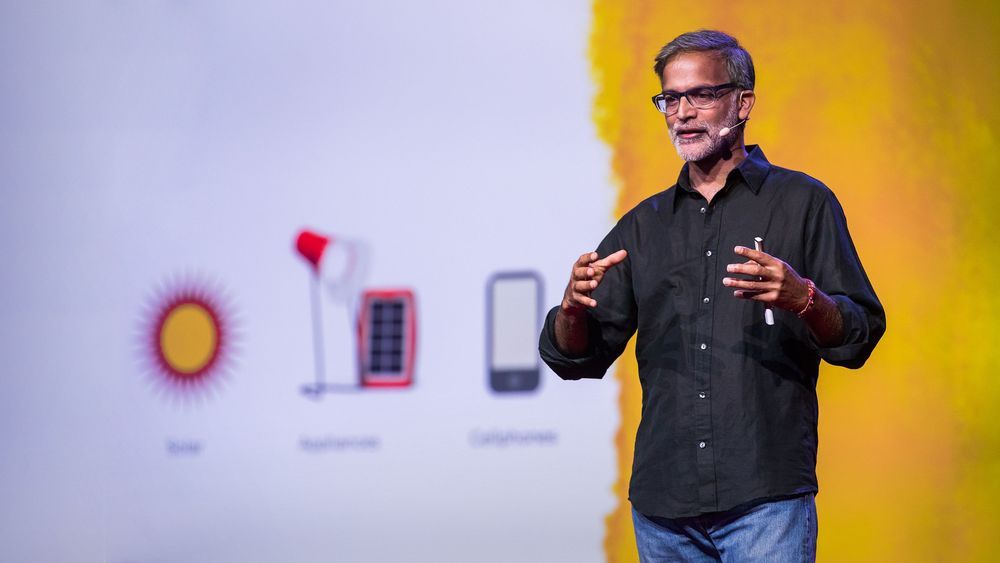

The thrilling potential for off-grid solar energy
There’s an energy revolution happening in villages and towns across Africa — off-grid solar energy is becoming a viable alternative to traditional electricity systems. In a bold talk about a true leapfrog moment, Amar Inamdar introduces us to proud owners of off-grid solar kits — and explains how this technology has the opportunity to meet two extraordinary goals: energy access for all and a low-carbon future. “Every household a proud producer as well as consumer of energy,” Inamdar says. “That’s the democracy of energy.” (Followed by a brief Q&A with TED Curator Chris Anderson)
Latest Space Based Solar Power Concepts and Experiments at Caltech
SSPI approach: • Enabling technologies developed at Caltech • Ultra-light deployable space structures • High efficiency ultra-light photovoltaic (PV) • Phased Array and Power Transmission • Integration of concentrating PV, radiators, MW power conversion and antennas in single cell unit • Localized electronics and control for system robustness, electronic beam steering • Identical spacecraft flying in formation • Target is specific power over 2000 Watts per kilogram. This would cost competitive with ground-based power.
Scientists use machine learning to identify high-performing solar materials
Finding the best light-harvesting chemicals for use in solar cells can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. Over the years, researchers have developed and tested thousands of different dyes and pigments to see how they absorb sunlight and convert it to electricity. Sorting through all of them requires an innovative approach.
Now, thanks to a study that combines the power of supercomputing with data science and experimental methods, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Cambridge in England have developed a novel “design to device” approach to identify promising materials for dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). DSSCs can be manufactured with low-cost, scalable techniques, allowing them to reach competitive performance-to-price ratios.
The team, led by Argonne materials scientist Jacqueline Cole, who is also head of the Molecular Engineering group at the University of Cambridge’s Cavendish Laboratory, used the Theta supercomputer at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility (ALCF) to pinpoint five high-performing, low-cost dye materials from a pool of nearly 10,000 candidates for fabrication and device testing. The ALCF is a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
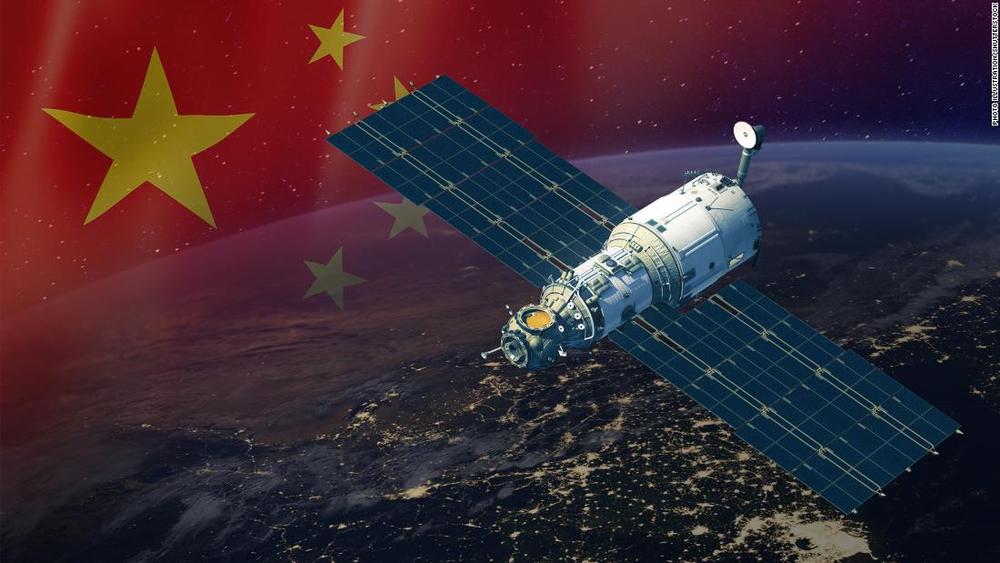

Exploring China’s latest space ambitions
China says it is working to develop a solar energy plant in space that could one day beam enough power back to Earth to light up an entire city.
If scientists can overcome the formidable technical challenges, the project would represent a monumental leap in combating the Earth’s addiction to dirty power sources which worsen air pollution and global warming.
A space-based solar power station could also provide an alternative to the current generation of earthbound and relatively ineffective renewable energy sources.
What our civilization needs is a billion-year plan
Circa 2012
Enlarge | + 
Lt Col Garretson — one of the USAF’s most farsighted and original thinkers — has been at the forefront of USAF strategy on the long-term future in projects such as Blue Horizons (on KurzweilAI — see video), Energy Horizons, Space Solar Power, the AF Futures Game, the USAF Strategic Environmental Assessment, and the USAF RPA Flight Plan. Now in this exclusive to KurzweilAI, he pushes the boundary of long-term thinking about humanity’s survival out to the edge … and beyond. — Ed.
The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Air Force or the U.S. government.
It isn’t enough just to plan for two or 20, or even the fabled Chinese 100 year periods. We need to be thinking and planning on the order of billions of years. Our civilization needs inter-generational plans and goals that span as far out as we can forecast significant events.