Home to the world’s largest floating solar energy plant.
ð
Home to the world’s largest floating solar energy plant.
ð

This op-ed originally appeared in the June 10, 2019 issue of SpaceNews magazine.
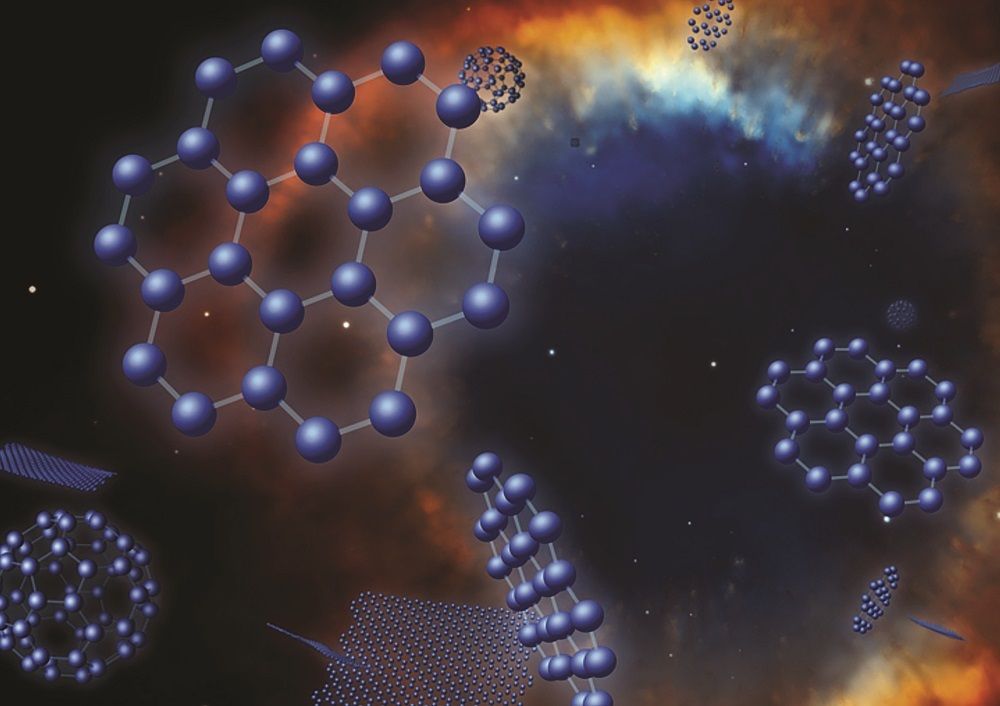
If humanity is to ever settle new planets, we will need radically new technologies; this much is obvious. But we may already have the perfect material to step up and fill the role: graphene. It is easily transported, easily manipulated, and an abundance of carbon in the galaxy could bode well for graphene, which is a carbon-based material. Its strength and versatility could well become a crucial component in colonization. For instance, spacecraft filled with advanced, massive 3D printers could ferry intrepid settlers to new corners of the galaxy, supplying a near-endless supply of material and equipment, perhaps even being used to construct homes that can withstand the conditions of other worlds.
Graphene’s discovery in 2004 sparked the flame of endless possibility within the science and technology communities due to its astounding properties. Only a single atomic layer thick and constructed in a lattice, honeycomb-like formation, graphene is nearly 200 times stronger than steel and better at conducting electricity and heat than any other conductor. It’s flexible, allows 97 percent of white light to pass through it (making it perfect for solar energy), and the list of properties continues.

Efficiently moving water upward against gravity is a major feat of human engineering, yet one that trees have mastered for hundreds of millions of years. In a new study, researchers have designed a tree-inspired water transport system that uses capillary forces to drive dirty water upward through a hierarchically structured aerogel, where it can then be converted into steam by solar energy to produce fresh, clean water.
The researchers, led by Aiping Liu at Zhejiang Sci-Tech University and Hao Bai at Zhejiang University, have published a paper on the new water transport and solar steam generation method in a recent issue of ACS Nano. In the future, efficient water transport methods have potential applications in water purification and desalination.
“Our preparation method is universal and can be industrialized,” Liu told Phys.org. “Our materials have excellent properties and good stability, and can be reused many times. This provides the possibility for large-scale desalination and sewage treatment in the future.”
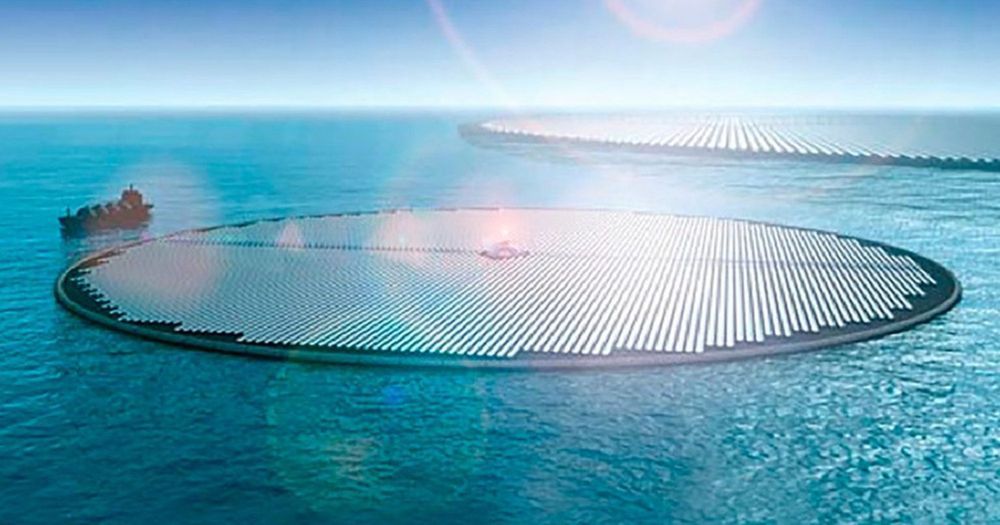

Millions of solar panels clustered together to form an island could convert carbon dioxide in seawater into methanol, which can fuel airplanes and trucks, according to new research from Norway and Switzerland and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal, PNAS, as NBC News reported. The floating islands could drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
Solar panels that don’t occupy valuable land.
Saving space whilst saving the planet.

For decades, slabs of crystalline silicon have dominated the solar industry. Other materials that can be layered in thin films, such as copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) and cadmium telluride (CdTe), have captured less than 5% of the market, because it’s hard to make them as efficient or cheap as conventional solar panels. Perovskites could be a different story. They should be cheaper to make and seem impressively efficient at converting sunlight into electricity — in the laboratory, at least.
Companies say they are close to commercializing cheap perovskite films that could disrupt solar power — but are they too optimistic?

Los Angeles Power and Water officials have struck a deal on the largest and cheapest solar + battery-storage project in the world, at prices that leave fossil fuels in the dust and may relegate nuclear power to the dustbin.
Later this month the LA Board of Water and Power Commissioners is expected to approve a 25-year contract that will serve 7 percent of the city’s electricity demand at 1.997¢/kwh for solar energy and 1.3¢ for power from batteries.
“This is the lowest solar-photovoltaic price in the United States,” said James Barner, the agency’s manager for strategic initiatives, “and it is the largest and lowest-cost solar and high-capacity battery-storage project in the U.S. and we believe in the world today. So this is, I believe, truly revolutionary in the industry.”
They used to call it RoboBee—a flying machine half the size of a paperclip that could flap its pair of wings 120 times a second. It was always tethered to a power source, limiting its freedom. Now, though, RoboBee becomes RoboBee X-Wing, as Harvard researchers have added solar cells and an extra pair of wings, freeing the robot to blast off to a galaxy far, far away. Or at least partway across the room, as it can sustain flight for only half a second, and only indoors.
But hey, baby steps. The teeniest of quadrotors measure a few inches across and weigh a third of an ounce. RoboBee X-Wing is about the same size as those untethered fliers, but weighs a hundredth of an ounce, which earns it the distinction of being the lightest aerial vehicle to manage sustained untethered flight. One day that could make it ideal for navigating tight, sensitive spaces in a galaxy very, very near.
You’ve read your last complimentary article this month. To read the full article, SUBSCRIBE NOW. If you’re already a subscriber, please sign in and and verify your subscription.
