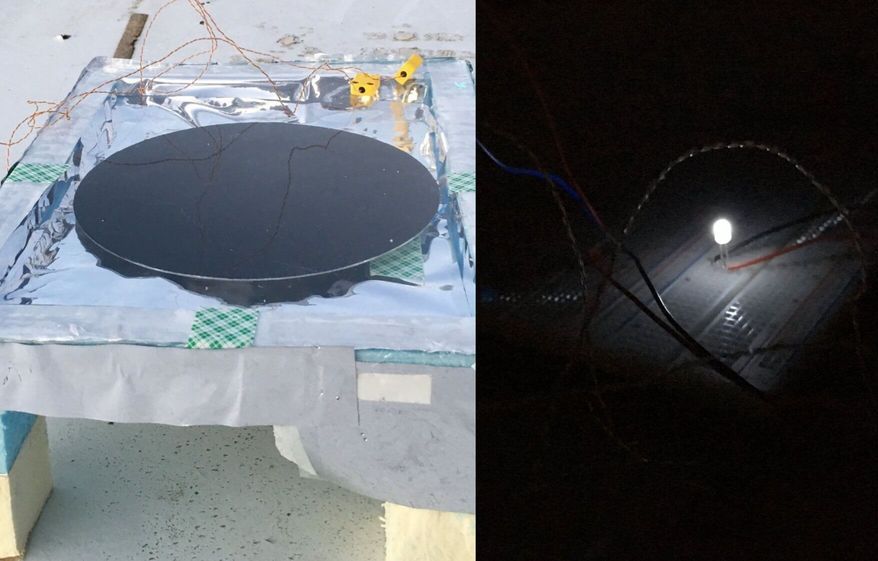
In a recent paper (Generating Light from Darkness), published on Joule, Stanford University researchers Aaswath P. Raman, Wei Li, and Shanhui Fan are reporting the successful creation of a device that is able to generate electricity by exploiting the difference of temperature that can be established during the night between the surrounding air and the surface of the device that is cooling itself by emitting infrared radiations towards the night sky.
In a recent paper, published on Joule, Stanford University researchers are reporting the successful creation of a device that is able to generate electricity by exploiting the difference of temperature that can be established during the night between the surrounding air and the surface of the device that is cooling itself by emitting infrared radiations towards the night sky.
The possibility to generate electricity by exploiting thermal difference is not new, what is new here is the idea of creating a temperature difference by having part of the device radiating energy into the outer space.
As shown in the graphic, the device contains a thermoelectric generator, one side exposed to the air temperature and the other in contact with an aluminum plate. This plate, like a solar panel, actually an anti-solar panel, is facing the night sky and radiates thermal energy towards the sky. This lowers the temperature of the plate, some 2 centigrades less than the lower part of the device that has the same temperature of the air. How is it possible the aluminum plate has not the same temperature of the air? Good question! Here is the trick. The aluminum plate is isolated from the ambient temperature with a transparent insulating panel that lets the radiating energy go through but blocks the heat exchange.