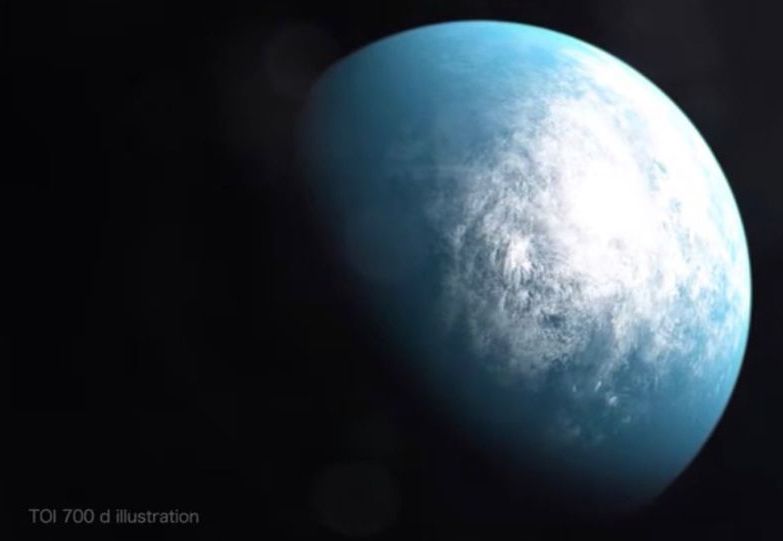
For the first time, the agency’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) has discovered a roughly Earth- planet in the habitable zone of its host star, the zone of orbital distances where liquid water could be stable on a world’s surface.
NASA’s TESS Planet Hunter Finds Its 1st Earth-Size World in ‘Habitable Zone’ : Read more
Interesting, perhaps pushing the paradigm limits here. 86% of solar energy is similar to Precambrian earth during the Faint Young Sun, a snow ball earth. Part of the report that is a bit confusing to me is the comment “One of the other planets is a red dwarf about 40% as massive, 40% as wide and 50% as hot as Earth’s sun.” I think this is about the host star being a red dwarf star. Red dwarfs can be flaring stars and cause problems for *habitable* exoplanets. The Sun spins about 2 km/s at the its equator, red dwarf stars can spin faster like 4 km/s or faster, rotation periods 1 day to 10 days so red dwarfs can emit more flares. The report does comment “In 11 months of data, we saw no flares from the star, which improves the chances TOI 700 d is habitable and makes it easier to model its atmospheric and surface conditions,” discovery team leader Emily Gilbert, a graduate student at the University of Chicago, said in the same statement.