https://goodmenproject.com/business-ethics-2/guys-saving-wor…ship-kldg/



Catch up on the top stories in #science this week. References to all studies are here: surg.ws/2oeEoCj
Video by The Surg.
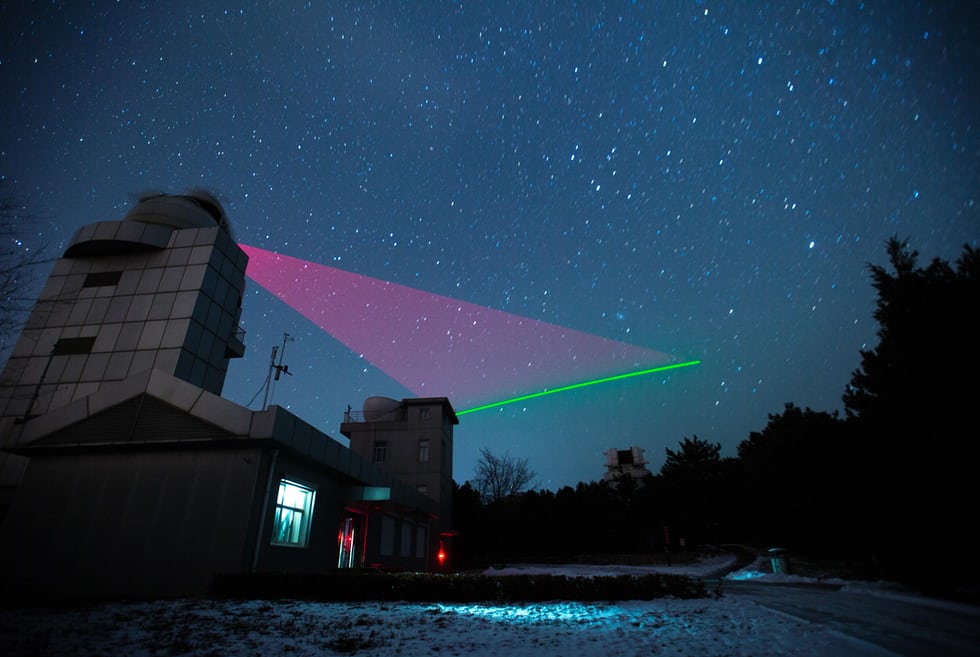

“These days, Chinese scientists stand at least as good a chance of making a global impact on science from within China itself.”

The dumbing down of society starts.
Because Trump has not nominated someone to head the Office of Science and Technology Policy, Michael Kratsios is the de facto leader.

To achieve this, the government is hoping to find more scientists like Koul, who sees his role as an “opportunity to address bigger social as well as scientific challenges”.
This is a tall order, and there’s an elephant in the room. Government funding for Indian research and development has stagnated at around 0.85% of gross domestic product for more than a decade, compared with at least 3% invested by technologically advanced nations such as Denmark, Japan and Sweden.
A push to reverse its brain drain is providing the expertise to tackle its domestic problems.
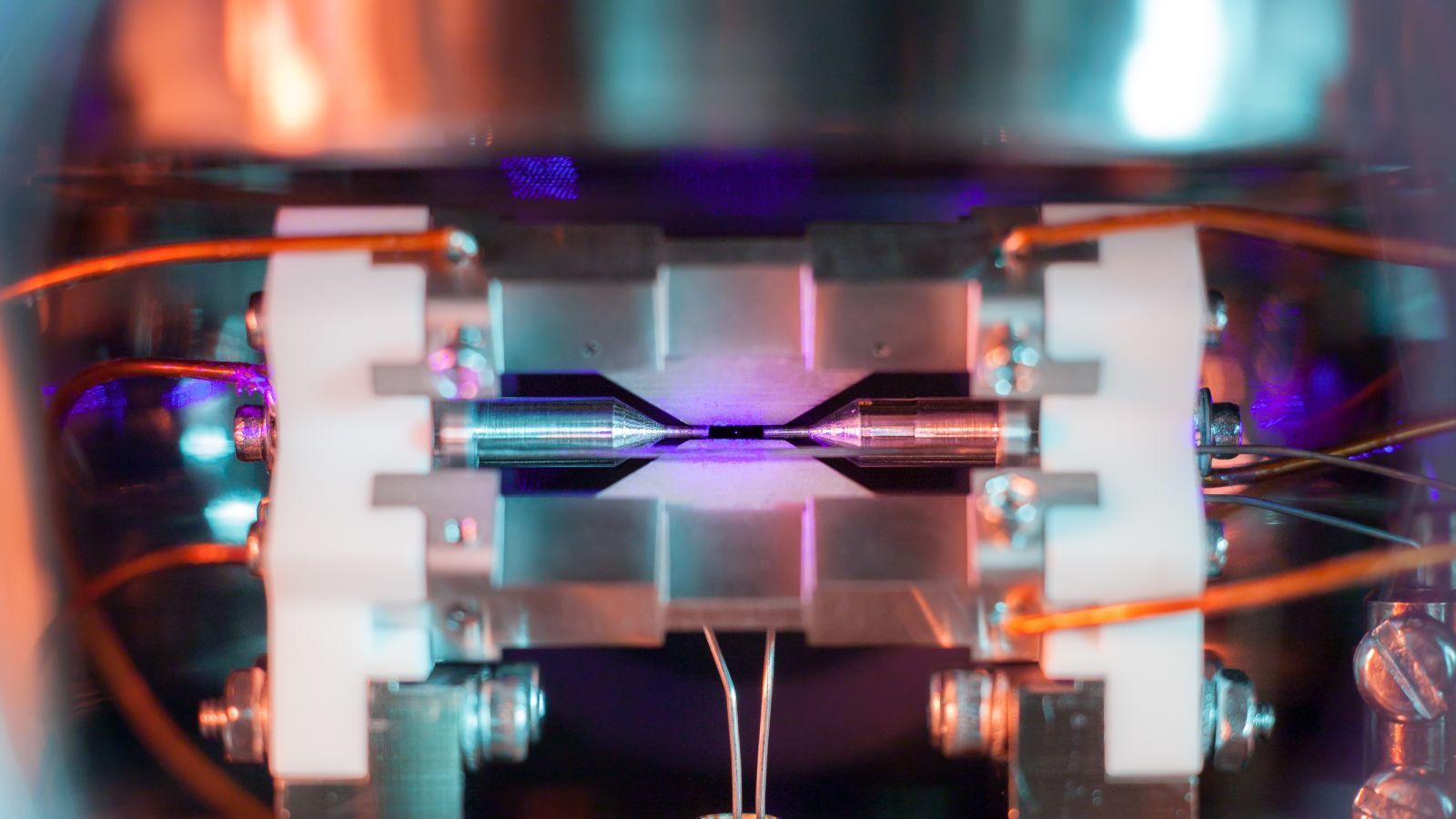
Zoom in close on the center of the picture above, and you can spot something you perhaps never thought you’d be able to see: a single atom. Here is a close-up if, you’re having trouble:
This strontium atom is emitting light after being excited by a laser, and it’s the winner of the UK’s Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) photography award. The EPSRC announced the winners of its fifth annual contest yesterday. Winning photographer David Nadlinger, graduate student at the University of Oxford, was just excited to be able to show off his research.
“It’s exciting to find a picture that resonates with other people that shows what I spend my days and nights working on,” Nadlinger told me. The best part, to him, was “the opportunity to excite people about my research, more than winning a competition.”

These campaigns could erode the base of the Legal Open Access movement: scientists’ awareness of their options for sharing research. Elbakyan, on the other hand, would be left unaffected. The legal campaigns against Sci-Hub have — through the Streisand effect — made the site more well-known than most mainstay repositories, and Elbakyan more famous than legal Open Access champions like Suber.
The threat posed by ACS’s injunction against Sci-Hub has increased support for the site from web activists organizations such as the EFF, which considesr the site “a symptom of a serious problem: people who can’t afford expensive journal subscriptions, and who don’t have institutional access to academic databases, are unable to use cutting-edge scientific research.”
In cramped quarters at Russia’s Higher School of Economics, shared by four students and a cat, sat a server with 13 hard drives. The server hosted Sci-Hub, a website with over 64 million academic papers available for free to anybody in the world. It was the reason that, one day in June 2015, Alexandra Elbakyan, the student and programmer with a futurist streak and a love for neuroscience blogs, opened her email to a message from the world’s largest publisher: “YOU HAVE BEEN SUED.”
It wasn’t long before an administrator at Library Genesis, another pirate repository named in the lawsuit, emailed her about the announcement. “I remember when the administrator at LibGen sent me this news and said something like ‘Well, that’s… that’s a real problem.’ There’s no literal translation,” Elbakyan tells me in Russian. “It’s basically ‘That’s an ass.’ But it doesn’t translate perfectly into English. It’s more like ‘That’s fucked up. We’re fucked.’”.
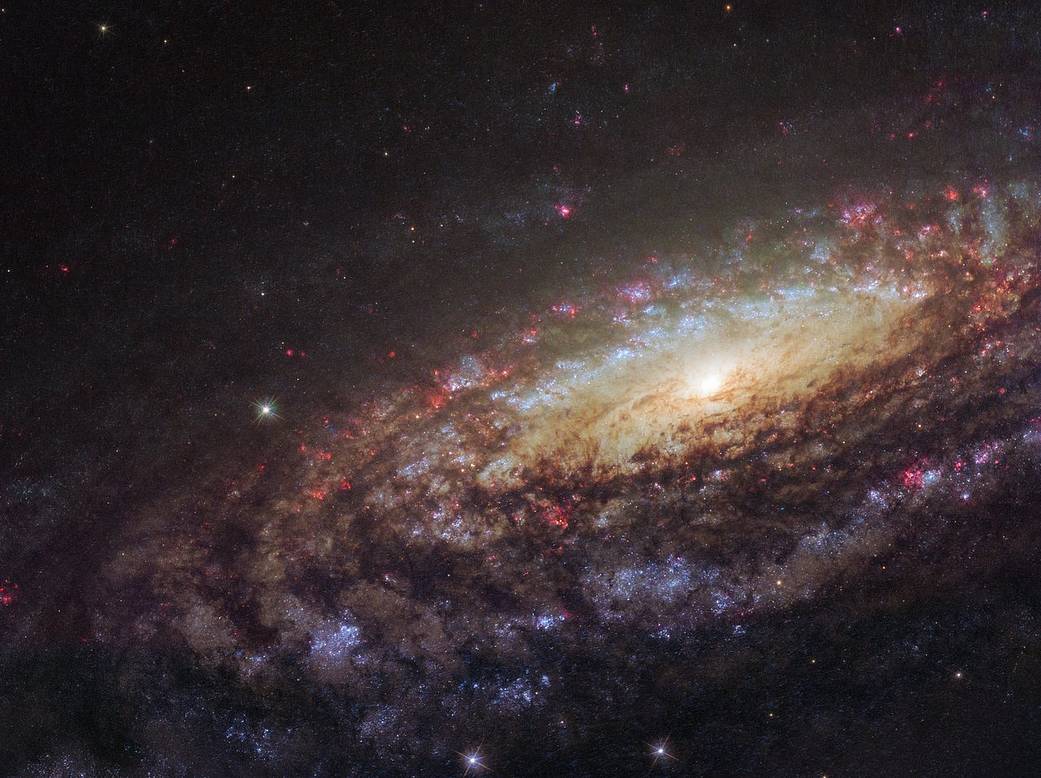

“This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows a spiral galaxy known as NGC 7331. First spotted by the prolific galaxy hunter William Herschel in 1784, NGC 7331 is located about 45 million light-years away in the constellation of Pegasus (the Winged Horse). Facing us partially edge-on, the galaxy showcases its beautiful arms, which swirl like a whirlpool around its bright central region.”