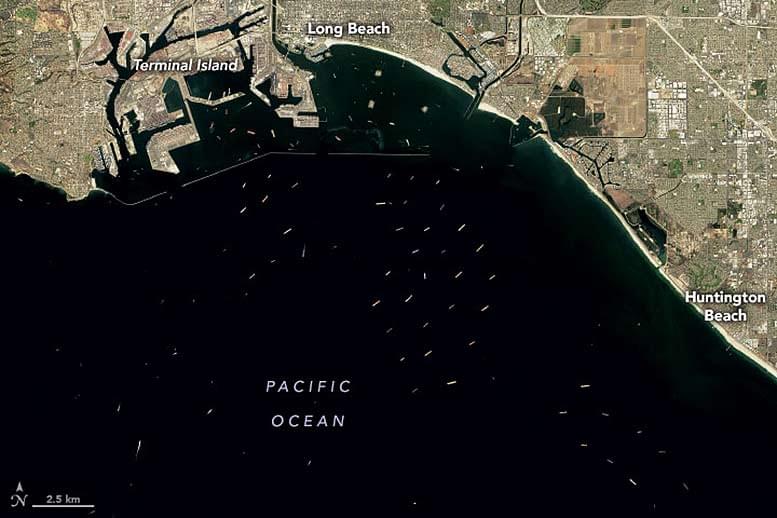
The pandemic has disrupted global supply chains and markets in ways that have led to backlogs of cargo ships at key ports.
Booming demand for consumer and goods, labor shortages, bad weather, and an array of COVID-related supply chain snarls are contributing to backlogs of cargo ships at ports around the world.
Among those seaports are the Port of Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach in Southern California, the two busiest container ports in the United States. On October 10 2021, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 captured this natural-color image of dozens of cargo ships waiting offshore for their turn to unload goods. On the same day, the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA.