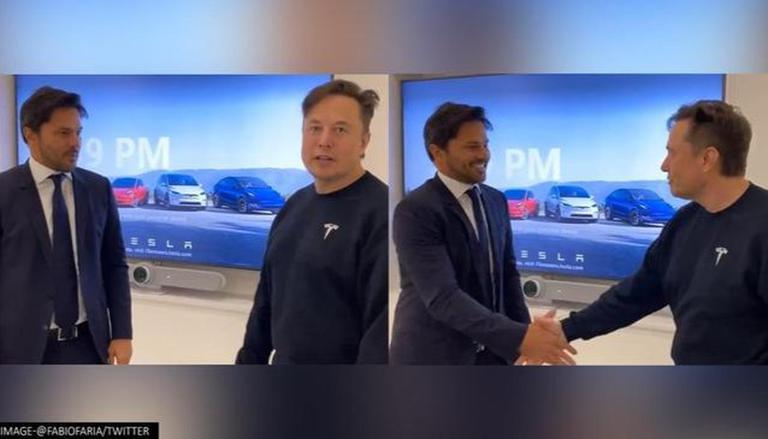
RIO DE JANEIRO, Nov 16 (Reuters) — Elon Musk and Brazilian Communications Minister Fabio Faria met in Austin on Tuesday to discuss a potential partnership that would leverage SpaceX technology to bring Internet to rural schools and cut back on illegal deforestation.
In a statement, the Brazilian government said the two talked about how SpaceX and Starlink, a satellite broadband service offered by the firm, could help monitor the Amazon rainforest for illegal cutting, while also providing Internet connections to remote schools and health centers.
“We’re working to seal this important partnership between the Brazilian government and SpaceX,” Faria said, according to the statement. “Our objective is to bring Internet to rural areas and remote places, in addition to helping control fires and illegal deforestation in the Amazon rainforest.”