The amount of digital data available is greater than ever before, including in health care, where doctors’ notes are routinely entered into electronic health record systems. Manually reviewing, analyzing, and sorting all these notes requires a vast amount of time and effort, which is exactly why computer scientists have developed artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to infer medical conditions, demographic traits, and other key information from this written text.
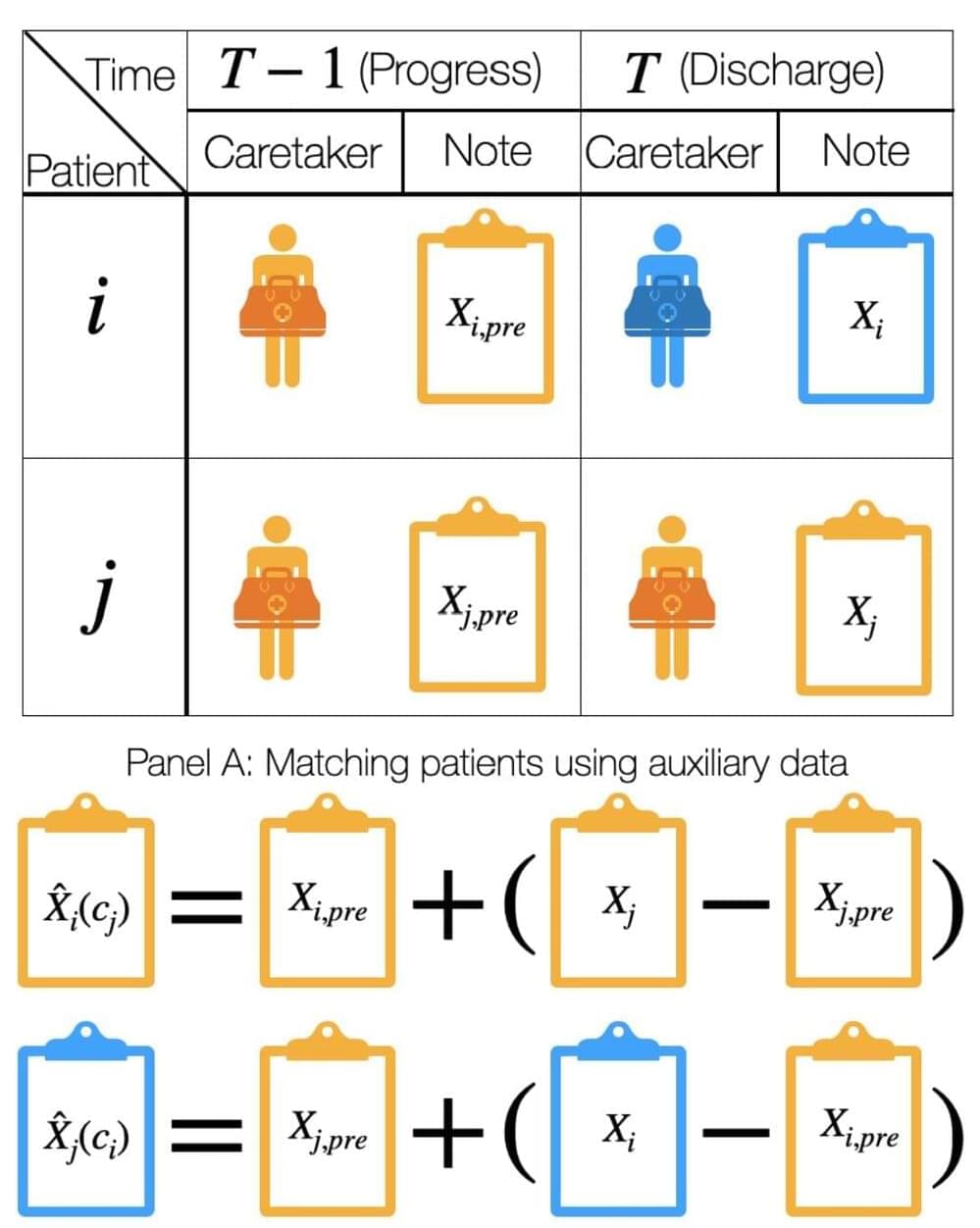
However, safety concerns limit the deployment of such models in practice. One key challenge is that the medical notes used to train and validate these models may differ greatly across hospitals, providers, and time. As a result, models trained at one hospital may not perform reliably when they’re deployed elsewhere.
Previous seminal works by Johns Hopkins University’s Suchi Saria—an associate professor of computer science at the Whiting School of Engineering—and researchers from other top institutions recognize these “dataset shifts” as a major concern in the safety of AI deployment.