The latest scandal involves a Google engineer accused of stealing AI secrets.



According to its website, the Grok 1.5V connects the physical and digital worlds. The company has highlighted seven examples of its capabilities to explain how the multimodal model works.
A user can share a picture of a flowchart with Grok, and the AI model can translate it into Python code. By simply showing the model a nutrition label, a user can inquire how many calories one would consume by consuming certain portions of the product.
While this might seem like an easy case of multiplication, the AI model can also take a child’s drawing and build an entire bedtime story using it. The model can do the converse, too. Show it a meme, and it will explain why it is funny and provide the context needed to understand it.

Taichi could potentially make artificial general intelligence a reality.
Researchers at Tsinghua University in China have developed a revolutionary new artificial intelligence (AI) chip that uses light instead of electricity to process data.
Researchers have developed a highly energy-efficient photonic AI chip called Taichi, which could accelerate the development of advanced computing solutions.

The highest-level Hidra chip will power Apple’s highest-end desktop, the Mac Pro. To give you an idea of how powerful the chip might be, Apple is working to support the Mac Pro with 512 GB RAM. Unlike Intel’s processor, which allows additional memory to be added later, Apple Silicon is more deeply integrated into the processor, and therefore, the RAM options will have come from Apple itself.
With the M4 chip nearing production, Apple could unveil its new and updated Mac lineup later this year and follow it up with releases through 2025, the Bloomberg report added.
A newer lineup also gives the Cupertino-based company an opportunity to join the league of tech giants working on AI. Compared to Microsoft and Google, which have already released their AI-powered products, Apple has been a laggard in the AI space.
The robot is controlled by a neural network trained in deep reinforcement learning via simulation.
Students at ETH Zurich are creating a robot that can move around in extremely low gravity by hopping like a human.
ETH Zurich students are developing a robot that can hop like humans for exploring challenging terrains featuring ultra-low gravity.
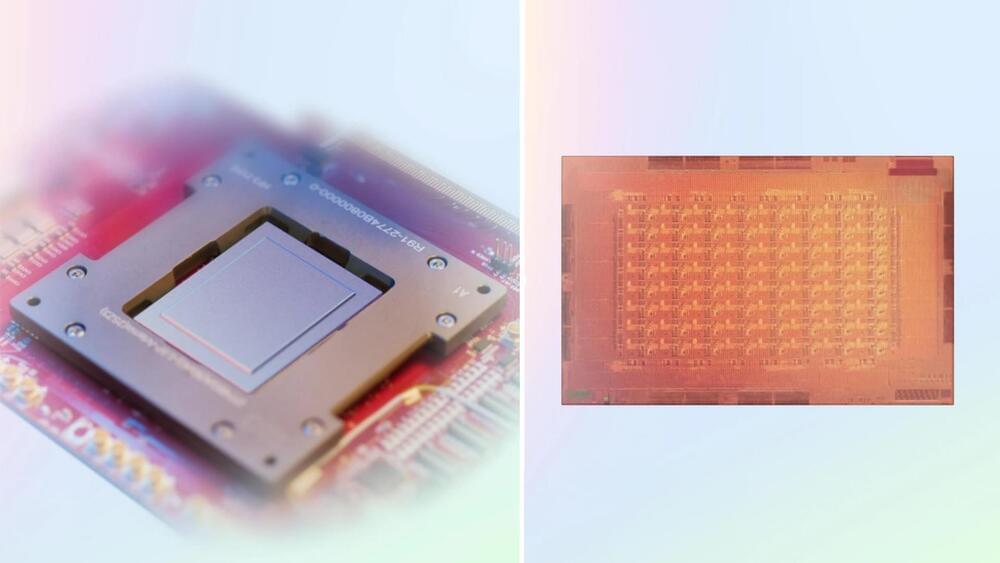
The design is intended to provide more computing power, bandwidth, and memory capacity to the chips. Initially, Meta aimed to perform inference functions such as ranking and generating responses to user prompts. Meta plans to use the chips for more intense operations, such as training AI models using large data sets.
A shift to its chips could help Meta save millions in energy costs every year, alongside the billions needed in capital expenditure to buy chips from Nvidia.
Meta isn’t the only tech company looking to design and build its own AI chips. Legacy chipmaker Intel, which has lagged in catering to industry requirements for AI chips, also announced its new Gaudi chips at an event on Tuesday.

Tesla CEO Elon Musk — who has an abysmal track record for making predictions — is predicting that we will achieve artificial general intelligence (AGI) by 2026.
“If you define AGI as smarter than the smartest human, I think it’s probably next year, within two years,” he told Norway wealth fund CEO Nicolai Tangen during an interview this week, as quoted by Reuters.
The mercurial billionaire also attempted to explain why his own AI venture, xAI, has been falling behind the competition. According to Musk, a shortage of chips was hampering his startup’s efforts to come up with the successor of Grok, a foul-mouthed, dad joke-generating AI chatbot.
DeepMind’s AI system achieved grandmaster-level chess playing ability by learning from playing against itself billions of times, challenging traditional AI development techniques and opening up possibilities for broader applications beyond chess Questions to inspire discussion What is the title of the video? —The title.
Herbert Ong Brighter with Herbert.