If electronics tried selling themselves by speaking to you, would you have a greater urge to buy them? This is what a recent study published in Decision Support Systems hopes to address as a research duo investigated how artificial intelligence (AI) could be used as a productive marketing and retail tool for selling their products. This study holds the potential to help researchers, businesses, and consumers better understand how AI can be sold using anthromorphism (possessing human attributes).
“Companies have long used cartoon-like characters to sell products. We are familiar with the ‘M&M spokescandies’, for example,” said Dr. Alan Dennis, who is a Professor of Information Systems in the Kelley School of Business at Indiana University and co-author on the study. “But adding human features to a product can be a powerful way to influence consumers’ perceptions and decision making, because it can trigger anthromorphism.”
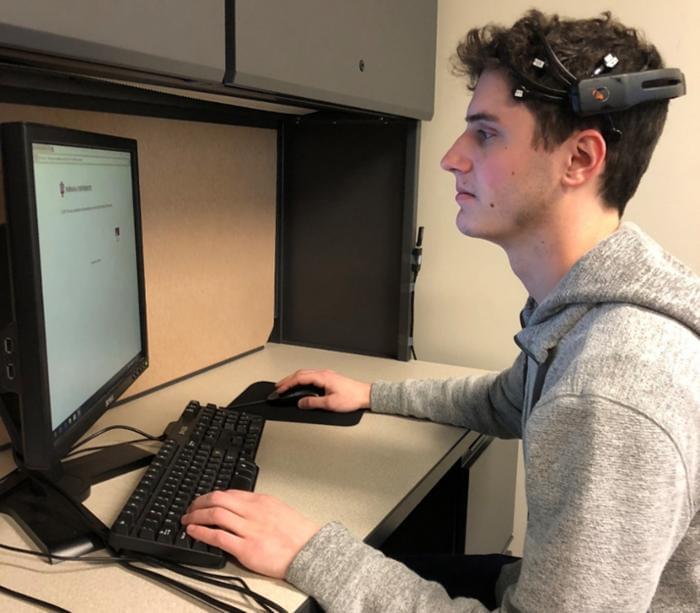
For the study, the researchers enlisted approximately 50 undergraduate students and asked them to pretend they were new master’s degree students who needed a new television, camera, or laptop for their studies. Using an eBay-style auction website, the students then bid on the products after watching a two-minute video exhibiting a speaker with human attributes which described the product. The goal of the study was to ascertain how much the students were willing to bid on the products with the video compared to products without, all while using an Emotiv EPOC EEG headset to gather data on their brain activity.