Armed with more than $750 million in funding, Brett Adcock vows that Figure will become one of the most important businesses in the world. First, he has a lot of work to do.


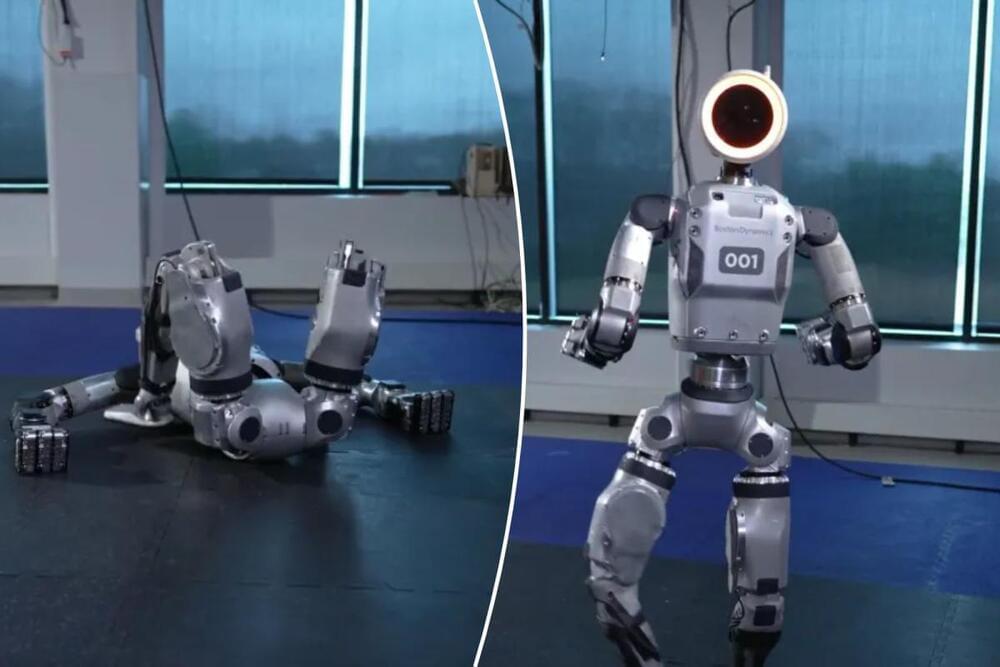
“This is the first look at a real product,” the company said. “But it certainly isn’t the last.”
“In the months and years ahead, we’re excited to show what the world’s most dynamic humanoid robot can really do – in the lab, in the factory, and in our lives,” the company also said.
Boston Dynamics partnered with the NYPD last year to roll out several crime-fighting robots to patrol Times Square and subway stations.
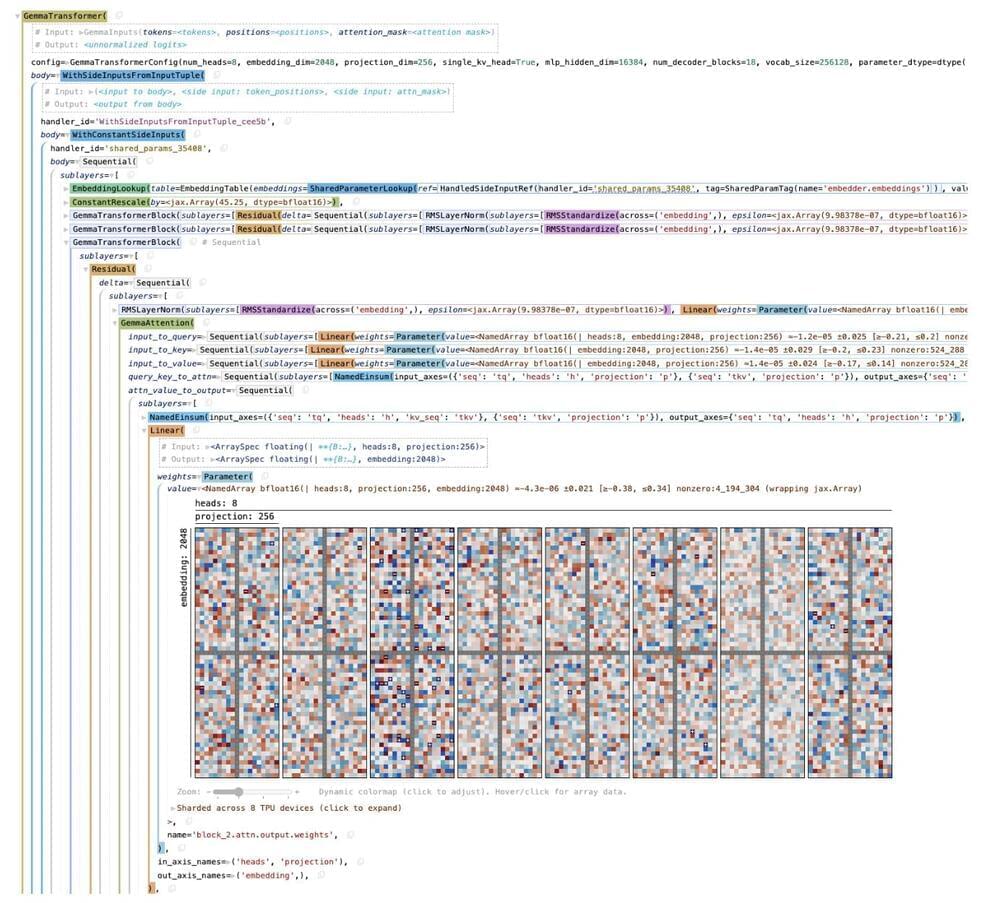
Google DeepMind has recently introduced Penzai, a new JAX library that has the potential to transform the way researchers construct, visualize, and alter neural networks. This innovative tool is designed to smoothly integrate with Google Colab and the JAX ecosystem, which is a major step forward in the accessibility and manipulability of AI models.
Penzai is a new approach to neural network development that emphasizes transparency and functionality. It allows users to view and edit models as legible pytree data structures, making it easier than ever to delve into the inner workings of a model. This feature is especially useful after a model has been trained, as it provides insights into how the model operates and allows for modifications that can help achieve desired outcomes.
Penzai aims to make AI research more accessible to researchers by simplifying the process of modifying pre-trained neural networks. This would enable a wider range of researchers to experiment and innovate on existing AI technologies, which is crucial for advancing the field and discovering new AI applications. Penzai’s user-friendly interface breaks down the barriers to AI research and makes it easier for everyone to benefit from the technology.



NVIDIA is all set to aid Japan in building the nation’s hybrid quantum supercomputer, fueled by the immense power of its HPC & AI GPUs.
Japan To Rapidly Progressing In Quantum and AI Computing Segments Through Large-Scale Developments With The Help of NVIDIA’s AI & HPC Infrastructure
Nikkei Asia reports that the National Institute of Advanced Industrial and Technology (AIST), Japan, is building a quantum supercomputer to excel in this particular segment for prospects. The new project is called ABCI-Q & will be entirely powered by NVIDIA’s accelerated & quantum computing platforms, hinting towards high-performance and efficiency results out of the system. The Japanese supercomputer will be built in collaboration with Fujitsu as well.


Global IT investments are expected to increase by 8% in 2024 compared to 2023 and amount to $5.06 trillion.
About it says in the latest forecast of the American research and consulting company Gartner, which specializes in IT markets.
The consulting company noted that «classic» enterprises still lag far behind IT companies in terms of spending.