If it ever gets built, it will dwarf all existing supercomputers.



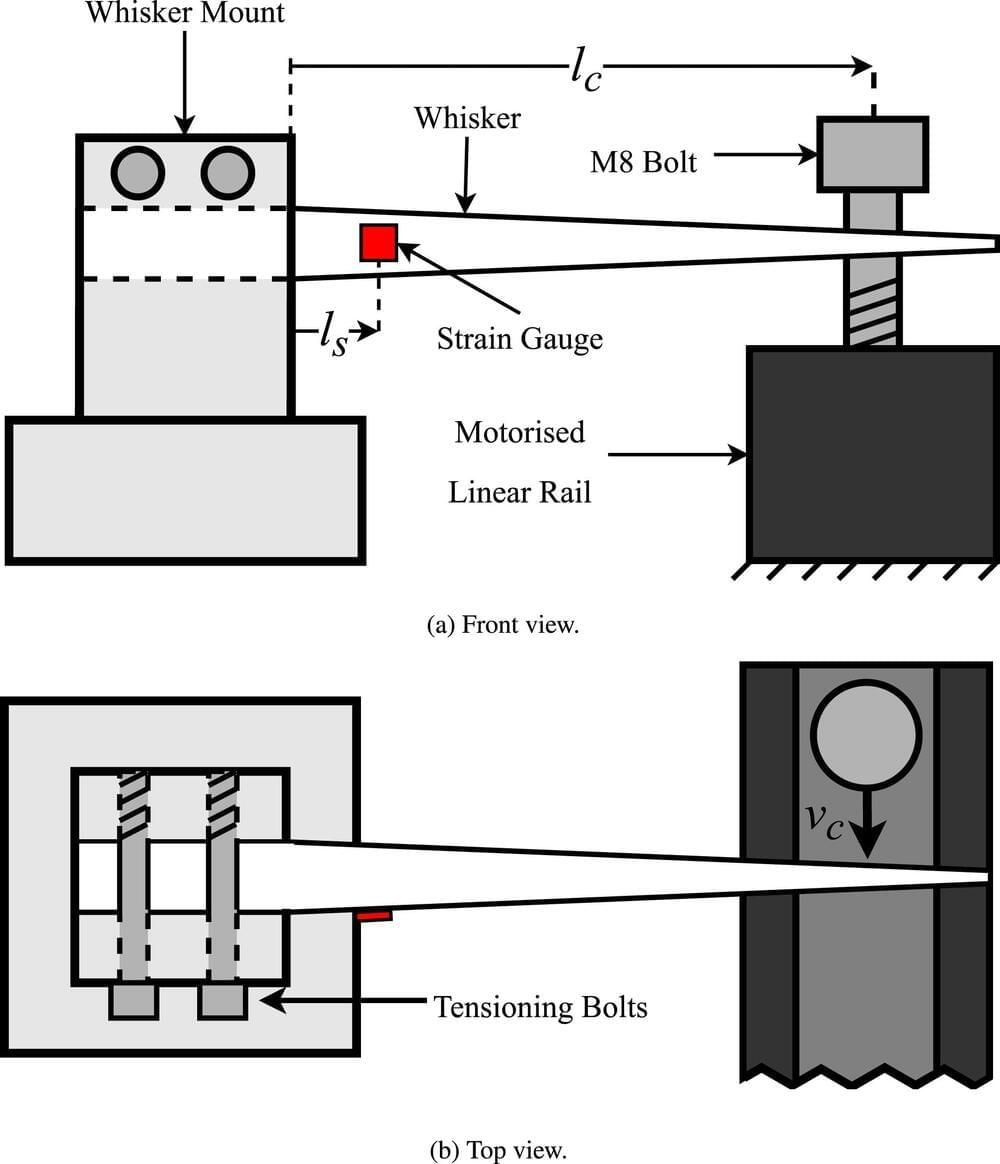
Taking inspiration from the animal kingdom, Flinders University researchers are developing affordable, flexible and highly responsive ‘whiskers’ to attach to robots. Their article, “Optimising electromechanical whisker design for contact localisation,” has been published in the journal Sensors and Actuators A: Physical.
While lasers and camera vision is used to instruct robot movement, the additional support of light-weight, cheap and flexible whiskers would give workplace and domestic robots additional tactile abilities in confined or cluttered spaces.
Like a rat’s whiskers, these sensors can be used to overcome a robot’s range-finder or camera blind spots which may not ‘see’ or register an object close by, says Flinders College of Science and Engineering Ph.D. candidate Simon Pegoli. Additionally, whiskers uncover properties of objects, such as moveability, not possible with camera or regular range-finder sensors.
Tesla’s autopilot technology and the increasing affordability of electric vehicles are set to revolutionize the transportation industry, making transportation as a service cheaper and safer, and leading to a significant drop in oil demand and potential geopolitical implications Questions to inspire discussion How safe.
In January 2024, Figure signed its first commercial agreement with BMW to deploy its humanoid robot in the German carmaker’s production facility in Spartanburg, South Carolina.
Now, the California-based robotics firm has released a video showcasing its 1 humanoid robot executing its first job by…
Figure’s humanoid robot, deployed at BMW’s facility, demonstrates full autonomy in vehicle assembly, guided by neural network-driven actions.

I used Adobe products for years, and even went to Adobe Seminars in Austin Texas.
Oh, you thought the possibilities of generative AI were already terrifying enough? Well, we’ve got some bad news for you. Adobe has just released a video showcasing its Adobe Firefly video model, and it comes with a whole host of unnerving generative AI tricks.
“Adobe is using the power of generative AI to deliver the most advanced and precise editing tools ever in Premiere Pro,” says the cheerful over-the-top narration, before showcasing how AI will soon be used to generate objects that weren’t there before, delete unwanted objects, extend scenes and create generated backdrops.
The video stresses that “content credentials” will “always make transparent whether AI was used”, but obviously that only goes so far as the Adobe programme itself. With streamers and movies already coming under fire for sneaking AI into their final products, it seems inevitable that advancing technology like this is only going to make it harder and harder to tell what’s real on our screens.

West Japan Railways (West JR), one of six companies that make up Japan Railways Group, has unveiled a giant “humanoid robot” to work on heavy machinery on its lines.
The as yet unnamed tool is described as “multifunctional railway heavy machinery for railway equipment maintenance” and is based off a prototype used by West JR to prove the concept of the odd-looking machine.

Lovely essay by Sara Walker on how tech is biology. She closely mirrors my own thinking on this. “The technologies we are and that we produce are part of the same ancient strand of information propagating through and structuring matter on our planet.”
Our best estimates place the origin of life on this planet at approximately 3.8 billion years ago. Biological beings alive today are part of a lineage of information that can be traced backward in time through genomes to the earliest life. But evolution produced information that is not just genomic. Evolution produced everything around us, including things not traditionally considered “life.” Human technology would not exist without humans, so it is therefore part of the same ancient lineage of information that emerged with the origin of life.
Technology, like biology, does not exist in the absence of evolution. Technology is not artificially replacing life — it is life.
It is important to separate what is meant by “life” here as distinct from “alive.” By “life,” I mean all objects that can only be produced in our universe through a process of evolution and selection. Being “alive,” by contrast, is the active implementation of the dynamics of evolution and selection. Some objects — like a dead cat — are representative of “life” (because they only emerge in the universe through evolution) but not themselves “alive.”