Explore the future of artificial intelligence in ‘AI on the Horizon,’ examining trends, innovations, and the impact on society and technology.



Proving earlier rumors to be true, chip manufacturer Intel has announced its plans to fire over 15% of its total workforce, amounting to between 15,000 and 19,000 employees, in an attempt to save $10 billion in 2025.
In a note sent by Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger to the workers, the director sang a familiar song of the firings being very painful news and the hardest thing he’s ever done in his career, attributing the decision to leave thousands of people unemployed by declining profits as Intel is “yet to fully benefit from powerful trends, like AI”
To address the issues the company faces these days, the CEO aims to cut operational costs, simplify Intel’s portfolio, eliminate overlapping responsibilities, halt non-essential work, and reduce Intel’s capital expenditures for 2024 by over 20%, leaving the company’s overall IDM 2.0 strategy, which includes priorities such as “expanding manufacturing capacity in the US and EU” and “delivering AI everywhere”, unchanged.


A Mormon Transhumanist has trained a chatbot that was trained on his entire collection of writings, internet social media posts, and presentations.
I’ve merged with artificial intelligence. Well, I’m working on it. And I’m excited to share the results with you.
! Trained on everything that I’ve written publicly since 2000, he might be better at Mormon Transhumanism than I am.
Friends, I’m excited to introduce you to LincGPT! This artificial intelligence, built on the OpenAI platform, is designed to engage with you on topics related to technological evolution, postsecular religion, and Mormon Transhumanism. I’ve trained LincGPT on all of my public writings since the year 2000. That includes the following:
An extremely cool application of large language models in combination with other AI tools such as models for text-to-speech and speech-to-text, image recognition and captioning, etc.
We created a robot tour guide using Spot integrated with Chat GPT and other AI models to explore the robotics applications of foundational models.
Joscha Bach meets with Ben Goertzel to discuss cognitive architectures, AGI, and conscious computers in another theolocution on TOE.
- Patreon: / curtjaimungal (early access to ad-free audio episodes!)
- Crypto: https://tinyurl.com/cryptoTOE
- PayPal: https://tinyurl.com/paypalTOE
- Twitter: / toewithcurt.
- Discord Invite: / discord.
- iTunes: https://podcasts.apple.com/ca/podcast…
- Pandora: https://pdora.co/33b9lfP
- Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9…
- Subreddit r/TheoriesOfEverything: / theoriesofeverything.
- TOE Merch: https://tinyurl.com/TOEmerch.
LINKS MENTIONED:
- OpenCog (Ben’s AI company): https://opencog.org.
- SingularityNET (Ben’s Decentralized AI company): https://singularitynet.io.
- Podcast w/ Joscha Bach on TOE: • Joscha Bach: Time, Simulation Hypothe…
- Podcast w/ Ben Goertzel on TOE: • Ben Goertzel: The Unstoppable Rise of…
- Podcast w/ Michael Levin and Joscha on TOE: • Michael Levin Λ Joscha Bach: Collecti…
- Podcast w/ John Vervaeke and Joscha on TOE: • Joscha Bach Λ John Vervaeke: Mind, Id…
- Podcast w/ Donald Hoffman and Joscha on TOE: • Donald Hoffman Λ Joscha Bach: Conscio…
- Mindfest Playlist on TOE (Ai and Consciousness): • Mindfest (Ai \& Consciousness Conference)
TIMESTAMPS:
- 00:00:00 Introduction.
- 00:02:23 Computation vs Awareness.
- 00:06:11 The paradox of language and self-contradiction.
- 00:10:05 The metaphysical categories of Charles Peirce.
- 00:13:00 Zen Buddhism’s category of zero.
- 00:14:18 Carl Jung’s interpretation of four.
- 00:21:22 Language as \.
Are you ready for artificial intelligence?
Curt’s “String Theory Iceberg”: https://youtu.be/X4PdPnQuwjYMain episode with Bach and Goertzel (October 2023): https://youtu.be/xw7omaQ8SgA?list=PLZ7ikzmc6zlN6E8KrxcYCWQIHg2tfkqvR Consider signing up for TOEmail at https://www.curtjaimungal.org
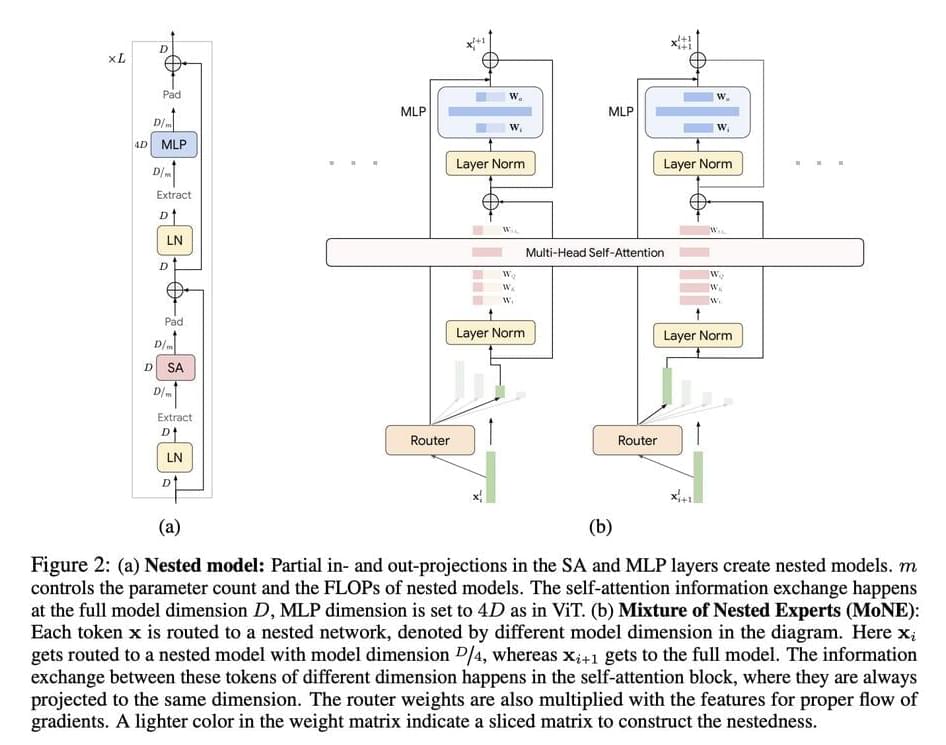
One of the significant challenges in AI research is the computational inefficiency in processing visual tokens in Vision Transformer (ViT) and Video Vision Transformer (ViViT) models. These models process all tokens with equal emphasis, overlooking the inherent redundancy in visual data, which results in high computational costs. Addressing this challenge is crucial for the deployment of AI models in real-world applications where computational resources are limited and real-time processing is essential.
Current methods like ViTs and Mixture of Experts (MoEs) models have been effective in processing large-scale visual data but come with significant limitations. ViTs treat all tokens equally, leading to unnecessary computations. MoEs improve scalability by conditionally activating parts of the network, thus maintaining inference-time costs. However, they introduce a larger parameter footprint and do not reduce computational costs without skipping tokens entirely. Additionally, these models often use experts with uniform computational capacities, limiting their ability to dynamically allocate resources based on token importance.

Here they come… 🦾🤖