Meet the inventors of Google Docs, Python, RSS feeds and more — now at Microsoft, where they’re leading the next wave of AI innovation.


Millennium Prize Problems Lecture 9/17/2025
Speaker: Michael Freedman, Harvard CMSA and Logical Intelligence.
Title: the poincaré conjecture and mathematical discovery.
Abstract: The AI age requires us to re-examine what mathematics is about. The Seven Millenium Problems provide an ideal lens for doing so. Five of the seven are core mathematical questions, two are meta-mathematical – asking about the scope of mathematics. The Poincare conjecture represents one of the core subjects, manifold topology. I’ll explain what it is about, its broader context, and why people cared so much about finding a solution, which ultimately arrived through the work of R. Hamilton and G. Perelman. Although stated in manifold topology, the proof requires vast developments in the theory of parabolic partial differential equations, some of which I will sketch. Like most powerful techniques, the methods survive their original objectives and are now deployed widely in both three-and four-dimensional manifold topology.

In this section, the authors reveal the findings of this review. The findings are categorized based on data modalities, showcasing the effectiveness of AI models in terms of evaluation metrics. Figure 1 summarizes the extraction process, providing a clear representation of the progression from article identification to final selection of studies. The initial search yielded a substantial total of 1,175 articles. Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the subsequent screening process excluded irrelevant articles. By meticulously filtering the literature, 25 studies were deemed suitable for inclusion into this review.
A chronology of research studies on the uses of AI in DS diagnosis is shown in Figure 2. This timeline highlights a considerable growth in academic interest over the course of the years. A single study was published per year between the years 2013 and 2017. Technical restrictions and the availability of datasets restricted the early attempts to integrate AI into DS diagnoses. Advancements in deep learning and machine learning technologies have been driven by continuous growth in research, representing a milestone in 2021. These developments are signs of increasing confidence in the ability of artificial intelligence to identify and resolve challenging diagnostic problems. The year 2021 reaches a high with four studies, indicating a surge of innovation. This may result from improved computing tools and a more extensive understanding of the usefulness of artificial intelligence in the medical field. However, the minor decline in 2022 and 2023, with three studies, may indicate difficulties in maintaining the rapid pace of research. These challenges may include restricted access to different datasets or limitations to clinical adoption.
In 2024, there was a significant increase in DS diagnostics approaches, achieving a total of seven studies. This increase is a result of developments in AI algorithms, collaborations across diverse fields, and the significant role of AI in medical diagnosis. It demonstrates the increased academic and multidisciplinary interest in developing effective AI-powered DS detection models. In addition, an increasing trajectory highlights the importance of maintaining research efforts in order to overcome current challenges in implementing AI applications in the healthcare sector.
Accelerating Promising Biotech Innovation — Dr. Aliza Apple, Ph.D. — Vice President, Catalyze360 AI/ML and Global Head, Lilly TuneLab, Eli Lilly and Company.
Dr. Aliza Apple, Ph.D. is a Vice President of Catalyze360 AI (https://www.lilly.com/science/partners/catalyze-360 and Global Head of Lilly TuneLab (https://tunelab.lilly.com/) at Eli Lilly where she leads the strategy, build and launch of Lilly’s external-facing AI/ML efforts for drug discovery.
Lilly Catalyze360 represents a comprehensive approach to enabling the early-stage biotech ecosystem, agnostic of the therapeutic area, designed to accelerate emerging and promising science, strategically removing barriers to support biotech innovation.
In her previous role at Lilly, Dr. Apple served as the COO and head of Lilly Gateway Labs West Coast, where she supported the local biotech ecosystem through early engagement and providing tailored offerings to meet their needs.
Prior to Lilly, Dr. Apple served as a co-founder at Santa Ana Bio, a venture-backed precision biologics company focused on autoimmune disease, and as an advisor to the founders of Firefly Biologics.

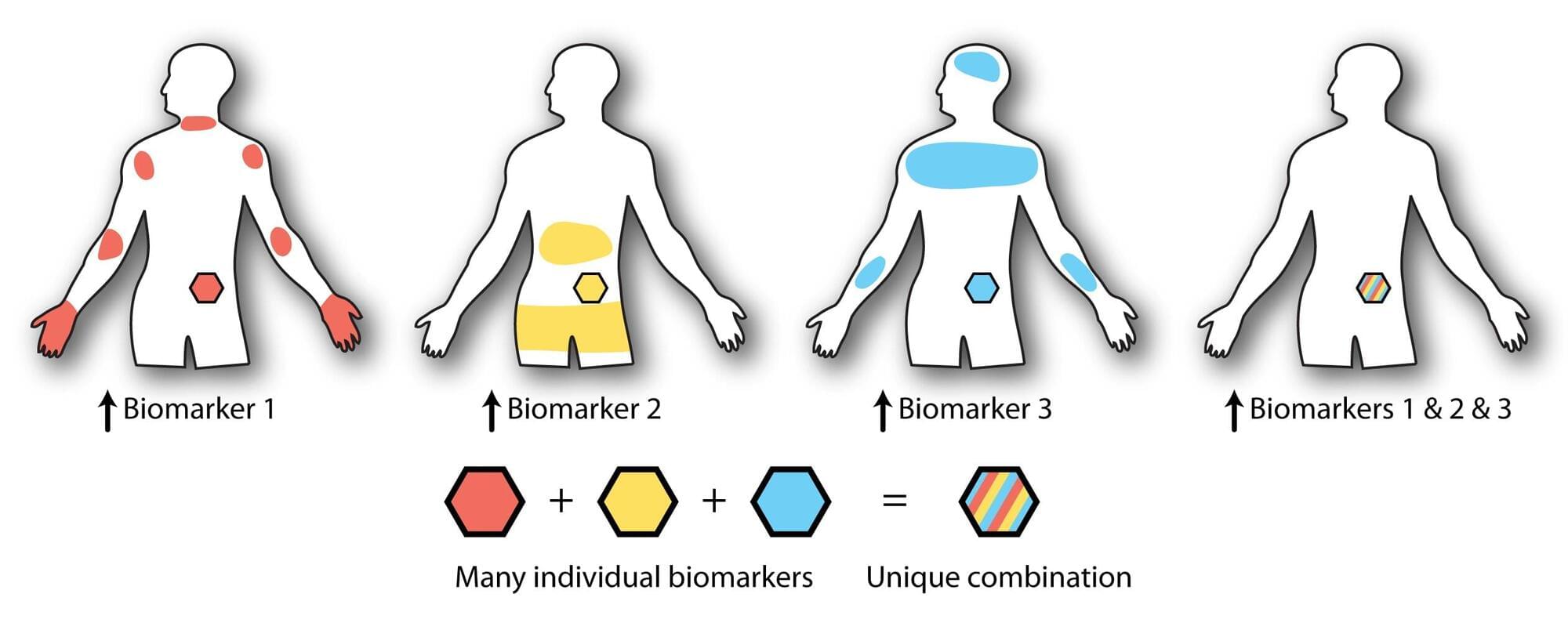
Targeted drug delivery is a powerful and promising area of medicine. Therapies that pinpoint the exact areas of the body where they’re needed—and nowhere they’re not—can reduce the medicine dosage and avoid potentially harmful off-target effects elsewhere in the body. A targeted immunotherapy, for example, might seek out cancerous tissues and activate immune cells to fight the disease only in those tissues.
The tricky part is making a therapy truly “smart,” where the medicine can move freely through the body and decide which areas to target.
Researchers at the University of Washington have taken a significant step toward that goal by designing proteins with autonomous decision-making capabilities. In a proof-of-principles study published in Nature Chemical Biology, researchers demonstrated that by adding smart tail structures to therapeutic proteins, they could control the proteins’ localization based on the presence of specific environmental cues.
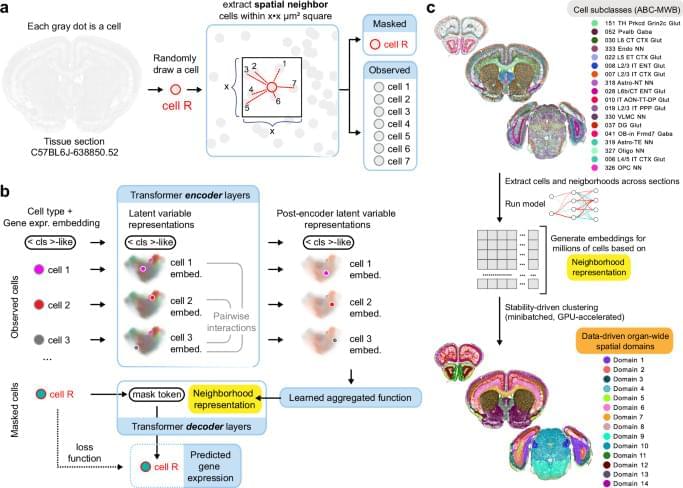
Defining the spatial organization of tissues and organs like the brain from large datasets is a major challenge. Here, authors introduce CellTransformer, an AI tool that defines spatial domains in the mouse brain based on spatial transcriptomics, a technology that measures which genes are active in different parts of tissue.

But the key is to see AI as fundamental, not a feature add. AI moves us from rule-based tasks to intelligent decision-making. When leaders rush to automate without analyzing and redesigning processes first, they implement smart tools on top of outdated workflows, expecting immediate gains.
I’ve seen it happen: When you apply AI to a flawed process, the consequences scale quickly. Instead, redesign workflows with AI at the core. Make sure the process makes sense before applying the technology.
Critically, when redesigning processes, understand that implementation is about leadership, not tools. IT teams often focus too much on tools and infrastructure without aligning automation efforts to clear business outcomes. Without engaging leadership and your workforce early and addressing cultural resistance, adoption stalls—even if the technology works perfectly.

OpenAI just unveiled HUGE developer updates at DevDay 2025 — Apps in ChatGPT, Agent Builder, Sora API, and Codex updates that can handle day-long tasks.
I sat down with Sam Altman for an exclusive interview about going viral on Sora, zero-person companies, and why he believes early AGI-like breakthroughs are starting to happen NOW.
In this conversation, we unpack:
Sam’s Sora AI deepfakes going viral.
Zero-person billion dollar companies run by agents.
AI starting to make scientific discoveries on Twitter.
ChatGPT’s 800M users and the new distribution platform.
Get 5-minute daily updates on the latest AI news: https://www.therundown.ai/subscribe.
Chapters: