AI agents have transformative potential for businesses, but implementing them effectively will take time and care. Here’s how to get started.


We knew this day would come. For years now, scientists have been trying to make Westworld a reality with their advances in android robots.
From lab-grown muscle tissue to robots with bones, ligaments and tendons, android robots have rapidly been getting more and more lifelike.
Now, a company named Clone Robotics has created something they are calling the Protoclone – a “faceless, anatomically accurate, synthetic human with over 200 degrees of freedom, over 1,000 Myofibers, and over 200 sensors.” Sound terrifying? Just wait until you see video of it twitching and spasming its way into action.
Simply outstanding progress with humanoid bots. I really like Figure — they seem to be making really good progress.
We’re introducing Helix, a generalist Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model that unifies perception, language understanding, and learned control to overcome multiple longstanding challenges in robotics.
Here’s a detailed report on Helix: https://www.figure.ai/news/helix

Incyte will partner with Genesis Therapeutics to research, discover, and develop small molecule treatments through a collaboration that could generate at least up to $620 million for Genesis, an artificial intelligence (AI)-based drug developer.
The companies have agreed to discover and optimize at least two initial small molecule programs through Genesis’s AI platform, Genesis Exploration of Molecular Space (GEMS). GEMS is designed to generate and optimize molecules for complex targets by integrating proprietary AI methods that include language models, diffusion models, and physical machine learning (ML) simulations.
Incyte has been granted exclusive rights for potential clinical development and commercialization of the products to be developed through the collaboration.
The pioneering scifi film Metropolis, directed by Fritz Lang in 1927, depicts a dystopian future in 2026 with society sharply divided between wealthy elitists and the working poor. Gustav Fröhlich is Freder, the wealthy son of city ruler who discovers the grim conditions of the workers when he ventures into the city’s depths. After meeting Maria and her robotic double, both played by Brigitte Helm, he becomes determined to bridge the social divide. The story unfolds with dramatic visuals of towering skyscrapers and massive factories. The world of Metropolis is full of technological wonder and social turmoil. The film’s depiction of large-scale automation and robotics aligns with current trends in manufacturing, though fully sentient robots are unlikely to materialize by 2026. #silentfilm #silentfilms #manufacturing #industry40 #metropolis #fritzlang #sciencefiction #scifi #movies #filmanalysis #robotics #robots #industrialautomation …

How can programmed failure protocols help improve sheet-based fluidic devices, the latter of which have become a cornerstone in enhancing soft robotics worldwide? This is what a recent study published in Cell Reports Physical Science hopes to address as an international team of researchers have developed a method for overcoming common failures of sheet-based systems, specifically due to their lightweight and flexible characteristics. This study has the potential to help engineers develop more efficient sheet-based devices, resulting in improved soft robotics designs.
For the study, the researchers examined how pressure changes could damage heat-sealable textiles that are used in sheet-based devices. Once they determined specific failure thresholds, the team incorporated programmed failures into the design, enabling the device to determine specific failure points and prevent further damage.
“Put simply, we are making soft, flexible machines smarter by designing their internal components to fail intentionally in a well-understood manner,” said Dr. Daniel J. Preston, who is an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Rice University and a co-author on the study. “In doing so, the resulting systems can recover from pressure surges and even complete multiple tasks using a single control input.” Going forward, the team hopes their research will lead to improved sheet-based fluidic systems, which, as noted, have become a cornerstone of soft robotics.

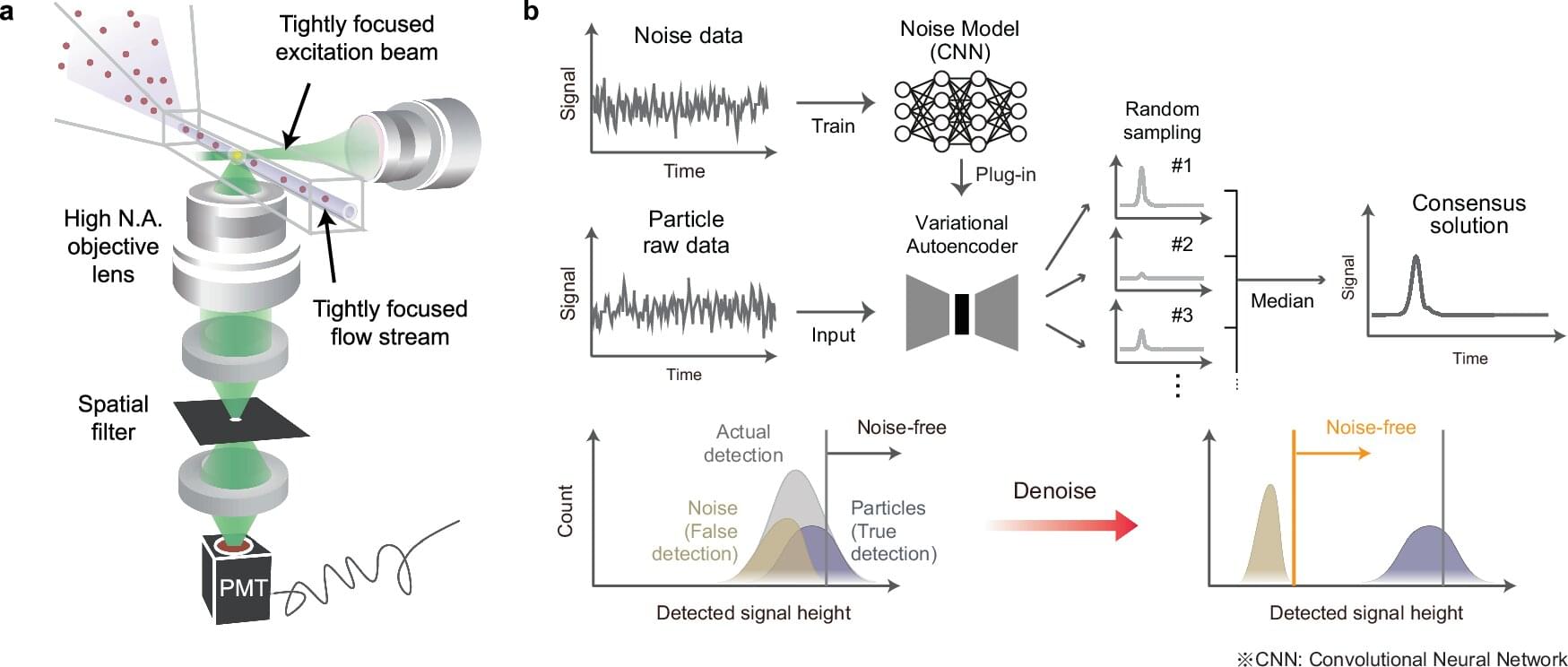
Researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, developed Deep Nanometry, an analytical technique combining advanced optical equipment with a noise removal algorithm based on unsupervised deep learning.
Deep Nanometry can analyze nanoparticles in medical samples at high speed, making it possible to accurately detect even trace amounts of rare particles. This has proven its potential for detecting extracellular vesicles indicating early signs of colon cancer, and it is hoped that it can be applied to other medical and industrial fields.
The body is full of microscopic particles smaller than cells. These include extracellular vesicles (EVs), which can be useful in early disease detection and also in drug delivery.
