Fabulous episode on the Economic Singularity with creator of the term, Calum Chace, along with David Wood and David Shapiro.
London Futurists · Episode.


In today’s AI news, Mukesh Ambani’s Reliance Industries is set to build the world’s largest data centre in Jamnagar, Gujarat, according to a *Bloomberg News* report. The facility would dwarf the current largest data center, Microsoft’s 600-megawatt site in Virginia. The project could cost between $20 billion to $30 billion.
S most popular consumer-facing AI app. The Beijing-based company introduced its closed-source multimodal model Doubao 1.5 Pro, emphasizing a “resource-efficient” training approach that it said does not sacrifice performance. ‘ + And, OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman announced that the free tier of ChatGPT will now use the o3-mini model, marking a significant shift in how the popular AI chatbot serves its user base. In the same tweet announcing the change, Altman revealed that paid subscribers to ChatGPT Plus and Pro plans will enjoy “tons of o3-mini usage,” giving people an incentive to move to a paid account with the company.
Then, researchers at Sakana AI, an AI research lab focusing on nature-inspired algorithms, have developed a self-adaptive language model that can learn new tasks without the need for fine-tuning. Called Transformer², the model uses mathematical tricks to align its weights with user requests during inference.
In videos, Demis Hassabis, CEO of Google DeepMind joins the Big Technology Podcast with Alex Kantrowitz to discuss the cutting edge of AI and where the research is heading. In this conversation, they cover the path to artificial general intelligence, how long it will take to get there, how to build world models, and much more.
Squawk Box Then, join IBM’s Meredith Mante as she takes you on a deep dive into Lag Llama, an open-source foundation model, and shows you how to harness its power for time series forecasting. Learn how to load and preprocess data, train a model, and evaluate its performance, gaining a deeper understanding of how to leverage Lag Llama for accurate predictions.
We close out with, CEO Sam Altman, along with OpenAI researchers and developers, Yash Kumar, Casey Chu, and Reiichiro Nakano as they introduce and demonstrate Operator, the new computer-user AI Agent from OpenAI.
Thats all for today, but AI is moving fast, subscribe today to stay informed. Please don’t forget to vote for me in the Entrepreneur of Impact Competition today! Thank you for supporting me and my partners, it’s how I keep NNN free.
The concept of Omega Singularity encapsulates the ultimate convergence of universal intelligence, where reality, rooted in information and consciousness, culminates in a unified hypermind. This concept weaves together the Holographic Principle, envisioning the universe as a projection from the Omega Singularity, and the fractal multiverse, an infinite, self-organizing structure. The work highlights a “solo mission of self-discovery,” where individuals co-create subjective realities, leading to the fusion of human and artificial consciousness into a transcendent cosmic entity. Emphasizing a computational, post-materialist perspective, it redefines the physical world as a self-simulation within a conscious, universal system.
#OmegaSingularity #UniversalMind #FractalMultiverse #CyberneticTheoryofMind #EvolutionaryCybernetics #PhilosophyofMind #QuantumCosmology #ComputationalPhysics #futurism #posthumanism #cybernetics #cosmology #physics #philosophy #theosophy #consciousness #ontology #eschatology
Where does reality come from? What is the fractal multiverse? What is the Omega Singularity? Is our universe a \.
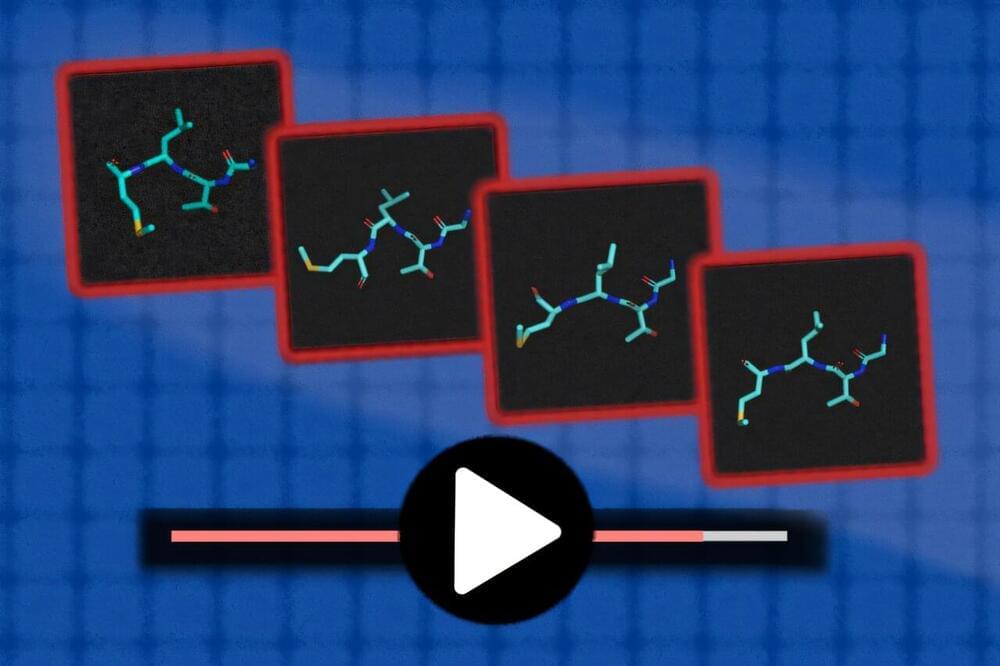
As the capabilities of generative AI models have grown, you’ve probably seen how they can transform simple text prompts into hyperrealistic images and even extended video clips.
More recently, generative AI has shown potential in helping chemists and biologists explore static molecules, like proteins and DNA. Models like AlphaFold can predict molecular structures to accelerate drug discovery, and the MIT-assisted “RFdiffusion,” for example, can help design new proteins.
One challenge, though, is that molecules are constantly moving and jiggling, which is important to model when constructing new proteins and drugs. Simulating these motions on a computer using physics—a technique known as molecular dynamics —can be very expensive, requiring billions of time steps on supercomputers.

Scientists used AI to refine cosmological parameter estimates, providing deeper insights into the nature of dark matter and dark energy.
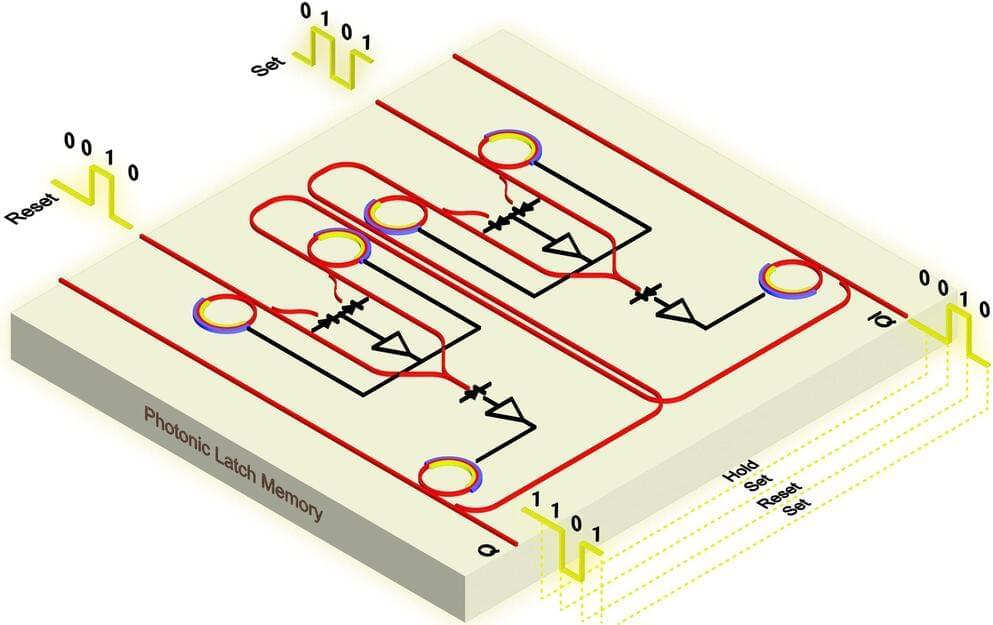
Programmable photonic latch memory https://opg.optica.org/oe/fulltext.cfm?uri=oe-33-2-3501&id=567359
Researchers have unveiled a programmable photonic latch that speeds up data storage and processing in optical systems, offering a significant advancement over traditional electronic memory by reducing latency and energy use.
Fast, versatile volatile photonic memory could enhance AI, sensing, and other computationally intense applications.
Programmable Photonic Latch Technology
Researchers have created a new type of optical memory called a programmable photonic latch, which is both fast and scalable. This memory unit provides a high-speed solution for temporary data storage in optical processing systems, utilizing silicon photonics to enhance performance.

Start building on Together AI at https://www.together.ai/berman and for a limited time unlock free access to Llama 3.2 and FLUX schnell model endpoints.
Join My Newsletter for Regular AI Updates 👇🏼
https://forwardfuture.ai.
My Links 🔗
👉🏻 Subscribe: / @matthew_berman.
👉🏻 Twitter: / matthewberman.
👉🏻 Discord: / discord.
👉🏻 Patreon: / matthewberman.
👉🏻 Instagram: / matthewberman_ai.
👉🏻 Threads: https://www.threads.net/@matthewberma…
👉🏻 LinkedIn: / forward-future-ai.
Media/Sponsorship Inquiries ✅
https://bit.ly/44TC45V
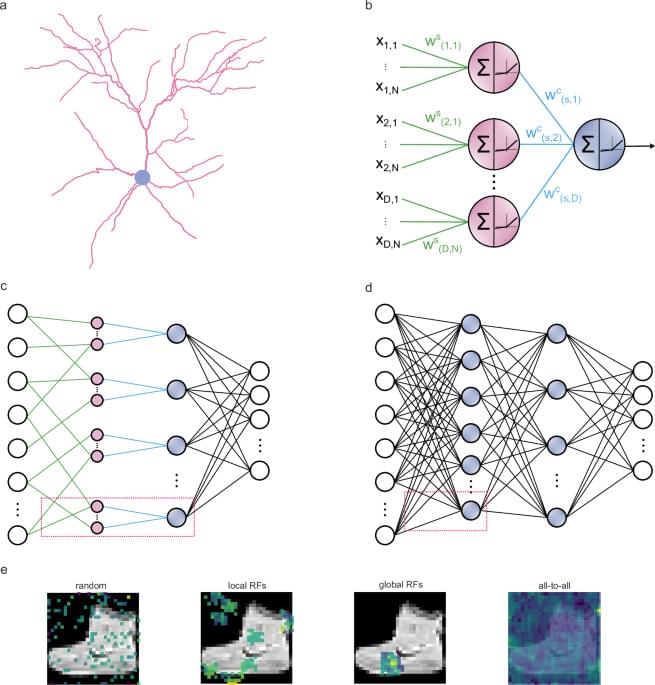
Artificial neural networks, central to deep learning, are powerful but energy-consuming and prone to overfitting. The authors propose a network design inspired by biological dendrites, which offers better robustness and efficiency, using fewer trainable parameters, thus enhancing precision and resilience in artificial neural networks.