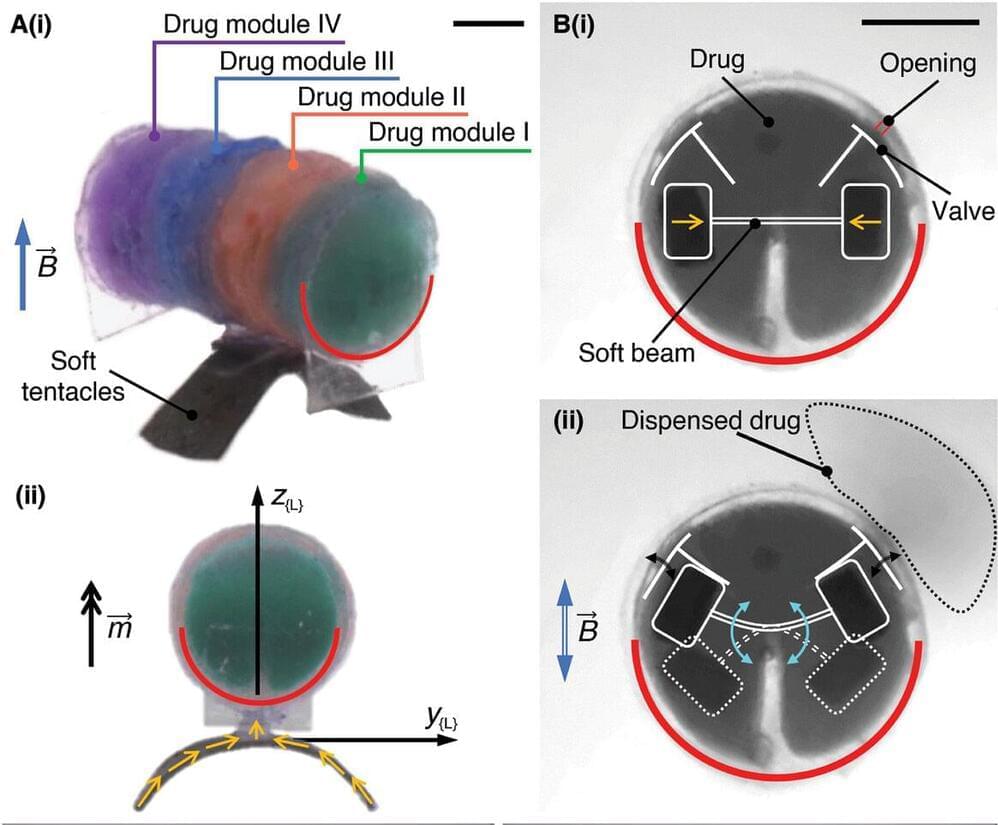
Sierra Space’s oxygen tech boosts lunar sustainability, aiding NASA’s Artemis goal for a permanent moon base and future Mars missions.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 351

Generative AI brings us Closer to Automating Investment Expertise
Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and Google Gemini excel at being trained on large data-sets to generate informative responses to prompts. Yi Cao, an assistant professor of accounting at the Donald G. Costello College of Business at George Mason University, and Long Chen, associate professor and area chair of accounting at Costello, are actively exploring how individual investors can use LLMs to glean market insights from the dizzying array of available data about companies.
Their new working paper, appearing in SSRN Electronic Journal and co-authored with Jennifer Wu Tucker of the University of Florida and Chi Wan of University of Massachusetts Boston, examines AI’s ability to identify “peer firms,” or product market competitors in an industry.
Cao explains the significance of selecting peers by relating this process to the real-estate market. “The capital market is similar to the real-estate market in that a firm’s value is partially determined by the value of its peers. In the real-estate market, we price a home based on the value of comparable properties in the neighborhood, or the so-called ‘comps.’ In our paper, we aim to leverage the power of LLMs to identify comps for evaluating firm value.”
Surgery-free Neuralink rival enables thought-controlled smart home
Neurotech company Synchron has been making massive strides over the past couple of years. It’s just announced that a trial participant has used its brain-computer interface (BCI) to turn on the lights in his home, see who is at the door, and choose what to watch on the TV – hands-free and without even a voice command.
That’s thanks to Synchron’s interface translating his thoughts into commands relayed to Amazon’s Alexa service. The virtual assistant is set up on his tablet and connected to his smart home devices. The trial participant, who is living with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and can’t use his hands, can simply think about navigating through options displayed on the tablet to engage them.
A ‘Stentrode’ embedded in a blood vessel on the surface of his brain houses electrodes that detect motor intent. The participant uses his thoughts to select which tiles to press on the interface and perform actions via Alexa. Watch him use the system in the video below.

Brains Could Help Solve a Fundamental Problem in Computer Engineering
In recent years, these technological limitations have become far more pressing. Deep neural networks have radically expanded the limits of artificial intelligence—but they have also created a monstrous demand for computational resources, and these resources present an enormous financial and environmental burden. Training GPT-3, a text predictor so accurate that it easily tricks people into thinking its words were written by a human, costs $4.6 million and emits a sobering volume of carbon dioxide—as much as 1,300 cars, according to Boahen.
With the free time afforded by the pandemic, Boahen, who is faculty affiliate at the Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute at Stanford and the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered AI (HAI), applied himself single mindedly to this problem. “Every 10 years, I realize some blind spot that I have or some dogma that I’ve accepted,” he says. “I call it ‘raising my consciousness.’”
This time around, raising his consciousness meant looking toward dendrites, the spindly protrusions that neurons use to detect signals, for a completely novel way of thinking about computer chips. And, as he writes in Nature, he thinks he’s figured out how to make chips so efficient that the enormous GPT-3 language prediction neural network could one day be run on a cell phone. Just as Feynman posited the “quantum supremacy” of quantum computers over traditional computers, Boahen wants to work toward a “neural supremacy.”

Researchers build AI model database to find new alloys for nuclear fusion facilities
A study led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory details how artificial intelligence researchers have created an AI model to help identify new alloys used as shielding for housing fusion applications components in a nuclear fusion reactor. The findings mark a major step towards improving nuclear fusion facilities.
A quantum neural network can see optical illusions like humans do. Could it be the future of AI?
Optical illusions, quantum mechanics and neural networks might seem to be quite unrelated topics at first glance. However, in new research published in APL Machine Learning, I have used a phenomenon called “quantum tunneling” to design a neural network that can “see” optical illusions in much the same way humans do.
My neural network did well at simulating human perception of the famous Necker cube and Rubin’s vase illusions—and in fact better than some much larger conventional neural networks used in computer vision.
This work may also shed light on the question of whether artificial intelligence (AI) systems can ever truly achieve something like human cognition.
Assessing China’s AI development and forecasting its future tech priorities
SUBJECT: Assessing China’s current AI development and forecasting its future technology priorities.
In July 2024, the Atlantic Council Global China Hub (AC GCH) and the Special Competitive Studies Project (SCSP) convened experts and policymakers in the second of a two-part private workshop series to gather insights into China’s technology priorities today and in the future. Participants discussed Beijing’s posture on artificial intelligence (AI) development and deployment today, including the hurdles China’s AI industry faces amid US-China technology competition, as well as Beijing’s policy priorities over the next decade. This memo summarizes insights gathered during the workshop.
In today’s strategic competition between the United States and China, both countries seek to bolster their nations’ innovation ecosystems and enhance their ability to develop and deploy breakthrough technologies. The United States is committed to maintaining US technological leadership in the long term, as Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo demonstrated at the Reagan National Defense Forum in December 2023, when she stated that “America leads the world in artificial intelligence. America leads the world in advanced semiconductor design, period… e’re a couple years ahead of China. No way are we going to let them catch up. We cannot let them catch up.”
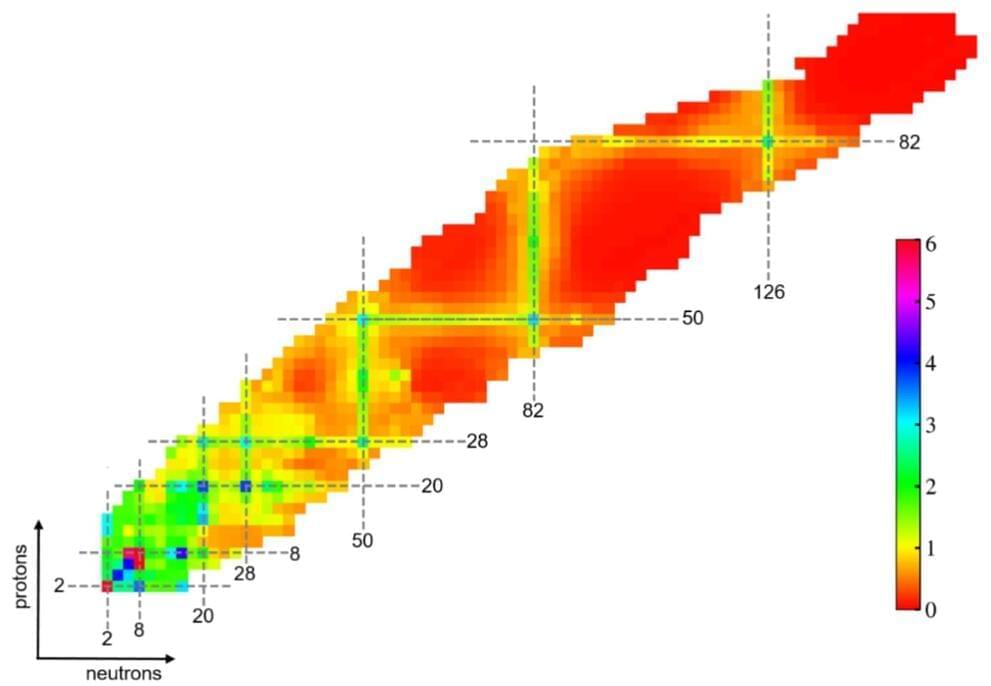
Physicists reveal evolution of shell structure using machine learning
A research team has used a machine learning approach to investigate the evolution of shell structure for nuclei far from the stability valley. The study, published in Physics Letters B and conducted by researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Huzhou University, and the University of Paris-Saclay, reveals the double-magic nature of tin-100 and the disappearance of the magic number 20 in oxygen-28.

The path to more general artificial intelligence
A small-N comparative analysis of six different areas of applied artificial intelligence (AI) suggests that the next period of development will require a merging of narrow-AI and strong-AI approaches. This will be necessary as programmers seek to move beyond developing narrowly defined tools to developing software agents capable of acting independently in complex environments. The present stage of artificial intelligence development is propitious for this because of the exponential increases in computer power and in available data streams over the last 25 years, and because of better understanding of the complex logic of intelligence. Applied areas chosen for examination were heart pacemakers, socialist economic planning, computer-based trading, self-driving automobiles, surveillance and sousveillance and artificial intelligence in medicine.