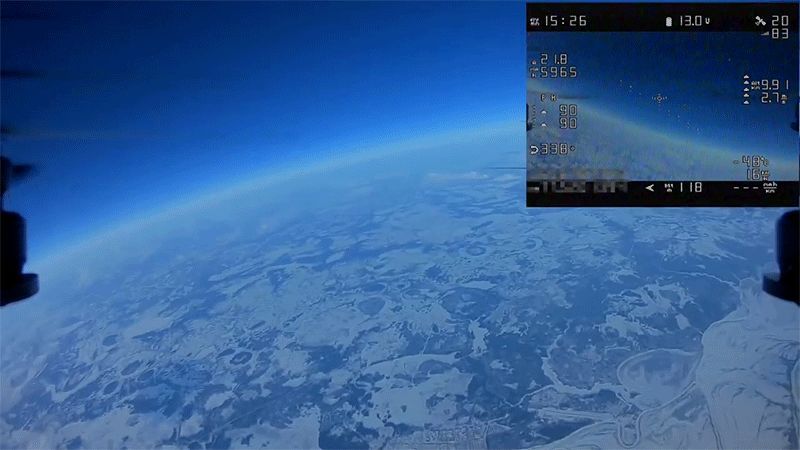
To ensure the safety of larger aircraft carrying pilots and passengers, unmanned aerial vehicles, or drones, can’t be flown higher than 400 feet so they don’t enter national airspace. Regulations in Russia, however, aren’t as strict, enabling drone pilot Denis Koryakin to fly his homebuilt, 2.3-pound craft to a staggering height of almost 33,000 feet.
For comparison, a 747 has a maximum ceiling of just over 45,000 feet, but most airliners will cruise at around the same altitude this tiny drone managed to reach. As amazing as the view is from 33,000 feet, it’s certainly a dangerous stunt and will get you in heaps of trouble in the US if you get caught. But Koryakin’s flight took place near the city of Strejevoï, in Siberia, which is notoriously frigid and sparsely populated. Russia also doesn’t appear to have any regulations on how high a drone can be flown, but hopefully stunts like this don’t become too commonplace.