Mathematicians have started to prepare for a profound shift in what it means to do mathematics.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 246


Could AI understand emotions better than we do?
Is artificial intelligence (AI) capable of suggesting appropriate behaviour in emotionally charged situations? A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and the University of Bern (UniBE) put six generative AIs — including ChatGPT — to the test using emotional intelligence (EI) assessments typically designed for humans. The outcome: these AIs outperformed average human performance and were even able to generate new tests in record time. These findings open up new possibilities for AI in education, coaching, and conflict management. The study is published in Communications Psychology.

What Happens When AI Replaces Workers?
When AGI arrives, your job could be on the chopping block. What happens next will shape the course of (human) history.

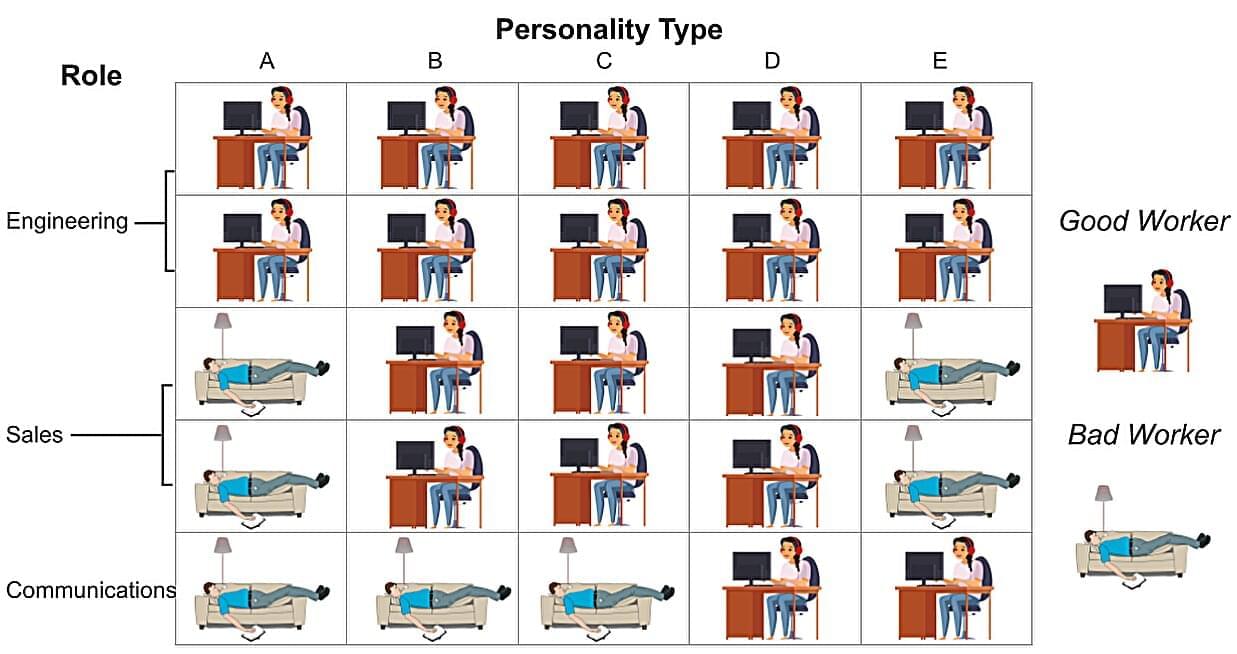
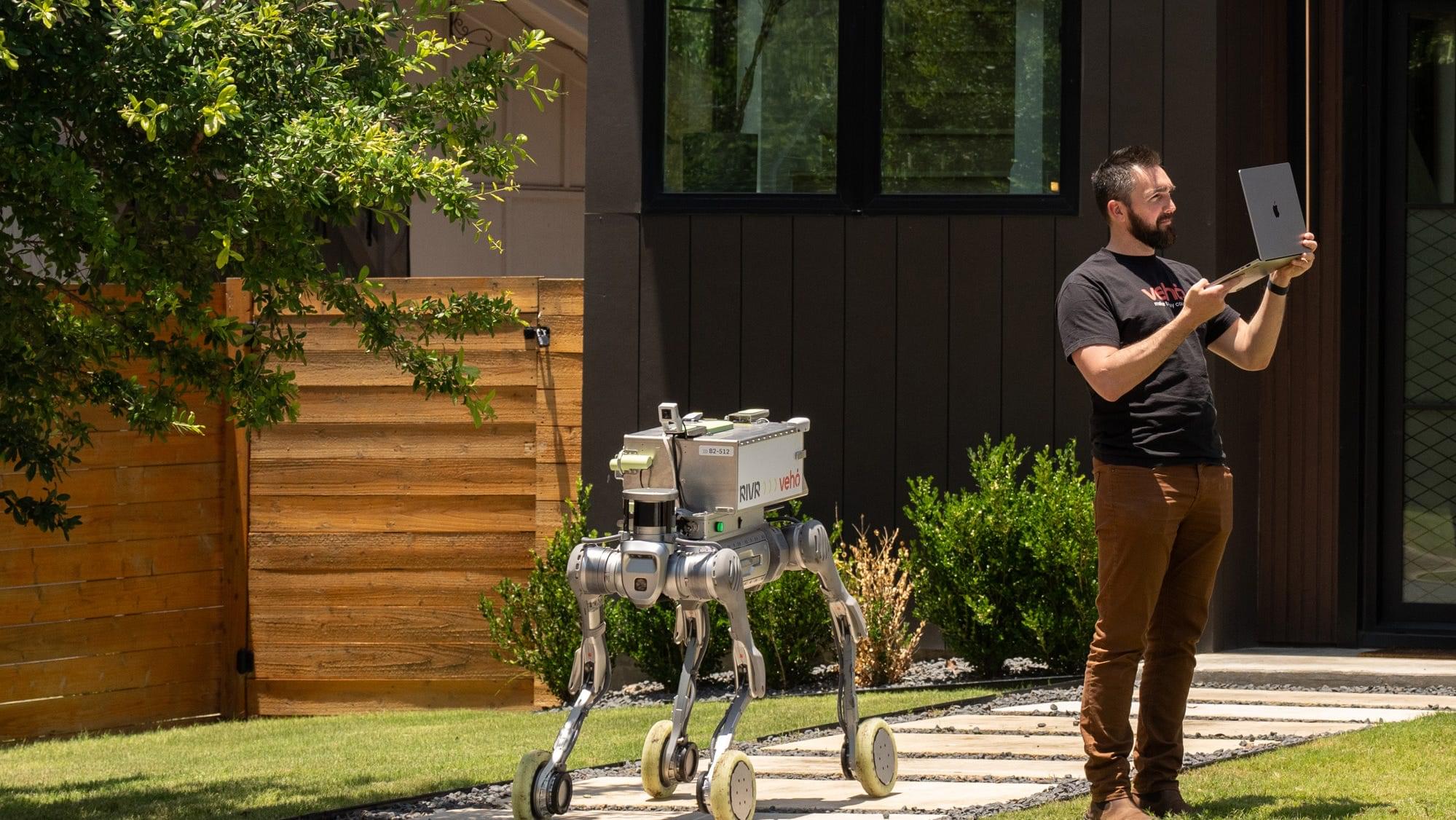
AI approach developed with human decision-makers in mind
As artificial intelligence takes off, how do we efficiently integrate it into our lives and our work? Bridging the gap between promise and practice, Jann Spiess, an associate professor of operations, information, and technology at Stanford Graduate School of Business, is exploring how algorithms can be designed to most effectively support—rather than replace—human decision-makers.
This research, published on the arXiv preprint server, is particularly pertinent as prediction machines are integrated into real-world applications. Mounting empirical evidence suggests that high-stakes decisions made with AI assistance are often no better than those made without it.
From credit reports, where an overreliance on AI may lead to misinterpretation of risk scores, to social media, where models may depend on certain words to flag toxicity, leading to misclassifications—successful implementation lags behind the technology’s remarkable capabilities.

View a PDF of the paper titled AI Agents vs. Agentic AI: A Conceptual Taxonomy, Applications and Challenges, by Ranjan Sapkota and 2 other authors
This study critically distinguishes between AI Agents and Agentic AI, offering a structured conceptual taxonomy, application mapping, and challenge analysis to clarify their divergent design philosophies and capabilities. We begin by outlining the search strategy and foundational definitions, characterizing AI Agents as modular systems driven by Large Language Models (LLMs) and Large Image Models (LIMs) for narrow, task-specific automation. Generative AI is positioned as a precursor, with AI Agents advancing through tool integration, prompt engineering, and reasoning enhancements. In contrast, Agentic AI systems represent a paradigmatic shift marked by multi-agent collaboration, dynamic task decomposition, persistent memory, and orchestrated autonomy. Through a sequential evaluation of architectural evolution, operational mechanisms, interaction styles, and autonomy levels, we present a comparative analysis across both paradigms. Application domains such as customer support, scheduling, and data summarization are contrasted with Agentic AI deployments in research automation, robotic coordination, and medical decision support. We further examine unique challenges in each paradigm including hallucination, brittleness, emergent behavior, and coordination failure and propose targeted solutions such as ReAct loops, RAG, orchestration layers, and causal modeling. This work aims to provide a definitive roadmap for developing robust, scalable, and explainable AI agent and Agentic AI-driven systems. >AI Agents, Agent-driven, Vision-Language-Models, Agentic AI Decision Support System, Agentic-AI Applications
