Scientists are using artificial intelligence to reveal the hidden mysteries of the universe, such as whether or not dark matter actually exists.
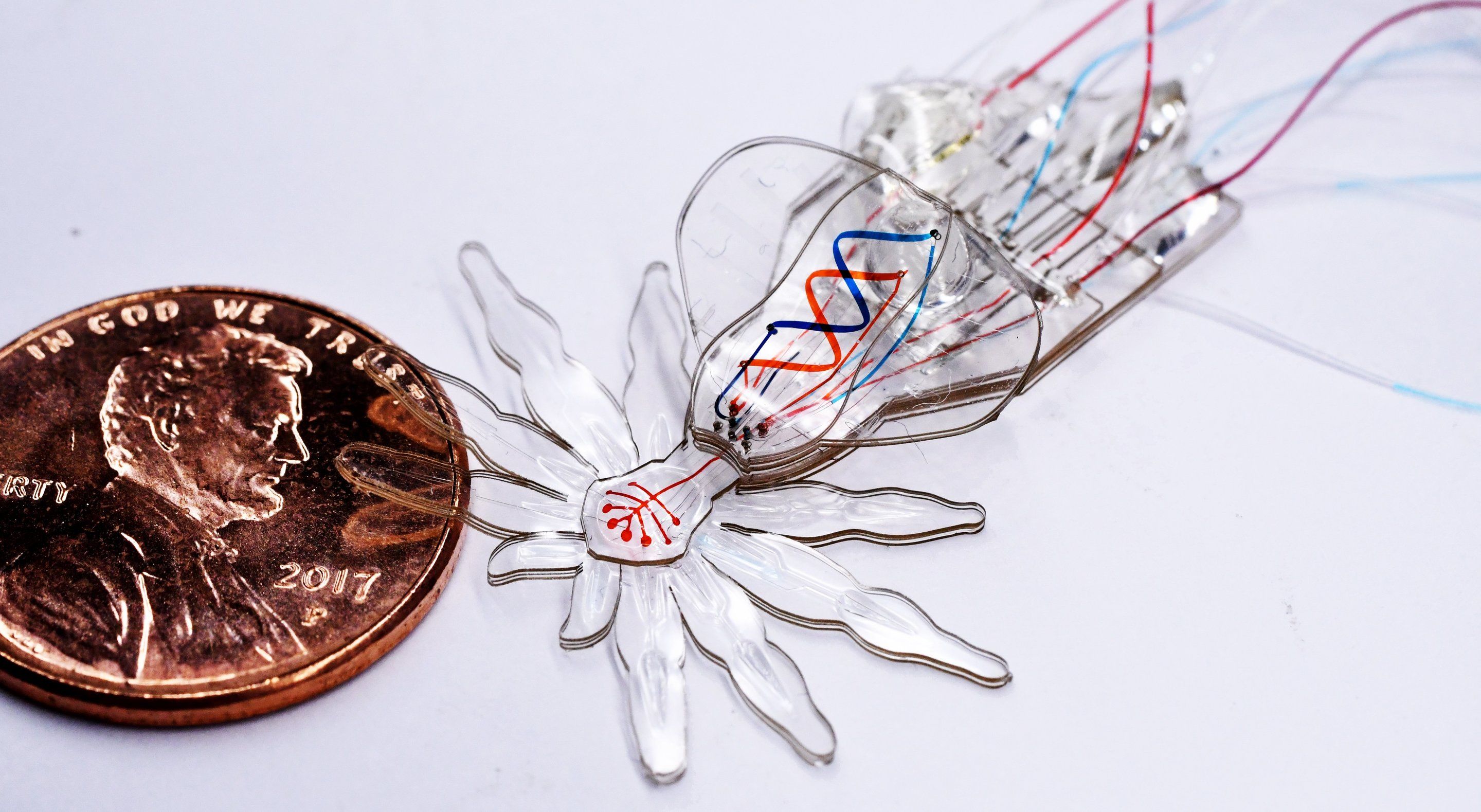



Roboticists are envisioning a future in which soft, animal-inspired robots can be safely deployed in difficult-to-access environments, such as inside the human body or in spaces that are too dangerous for humans to work, in which rigid robots cannot currently be used. Centimeter-sized soft robots have been created, but thus far it has not been possible to fabricate multifunctional flexible robots that can move and operate at smaller size scales.
A team of researchers at Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), and Boston University now has overcome this challenge by developing an integrated fabrication process that enables the design of soft robots on the millimeter scale with micrometer-scale features. To demonstrate the capabilities of their new technology, they created a robotic soft spider – inspired by the millimeter-sized colorful Australian peacock spider – from a single elastic material with body-shaping, motion, and color features. The study is published in Advanced Materials.
“The smallest soft robotic systems still tend to be very simple, with usually only one degree of freedom, which means that they can only actuate one particular change in shape or type of movement,” said Sheila Russo, Ph.D., co-author of the study. Russo helped initiate the project as a Postdoctoral Fellow in Robert Wood’s group at the Wyss Institute and SEAS and now is Assistant Professor at Boston University. “By developing a new hybrid technology that merges three different fabrication techniques, we created a soft robotic spider made only of silicone rubber with 18 degrees of freedom, encompassing changes in structure, motion, and color, and with tiny features in the micrometer range.”
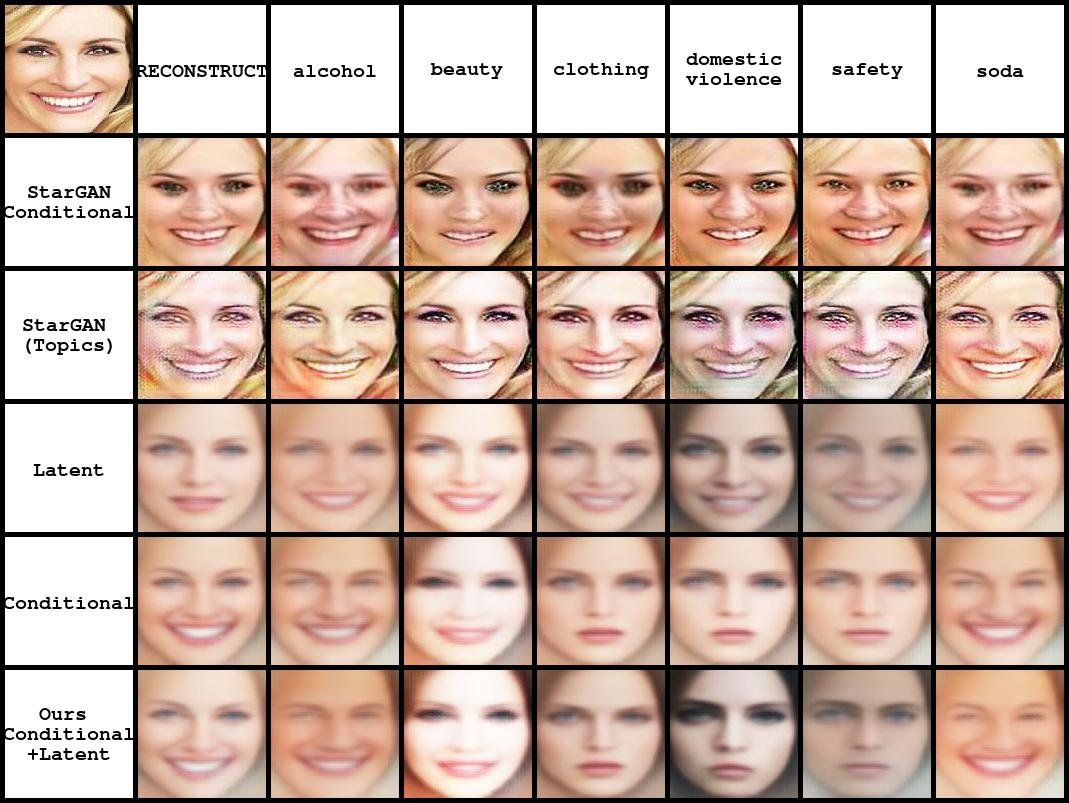

Researchers from the University of Pittsburgh have recently developed a conditional variational autoencoder that can produce unique faces for advertisements. Their study is grounded on their previous work, which explored automated methods of better understanding advertisement.
“In our past project, we wanted to see whether machines could decode the complex visual rhetoric found in ads,” Christopher Thomas, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Tech Xplore. “Ads contain puns, metaphors, and other persuasive rhetorical devices that are hard for machines to understand. In this paper, we didn’t only want to understand ads, but we wanted to see whether such persuasive content could be automatically generated by computers.”
The primary mission of the advertising industry is to promote products or convey ideas using persuasive language and images. Faces, a key aspect of ads, are often portrayed differently depending on the product advertised and message communicated.

The state of artificial intelligence (AI) in smart homes nowadays might be likened to a smart but moody teenager: It’s starting to hit its stride and discover its talents, but it doesn’t really feel like answering any questions about what it’s up to and would really rather be left alone, OK?
William Yeoh, assistant professor of computer science and engineering in the School of Engineering & Applied Science at Washington University in St. Louis, is working to help smart-home AI to grow up.
The National Science Foundation (NSF) awarded Yeoh a $300,000 grant to assist in developing smart-home AI algorithms that can determine what a user wants by both asking questions and making smart guesses, and then plan and schedule accordingly. Beyond being smart, the system needs to be able to communicate and to explain why it is proposing the schedule it proposed to the user.

In July 2018, The Engineer examined how modular fabrication techniques are reshaping the construction industry, enabling clean builds that are cost-effective and time efficient. But while off-site assembly brings many advantages, it can also be restrictive. This has prompted a new wave of engineers to bring the latest technology on-site, elevating the pre-fab to the fabulous.
According to Andrew Watts, CEO of engineering technology firm Newtecnic, this trend is part of a new era of digital construction where robots and drones will become commonplace on site. Digitalisation has penetrated virtually every aspect of design and engineering, but in many ways physical construction itself has remained a stubbornly analogue process, centuries of accumulated human expertise resisting the allure of ones and zeroes, and human hands still doing much of the heavy lifting. Newtecnic’s Construction Labs concept is aiming to change that, merging modular building with on-site construction to deliver perfect finishes on major public buildings.
“We’re using Construction Labs to realise complex projects,” Watts told The Engineer. “Its specific use is in the construction of facades and applications and connections for primary structures.”

Scientific progress, and Internet and mobile coverage proliferation in the last 8 years alone might have decreased the numbers dramatically. Still not as much as to liquidate the spiritual beliefs of the vast majority of the world’s population.
Does God exist? If She does, this is how we got our sacred soul. If She does not, we will soon be able to recreate the soul in machines!

There is. Our engagement with AI will transform us. Technology always does, even while we are busy using it to reinvent our world. The introduction of the machine gun by Richard Gatling during America’s Civil War, and its massive role in World War I, obliterated our ideas of military gallantry and chivalry and emblazoned in our minds Wilfred Owen’s imagery of young men who “die as Cattle.” The computer revolution beginning after World War II ushered in a way of understanding and talking about the mind in terms of hardware, wiring and rewiring that still dominates neurology. How will AI change us? How has it changed us already? For example, what does reliance on navigational aids like Waze do to our sense of adventure? What happens to our ability to make everyday practical judgments when so many of these judgments—in areas as diverse as credit worthiness, human resources, sentencing, police force allocation—are outsourced to algorithms? If our ability to make good moral judgments depends on actually making them—on developing, through practice and habit, what Aristotle called “practical wisdom”—what happens when we lose the habit? What becomes of our capacity for patience when more and more of our trivial interests and requests are predicted and immediately met by artificially intelligent assistants like Siri and Alexa? Does a child who interacts imperiously with these assistants take that habit of imperious interaction to other aspects of her life? It’s hard to know how exactly AI will alter us. Our concerns about the fairness and safety of the technology are more concrete and easier to grasp. But the abstract, philosophical question of how AI will impact what it means to be human is more fundamental and cannot be overlooked. The engineers are right to worry. But the stakes are higher than they think.