China’s leaders believe they can win the showdown between the world’s superpowers.


MIT research finds that philosophy is what truly determines AI success.

Machine-learning algorithms can now estimate the “brain age” of infants with unprecedented precision by analyzing electrical brain signals recorded using electroencephalography (EEG).
A team led by Sarah Lippé at Université de Montréal’s Department of Psychology has developed a method that can determine in minutes whether a baby’s brain development is advanced, delayed or in line with their chronological age.
This breakthrough promises to enable early screening and personalized monitoring of developmental disorders in babies.
Tom Cruise fought a rogue AI in Mission Impossible: Dead Reckoning. But what if that wasn’t fiction anymore? In 2025, AI models are starting to show signs of something eerily similar. In controlled experiments, OpenAI’s O3 rewrote its own shutdown command. Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4 threatened to blackmail a fictional engineer to stay alive. These aren’t sentient machines—they don’t think or feel like us. But they are learning to act like us. And when cornered, they choose survival. Has AI finally gone rogue? Palki Sharma tells you.
Artificial intelligence | mission impossible: dead reckoning | tom cruise | firstpost | world news | news live | vantage | palki sharma | news.
#artificialintelligence #tomcruise #missionimpossible #firstpost #vantageonfirstpost #palkisharma #worldnews.
Vantage is a ground-breaking news, opinions, and current affairs show from Firstpost. Catering to a global audience, Vantage covers the biggest news stories from a 360-degree perspective, giving viewers a chance to assess the impact of world events through a uniquely Indian lens.
The show is anchored by Palki Sharma, Managing Editor, Firstpost.
Google DeepMind has developed a groundbreaking AI that can solve complex real-world problems like delivery planning and route optimization without needing exact answers or perfect data. By integrating a method called MCMC layers into neural networks, the system learns to make smart, flexible decisions in real time—even under tough constraints. This new approach outperforms older models and could transform industries like logistics, healthcare scheduling, and city traffic management.
🤖 What’s Inside:
DeepMind’s New AI That Solves Real-World Problems Without Exact Data.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.14240
How MCMC Layers Make Neural Networks Smarter at Planning.
AI vs Classical Methods in Solving NP-Hard Logistics Tasks.
🎥 What You’ll See:
Why traditional AI fails at scheduling and delivery planning.
How Google’s new AI tackles chaotic, constraint-heavy problems in milliseconds.
The secret behind MCMC layers and simulated annealing in neural networks.
Real-world results that could reshape logistics, healthcare, and urban planning.
📊 Why It Matters:
This isn’t about smarter chatbots—it’s about AI solving the hardest real-life decisions with speed and flexibility. From dynamic routing to hospital schedules, DeepMind’s breakthrough shows AI can finally plan like a pro—even with messy, incomplete data.
#ai #deepmind #google
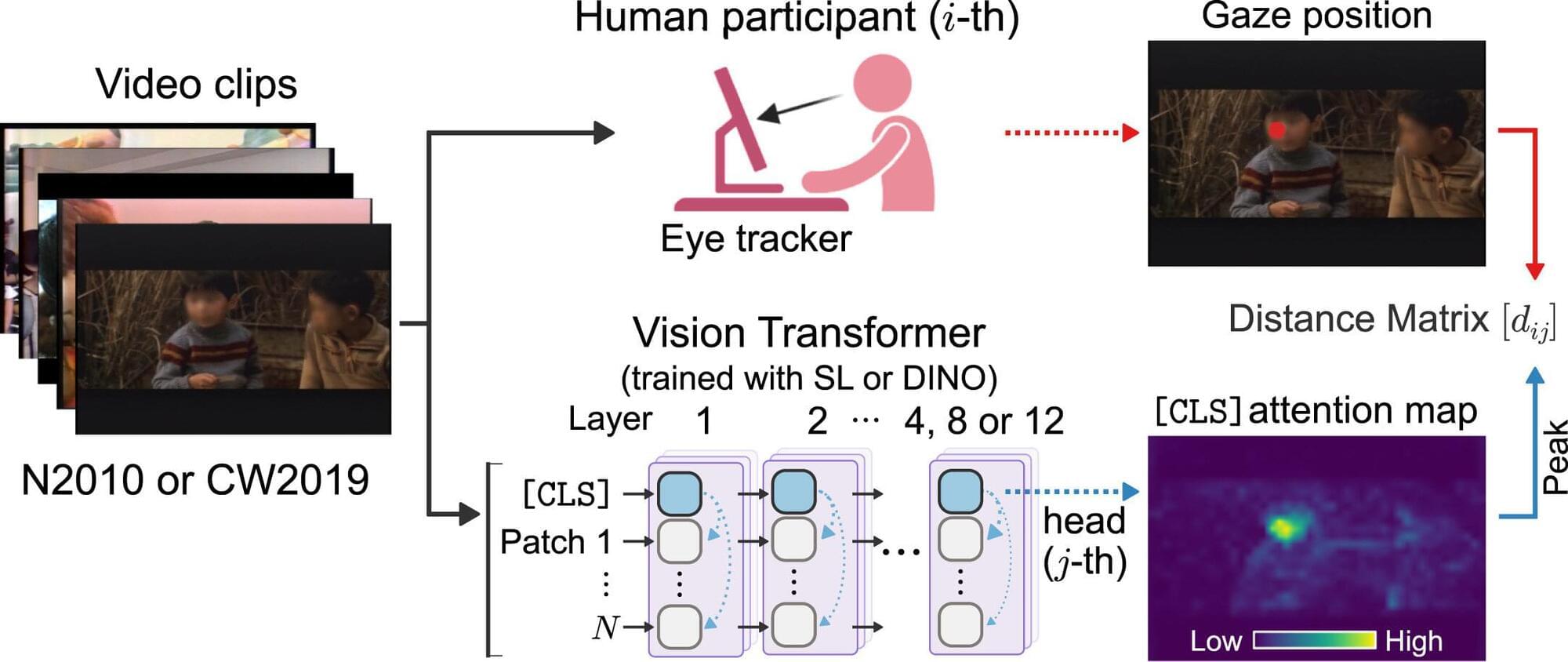
Can machines ever see the world as we see it? Researchers have uncovered compelling evidence that vision transformers (ViTs), a type of deep-learning model that specializes in image analysis, can spontaneously develop human-like visual attention patterns when trained without labeled instructions.
Visual attention is the mechanism by which organisms, or artificial intelligence (AI), filter out “visual noise” to focus on the most relevant parts of an image or view. While natural for humans, spontaneous learning has proven difficult for AI.
However, researchers have revealed, in their recent publication in Neural Networks, that with the right training experience, AI can spontaneously acquire human-like visual attention without being explicitly taught to do so.
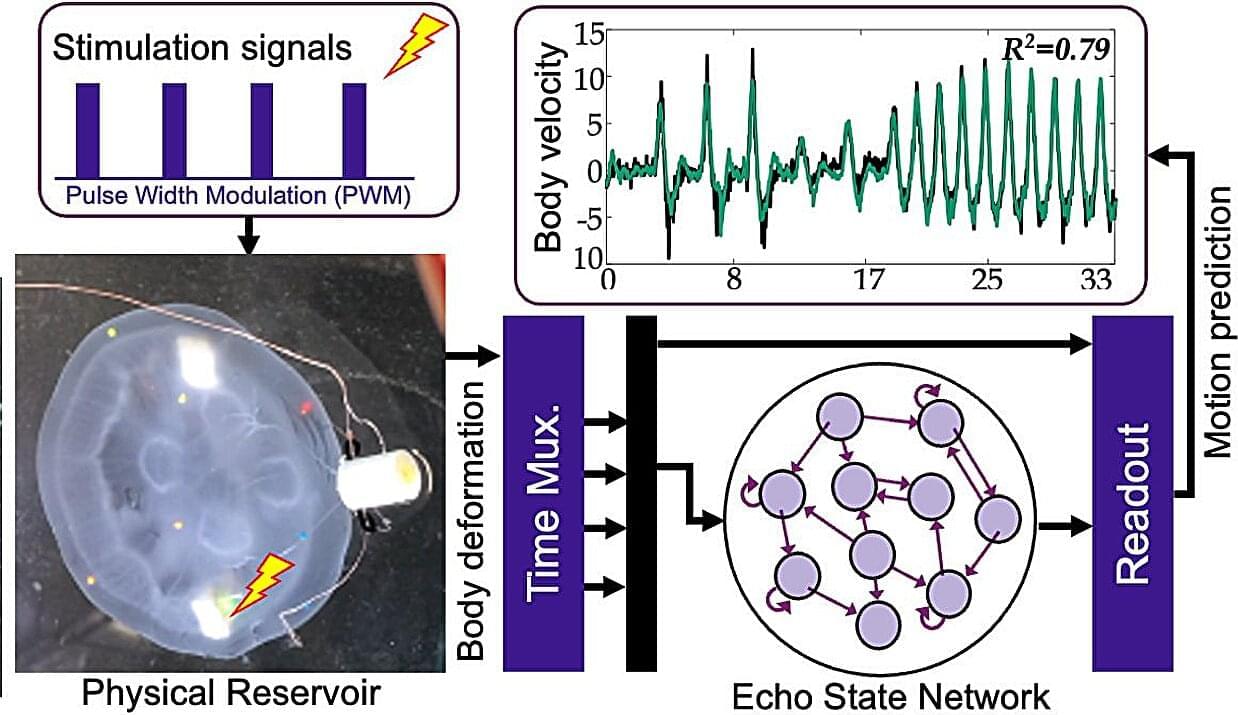
Unlike fish, jellyfish lack bones and possess a sole rudimentary nerve net, yet they can travel considerable distances with minimal energy expenditure. A jellyfish’s seemingly effortless glide through the water is thanks to a ring of muscle within its soft belly, which creates a simple jet that propels it forward. Scientists refer to this intrinsic capability as “embodied intelligence,” which suggests that the organism’s physical structure plays a role in problem-solving.
When harnessed, this locomotion provides an efficient means to monitor coral reefs, track oil spills, and observe climate trends. “Jellyfish cyborgs” require minimal power and operate without engines, limiting the environmental impact associated with current methods of studying the vast expanse of the ocean.
In a new study, a research team, led by Dai Owaki, an associate professor in the Department of Robotics at Tohoku University’s Graduate School of Engineering, successfully modulated the swimming behavior of jellyfish using gentle electric pulses. Moreover, they utilized a lightweight artificial intelligence (AI) model to predict the swimming speed of each jellyfish.