AI doesn’t know when it creates unintended consequences. As builders try to fix this, they may actually contribute to the problem.



As the cars we drive become increasingly sophisticated, the technology that underpins them poses a unique set of challenges.
“Currently, technology is more likely to create distractions in vehicles than it is to combat it,” Alain Dunoyer, SBD Automotive’s head of autonomous research and consulting, said in a statement sent to CNBC via email earlier this month.
“These days, cars have a shopping list of features which has led to tasks that were historically quite simple becoming drastically more complicated and distracting,” he added.

Rather than representing an entirely different take on the flying car, the helicopter’s new brains are more equivalent to the “self-driving” features you see in contemporary cars — an effort to make vehicles safer and more accessible than ever before.
“Today, we design our lives around traffic and make decisions about where we live and work based on how hard it is to get there,” Mark Groden, Skyryse CEO and founder, said in a statement. “To get there, we need to make urban flying as safe as riding an elevator and as accessible and affordable as riding a bus.”
The technology behind the feat called “Flight Stack” allows for either full or partial autonomous flight — think of it like cruise control on a car.

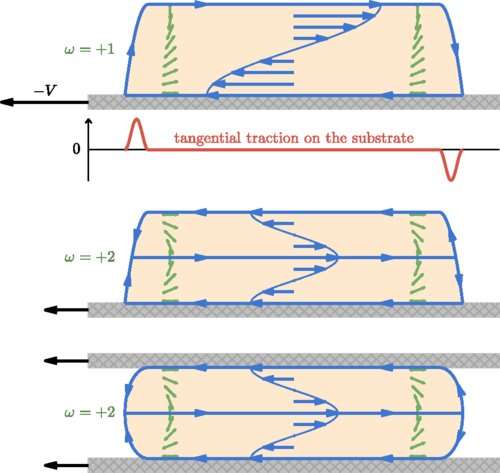
In an article published in Physical Review Letters, Bristol scientists have answered the fundamental question: “Is it possible to move without exerting force on the environment?”, by describing the tractionless self-propulsion of active matter.
Understanding how cells move autonomously is a fundamental question for both biologists and physicists.
Experiments on cell motility are commonly done by looking at the motion of a cell on a glass slide under a microscope.

Intel this morning issued a statement noting that it has picked up Israeli AI chipmaker Habana Labs. The deal, valued at around $2 billion, is the latest piece of some hefty investments in artificial intelligence that include names like Nervana Systems and Movidius.
In July, Habana announced its Gaudi AI training processor, which the Tel Aviv startup promised was capable of beating GPU-based systems by 4x. The company has been rumored to be a target for an Intel acquisition for a while now, as Intel looks to get out in front of the AI market. The company clearly doesn’t want to repeat past mistakes like missing the boat on mobile.
So far, the strategy looks like it just may pay off, giving Intel a marked advantage in a category it notes will be worth around $24 billion by 2024. In 2019 alone, Intel notes, the company expects to generate in excess of $3.5 billion in “AI-driven revenue,” a 20% increase over the year prior.

Studying how a set of conjoined twins know what the other is seeing has “validated” a ground-breaking approach to brain implants that could have come straight from the science fiction TV series Black Mirror.
Despite having separate brains, the twins in Canada can communicate thoughts and see or feel each other’s sensory input, even if their respective eyes are closed, prompting scientists from a US-based artificial intelligence (AI) developer to take a closer look.
Dr Phillip Alveda, founding chief executive of Corticol.ai, said functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI) showed the twins’ brains were connected via a single passage which led into each thalamus.

In 1965, American engineer Gordon Moore made the prediction that the number of transistors integrated on a silicon chip doubles every two years or so. This has proven to be true to this day, allowing software developers to double the performance of their applications. However, the performance of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms seems to have outpaced Moore’s Law.
According to a new report produced by Stanford University, AI computational power is accelerating at a much higher rate than the development of processor chips.
“Prior to 2012, AI results closely tracked Moore’s Law, with compute doubling every two years,” the authors of the report wrote. “Post-2012, compute has been doubling every 3.4 months.”

Intel just spent approximately $2 billion to acquire Israel-based AI firm Habana Labs. The partnership will “turbo-charge” Intel’s AI offerings for data centers, Intel said in a press release.