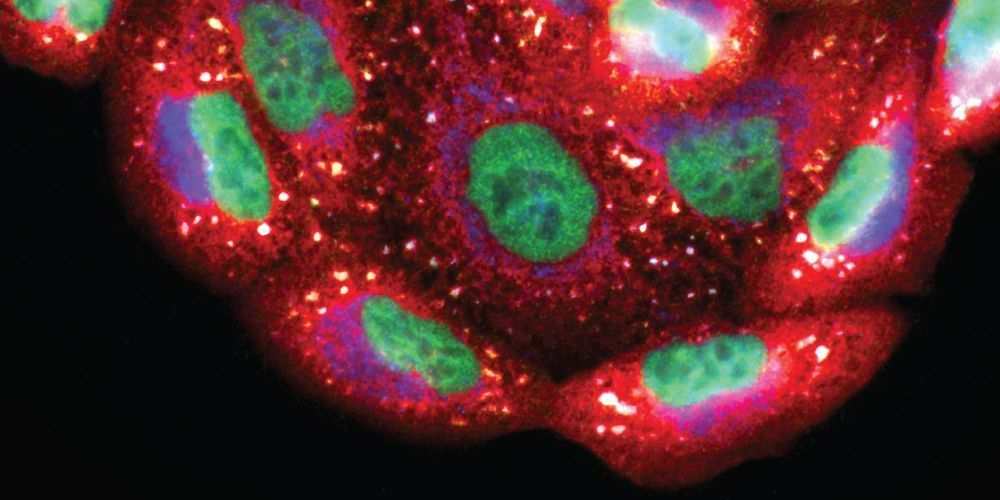
Aging is by far the dominant risk factor for the development of cardiovascular diseases, whose prevalence dramatically increases with increasing age reaching epidemic proportions. In the elderly, pathologic cellular and molecular changes in cardiac tissue homeostasis and response to injury result in progressive deteriorations in the structure and function of the heart. Although the phenotypes of cardiac aging have been the subject of intense study, the recent discovery that cardiac homeostasis during mammalian lifespan is maintained and regulated by regenerative events associated with endogenous cardiac stem cell (CSC) activation has produced a crucial reconsideration of the biology of the adult and aged mammalian myocardium. The classical notion of the adult heart as a static organ, in terms of cell turnover and renewal, has now been replaced by a dynamic model in which cardiac cells continuously die and are then replaced by CSC progeny differentiation. However, CSCs are not immortal. They undergo cellular senescence characterized by increased ROS production and oxidative stress and loss of telomere/telomerase integrity in response to a variety of physiological and pathological demands with aging. Nevertheless, the old myocardium preserves an endogenous functionally competent CSC cohort which appears to be resistant to the senescent phenotype occurring with aging. The latter envisions the phenomenon of CSC ageing as a result of a stochastic and therefore reversible cell autonomous process. However, CSC aging could be a programmed cell cycle-dependent process, which affects all or most of the endogenous CSC population. The latter would infer that the loss of CSC regenerative capacity with aging is an inevitable phenomenon that cannot be rescued by stimulating their growth, which would only speed their progressive exhaustion. The resolution of these two biological views will be crucial to design and develop effective CSC-based interventions to counteract cardiac aging not only improving health span of the elderly but also extending lifespan by delaying cardiovascular disease-related deaths.
Over the last decades, average life expectancy has significantly increased worldwide although several chronic diseases continue to grow, with aging as their main risk factor [1]. Aging is a natural and inevitable degenerative process of biological functions characterized by the progressive decline in tissue and organ homeostasis and function. Despite the significant improvements in diagnosis and treatment, the majority of individuals older than 65 years of age suffer from an elevated risk to develop cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), with a decline in the quality of life and in the ability to perform the normal activities of daily living [1]. Aging produces numerous changes in the human heart at structural, molecular, and functional levels [2].
Read more