A new AI algorithm developed by the University of Pittsburgh has achieved the highest accuracy to date in identifying prostate cancer, with 98% sensitivity and 97% specificity.


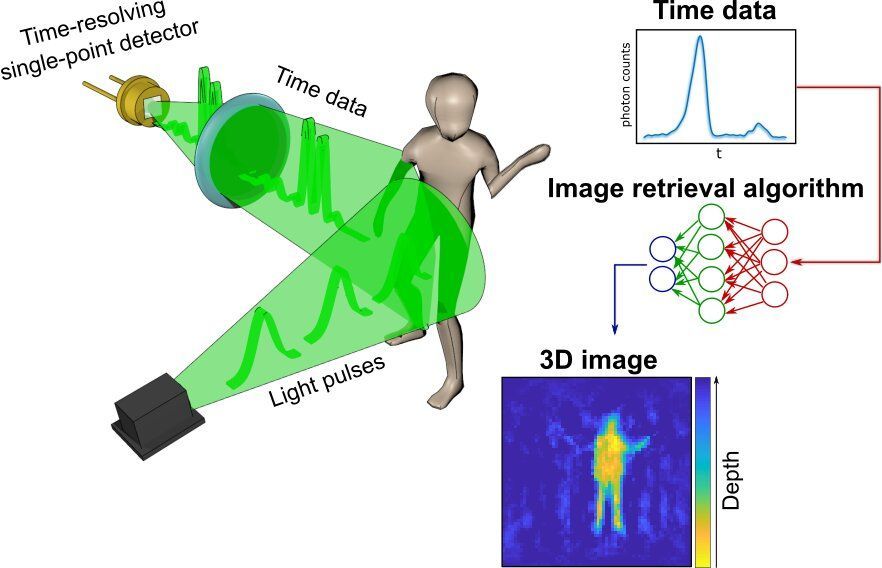
A radical new method of imaging that harnesses artificial intelligence to turn time into visions of 3D space could help cars, mobile devices and health monitors develop 360-degree awareness.
Photos and videos are usually produced by capturing photons—the building blocks of light—with digital sensors. For instance, digital cameras consist of millions of pixels that form images by detecting the intensity and color of the light at every point of space. 3D images can then be generated either by positioning two or more cameras around the subject to photograph it from multiple angles, or by using streams of photons to scan the scene and reconstruct it in three dimensions. Either way, an image is only built by gathering spatial information of the scene.
In a new paper published today in the journal Optica, researchers based in the U.K., Italy and the Netherlands describe an entirely new way to make animated 3D images: by capturing temporal information about photons instead of their spatial coordinates.


How true?
This video is about driverless cars and why China could be ahead of the world in self-driving car technology. We talk about how they are the biggest adopters of autonomous vehicles and how one day Chinese companies could be giving us a future of true autonomous travel. We also look at the issues that may set China back. Let’s take a look at why.
Subscribe for weekly videos on transhumanism tech:
I’m Alyse Sue and this is the Transhumanism Tech channel.
Connect with me:
“Just the nature of the AI that they’re building is one that crushes all humans at all games,” Musk told The New York Times in an interview published on Saturday. “I mean, it’s basically the plotline in ‘War Games.’”
DeepMind declined to comment when contacted by CNBC.
Musk has repeatedly warned that AI will soon become just as smart as humans and said that when it does we should all be scared because humanity’s very existence is at stake.
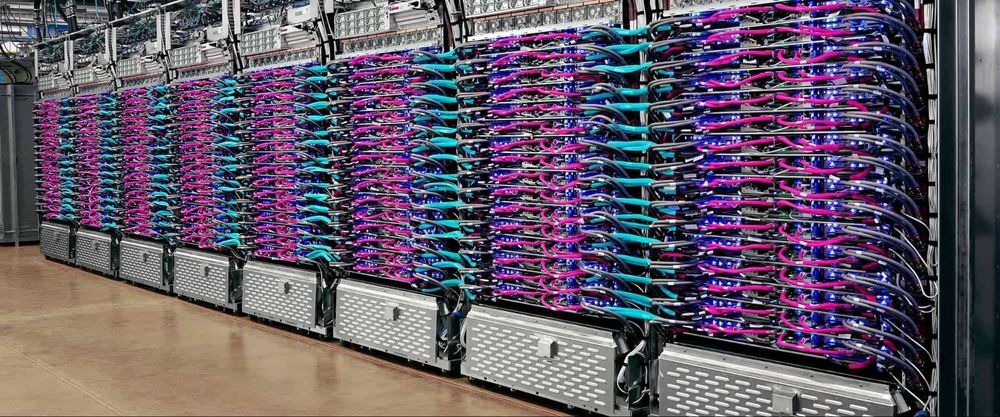

Fast training of machine learning (ML) models is critical for research and engineering teams that deliver new products, services, and research breakthroughs that were previously out of reach. Here at Google, recent ML-enabled advances have included more helpful search results and a single ML model that can translate 100 different languages.
The latest results from the industry-standard MLPerf benchmark competition demonstrate that Google has built the world’s fastest ML training supercomputer. Using this supercomputer, as well as our latest Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) chip, Google set performance records in six out of eight MLPerf benchmarks.
Recent advances give theoretical insight into why deep learning networks are successful.
If you are interested in brain computer interfaces (BCI), then you need to listen to this very exciting podcast!
I have only been aware of this DARPA NNN (Next-generation Non-surgical Neurotechnology) program since mid-March, and it is my number one topic of interest. I am interested in it because I have a plan for mind uploading to extend my life indefinitely — otherwise known as superlongevity in our group — but I have no interest in allowing anyone to drill holes in my head! DARPA is looking at ways for non-invasive methods of connecting the thoughts in our brains to computers. Over time, this could be a method to capture the thoughts and memories and emotions within my mind and transfer them into a computer substrate. And, to be clear, this mind upload will, in fact, be me.
Naturally, DARPA is not developing this so that I can upload my mind. This is part of their wounded warrior project, where they are trying to rehabilitate soldiers who have had the misfortune to have lost a limb. In addition to the non-invasive neural technology, they are working on haptics to provide a feedback loop for the sense of touch and temperature. They are also working on what they describe as third wave AI to support this technology.
The interview is with Dr Al Emondi, who has had a fascinating career in technology. He is the DARPA program manager in the Biological Technologies department.
I will always admire DARPA for its world-changing technology innovations!