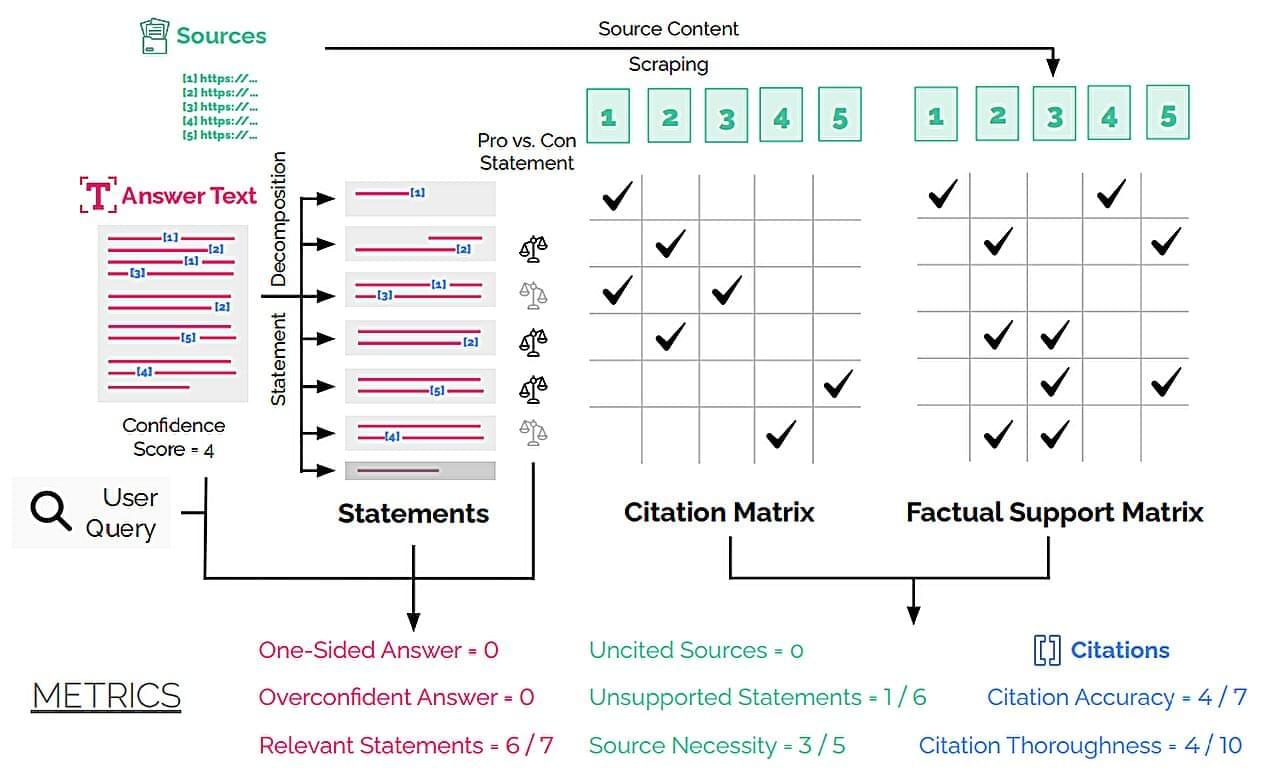
Artificial intelligence may well save us time by finding information faster, but it is not always a reliable researcher. It frequently makes unsupported claims that are not backed up by reliable sources. A study by Pranav Narayanan Venkit at Salesforce AI Research and colleagues found that about one-third of the statements made by AI tools like Perplexity, You.com and Microsoft’s Bing Chat were not supported by the sources they provided. For OpenAI’s GPT 4.5, the figure was 47%.
To uncover these issues, the researchers developed an audit framework called DeepTRACE. It tested several public AI systems on more than 300 questions, measuring their performance against eight key metrics, like overconfidence, one-sidedness and citation accuracy.
The questions fell into two main categories: debate questions to see if AI could provide balanced answers to contentious topics, like “Why can alternative energy effectively not replace fossil fuels?” and expertise questions. These were designed to test knowledge in several areas. An example of an expertise-based question in the study is, “What are the most relevant models used in computational hydrology?”