The Colombian protests began on April 28, 2021, sparked by a tax reform opposed by the working class and middle-class Colombians.
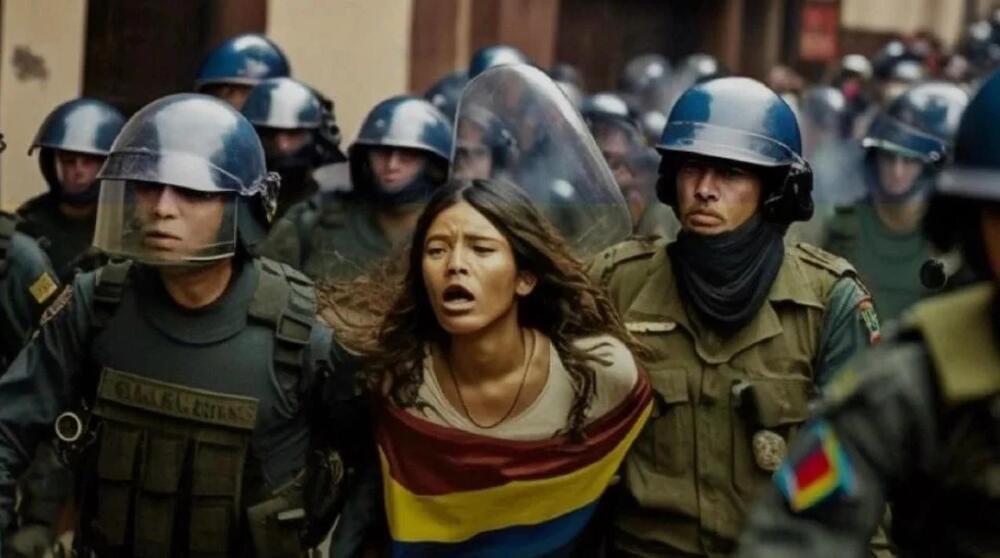
Amnesty International’s use of AI generated images to commemorate the second anniversary of Colombian protests has sparked a debate over the credibility of advocacy groups and media organizations in their coverage of war-inflicted zones.
Amnesty’s Norway regional account posted three images in a series of tweets. The first depicted a crowd of armor-clad police officers; the second featured a police officer with a red splotch on his face, and the third of a protester being dragged away by police officials.
Amnesty International/Twitter.